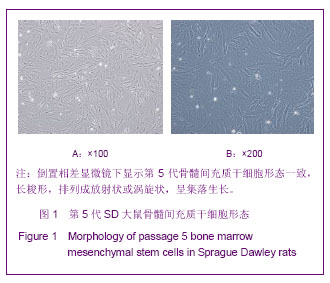
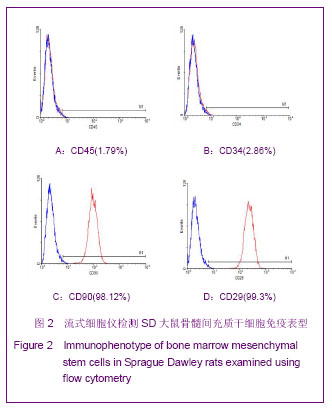
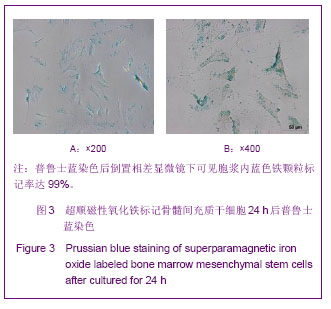
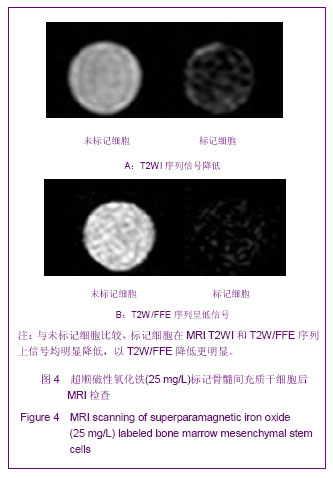
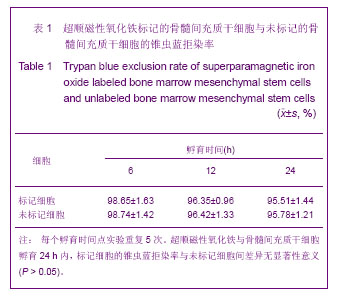
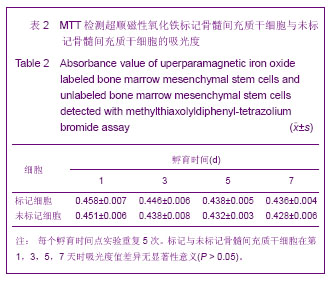
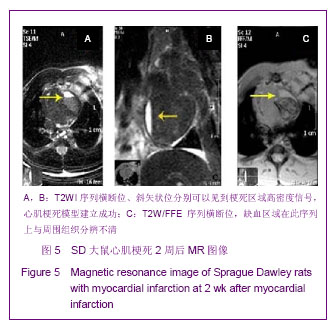
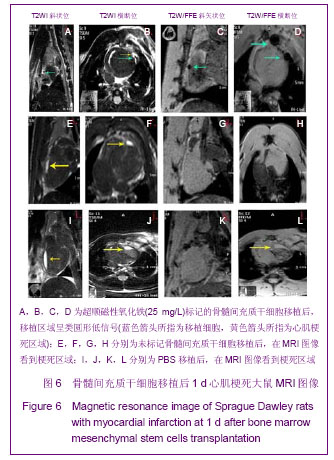
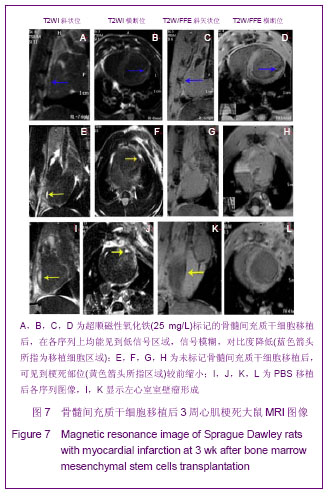
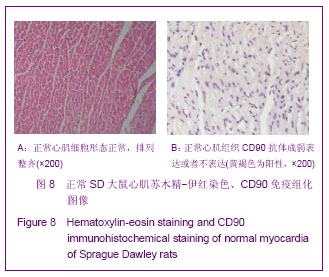
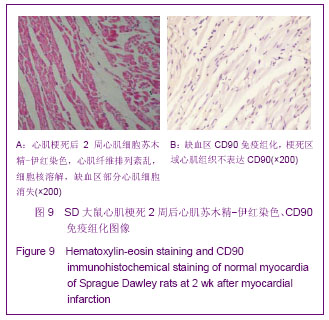
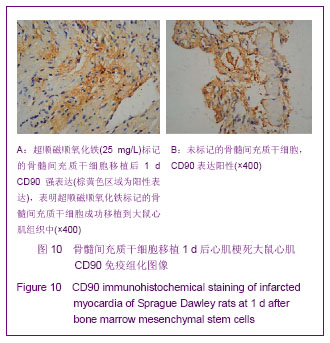
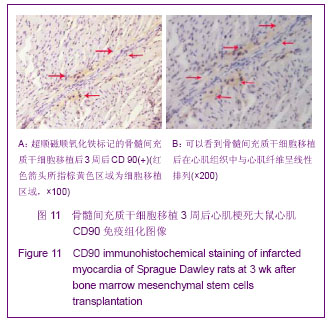
| [1] Huang P,Xiong LH,Zhang H,et al. Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Kexueban. 2004;25(1):67-69.华平,熊利华,张华,等. 体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分化为心肌样细胞[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2004,25(1):67-69.[2] Zhou CP,Shen J,Liang BL. Guoji Fangshe Yixue Heyixue Zazhi. 2006;30(4):253-256.周翠屏,沈君,梁碧玲.干细胞移植的磁性标记及磁共振成像活体示踪[J].国际放射医学核医学杂志,2006,30(4):253-256.[3] Teng AJ,Ju SH. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2006; 40(2): 117-119.滕皋军,居胜红.开展干细胞标记和MR活体示踪研究推进分子影像学发展[J].中华放射学杂志,2006,40(2):117-119.[4] Weissleder R.Molecular imaging: exploring the next frontier. Radiology. 1999;212(3):609-614.[5] Bulte JW, Kraitchman DL.Iron oxide MR contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging.NMR Biomed. 2004;17(7): 484-499.[6] Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR,et al. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging.Radiology. 2003;229(3): 838-846.[7] Matuszewski L, Persigehl T, Wall A,et al. Cell tagging with clinically approved iron oxides: feasibility and effect of lipofection, particle size, and surface coating on labeling efficiency.Radiology. 2005;235(1):155-161.[8] Ju S, Teng GJ, Lu H,et al. In vivo MR tracking of mesenchymal stem cells in rat liver after intrasplenic transplantation.Radiology. 2007;245(1):206-215.[9] Bos C, Delmas Y, Desmoulière A, et al. In vivo MR imaging of intravascularly injected magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells in rat kidney and liver. Radiology. 2004;233(3): 781-789.[10] Kim D, Hong KS, Song J.The present status of cell tracking methods in animal models using magnetic resonance imaging technology.Mol Cells. 2007;23(2):132-137.[11] Henning TD, Saborowski O, Golovko D,et al. Cell labeling with the positive MR contrast agent Gadofluorine M.Eur Radiol. 2007;17(5):1226-1234.[12] Shen J,Zhou CP,Cheng LN,et al. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi. 2008;42(4):426-431.沈君,周翠屏,成丽娜,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的钆-荧光双标记及MRI体外示踪的研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2008, 42(4): 426-431.[13] Geraldes CF, Laurent S. Classification and basic properties of contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2009;4(1):1-23.[14] Bruce IJ, Sen T. Surface modification of magnetic nanoparticles with alkoxysilanes and their application in magnetic bioseparations. Langmuir. 2005;21(15):7029-7035.[15] Propeck T, Quinn TJ, Jacobson JA,et al. Sonography and MR imaging of bifid median nerve with anatomic and histologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175(6):1721-1725.[16] Hill JM, Dick AJ, Raman VK, et al. Serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of injected mesenchymal stem cells. Circulation. 2003;108(8):1009-1014.[17] Arbab AS, Yocum GT, Kalish H, et al. Efficient magnetic cell labeling with protamine sulfate complexed to ferumoxides for cellular MRI. Blood. 2004;104(4):1217-1223.[18] Tomita S, Li RK, Weisel RD, et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow cells improves damaged heart function. Circulation. 1999;100(19 Suppl):II247-256.[19] Chen SL, Fang WW, Ye F, et al. Effect on left ventricular function of intracoronary transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(1):92-95. |