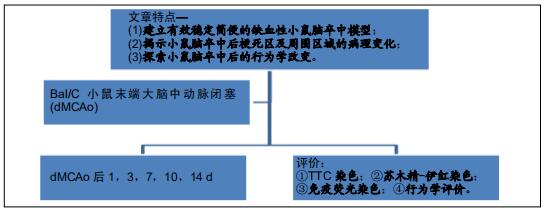
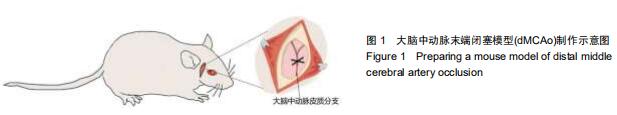
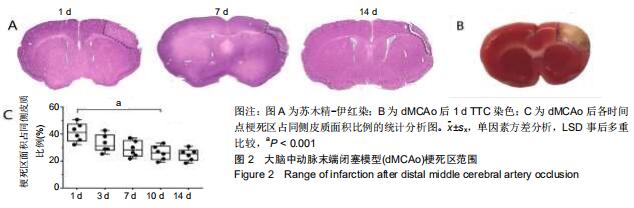
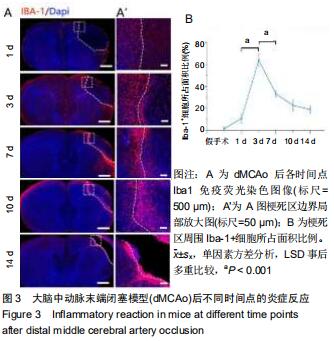
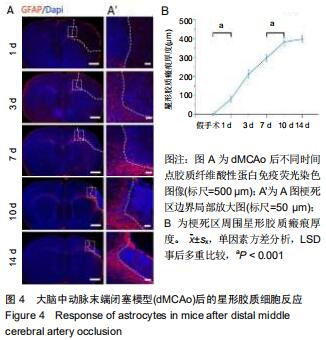
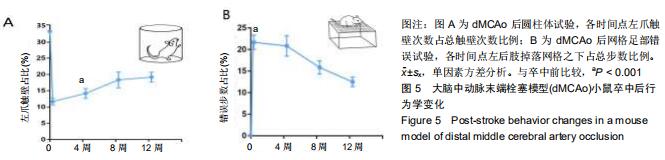
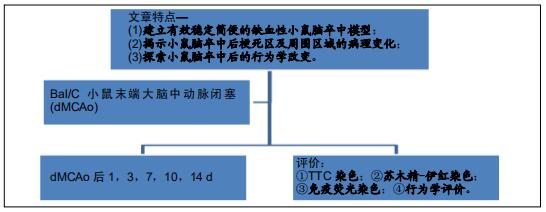
|
[1] WRITING GROUP MEMBERS, MOZAFFARIAN D, BENJAMIN EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation.2016;33(4):e38.
[2] VALERY L FEIGIN, THEO VOS, EMMA NICHOLS, et al.Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016.Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(5):459-480.
[3] DONNAN GA, FISHER M, MACLEOD M, et al.Stroke.Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1612-1623.
[4] JAYARAJ RL, AZIMULLAH S, BEIRAM R, et al. Neuroinflammation: friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation 2019;16(1):142.
[5] JOSHUA E BURDA, MICHAEL V SOFRONIEW. Reactive Gliosis and the Multicellular Response to CNS Damage and Disease. Neuron.2014;81(2):229-248.
[6] BERNHEISEL CR, SCHLAUDECKER JD, LEOPOLD K.Subacute Management of Ischemic Stroke. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84(12):1383-1388.
[7] MEMEZAWA H, MINAMISAWA H, SMITH ML, et al. Ischemic penumbra in a model of reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat.Exp Brain Res.1992; 89(1):67-78.
[8] DAVID W HOWELLS, MICHELLE J PORRITT, SARAH SJ REWELL, et al. Different strokes for different folks: the rich diversity of animal models of focal cerebral ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30(8):1412-1431.
[9] TAMURA A, GRAHAM DI, MCCULLOCH J, et al. Focal Cerebral Ischaemia in the Rat: 1. Description of Technique and Early Neuropathological Consequences Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.1981; 1(1):53-60.
[10] MCAULEY MA. Rodent models of focal ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev.1995;7(2):153-180.
[11] RANSOM BR, RANSOM CB. Astrocytes: multitalented stars of the central nervous system. Methods Mol Biol.2012;814: 3-7.
[12] SHIMIN LIU, GEHUA ZHEN, BRUNO P MELONI, et al. Rodent Stroke Model Guidelines for Preclinical Stroke Trials (1st Edition).J Exp Stroke Transl Med.2009;2(2):2-27.
[13] KONSTANTIN-ALEXANDER HOSSMANN. The two pathophysiologies of focal brain ischemia: implications for translational stroke research. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2012;32(7):1310-1316.
[14] SARAH LUNARDI BACCETTO, CHRISTIAN LEHMANN. Microcirculatory Changes in Experimental Models of Stroke and CNS-Injury Induced Immunodepression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5184.
[15] DOYLE KP, BUCKWALTER MS.A Mouse Model of Permanent Focal Ischemia: Distal Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1135:103-110.
[16] GELDERBLOM M, LEYPOLDT F, STEINBACH K, et al. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Cerebral Immune Cell Accumulation in Stroke. Stroke.2009;40(5):1849-1857.
[17] XIAOMING HU, REHANA K LEAK, YEJIE SHI, et al.Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(1):56-64.
[18] AMANTEA D, TASSORELLI C, PETRELLI F, et al. Understanding the Multifaceted Role of Inflammatory Mediators in Ischemic Stroke.Curr Med Chem.2014;21(18): 2098-2117.
[19] YOUL KJ, JOOHYUN P, YOUNG CJ, et al. Inflammation after Ischemic Stroke: The Role of Leukocytes and Glial Cells.Exp Neurobiol.2016;25(5):241-251.
[20] XU S, LU J, SHAO A, et al. Glial Cells: Role of the Immune Response in Ischemic Stroke.Front Immunol. 2020;11:294.
[21] CHECHNEVA OV, DENG W. Mitochondrial translocator protein (TSPO), astrocytes and neuroinflammation. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(7):1056-1057.
[22] ASYA ROLLS, RAVID SHECHTER, MICHAL SCHWARTZ. The bright side of the glial scar in CNS repair. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(3):235-241.
[23] MOFTAH M, JADAVJI NM. Role of behavioral training in reducing functional impairments after stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9):1507-1508.
[24] CLAUDIA ALIA, CRISTINA SPALLETTI, STEFANO LAI, et al.Neuroplastic Changes Following Brain Ischemia and their Contribution to Stroke Recovery: Novel Approaches in Neurorehabilitation.Front Cell Neurosci.2017;11:76.
[25] PATRICE VOSS, MARYSE E THOMAS, J MIGUEL CISNEROS-FRANCO, et al. Dynamic Brains and the Changing Rules of Neuroplasticity: Implications for Learning and Recovery.Front Psychol.2017;8:1657.
[26] YANG JP, LIU HJ, LIU XF. VEGF Promotes Angiogenesis and Functional Recovery in Stroke Rats.J Invest Surg. 2010;23(3): 149-155.
[27] ANTINA DE BOER, ANNET STORM, MARICEL GOMEZ-SOLER, et al.Environmental enrichment during the chronic phase after experimental stroke promotes functional recovery without synergistic effects of EphA4 targeted therapy.Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(4):605-617.
[28] CARACCIOLO L, MAROSI M, MAZZITELLI J, et al. CREB controls cortical circuit plasticity and functional recovery after stroke.Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2250.
[29] LI F, ZHANG T, LI BJ, et al. Motor imagery training induces changes in brain neural networks in stroke patients. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(10):1771-1781.
[30] GERLINDE A METZ, IWA ANTONOW-SCHLORKE, OTTO W WITTEMETZ GA. Motor improvements after focal cortical ischemia in adult rats are mediated by compensatory mechanisms.Behav Brain Res. 2005;162(1):71-82.
[31] THERESA A. JONES, STEPHANIE C, JEFFERSON. Reflections of experience-expectant development in repair of the adult damaged brain.Dev Psychobiol.2011;53(5): 466-475.
[32] C LOIS, A ALVAREZ-BUYLLA. Proliferating Subventricular Zone Cells in the Adult Mammalian Forebrain can Differentiate into Neurons and Glia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(5):2074-2077.
[33] DUAN HM, LI XG, WANG C, et al. Functional hyaluronate collagen scaffolds induce NSCs differentiation into functional neurons in repairing the traumatic brain injury.Acta Biomater. 2016;45:182-195.
[34] PENG HAO, HONGMEI DUAN, FEI HAO, et al. Neural repair by NT3-chitosan via enhancement of endogenous neurogenesis after adult focal aspiration brain injury. Biomaterials. 2017;140:88-102.
[35] LINHONG MO, ZHAOYANG YANG, AIFENG ZHANG, et al. The repair of the injured adult rat hippocampus with NT-3-chitosan carriers.Biomaterials.2010;31(8):2184-2192.
[36] HIROFUMI NAKATOMI, TOSHIHIKO KURIU, SHIGEO OKABE, et al. Regeneration of Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons after Ischemic Brain Injury by Recruitment of Endogenous Neural Progenitors.Cell. 2002;110(4):429-441.
[37] JACK M PARENT, ZINAIDA S VEXLER, CHAO GONG, et al. Rat forebrain neurogenesis and striatal neuron replacement after focal stroke.Ann Neurol. 2002;52(6):802-813.
|