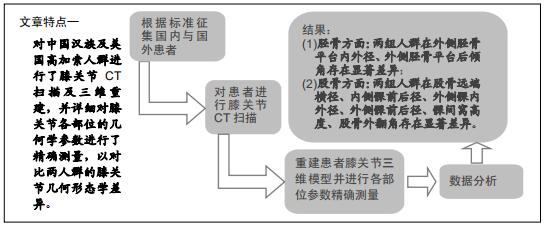
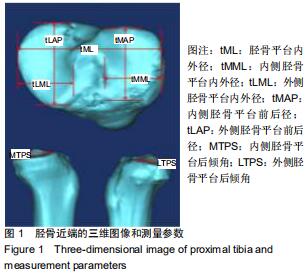
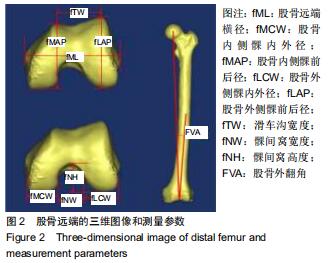
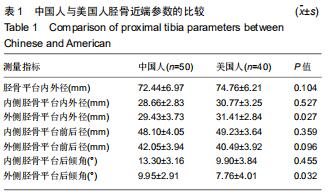
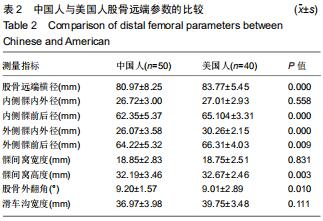
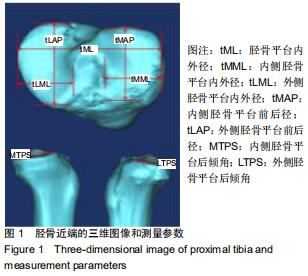
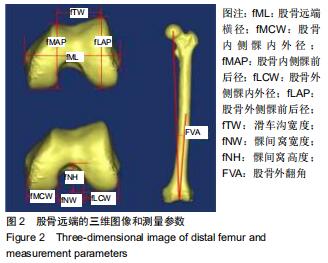
|
[1] YUE B, VARADARAJAN KM, AI S, et al. Differences of knee anthropometry between Chinese and white men and women. J Arthroplasty.2011;26(1):124-130.
[2] KAWAHARA S, OKAZAKI K, OKAMOTO S, et al. A lateralized anterior flange improves femoral component bone coverage in current total knee prostheses.Knee.2016;23(4):719-724.
[3] ROHILLA S, JAARSMA R, MAINI L, et al. Dimensions of distal femur in terms of total knee arthroplasty among different origins-A systematic review.Journal of Arthroscopy and Joint Surgery.2017;4(1):8-14.
[4] 严广斌.解剖轴与机械轴[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012, 6(4):653.
[5] WADA M, TATSUO H, BABA H, et al. Femoral intercondylar notch measurements in osteoarthritic knees.Rheumatology (Oxford).1999;38(6):554-558.
[6] CHENG CK, LUNG CY, LEE YM, et al. A new approach of designing the tibial baseplate of total knee prostheses.Clin Biomech(Bristol,Avon).1999:14(2):112-117.
[7] UEHARA K, KADOYA Y, KOBAYASHI A, et al. Anthropometry of the proximal tibia to design a total knee prosthesis for the Japanese population.J Arthroplasty.2002;17(8):1028-1032.
[8] MA QL, LIPMAN JD, CHENG CK, et al. A Comparison Between Chinese and Caucasian 3-Dimensional Bony Morphometry in Presimulated and Postsimulated Osteotomy for Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2017;32(9): 2878-2886.
[9] 曲铁兵,曾纪洲,林源,等.华北地区成人正常胫骨内侧平台后倾角的测量及临床意义[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(8):10-13.
[10] ERDEM M, GULABI D, CECEN GS, et al. Using fibula as a reference can be beneficial for the tibial component alignment after total knee arthroplasty, a retrospective study.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2015;23(7):2068-2073.
[11] IORIO R, BOLLE G, CONTEDUCA F, et al. Accuracy of manual instrumentation of tibial cutting guide in total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(10):2296-2300.
[12] STIJAK L, HERZOG RF, SCHAI P. Is there an influence of the tibial slope of the lateral condyle on the ACL lesion? A case-control study.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(2):112-117.
[13] CHIU KY, ZHANG SD, ZHANG GH. Posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese. J Arthroplasty.2000;15(2):224-227.
[14] ZHANG K, HAN Q, WANG H, et al. Measurement of proximal tibial morphology in northeast Chinese population based on three-dimensional reconstruction computer tomography. Medicine (Baltimore).2019;98(45):e17508.
[15] LIU Z, YUAN G, ZHANG W, et al. Anthropometry of the proximal tibia of patients with knee arthritis in Shanghai.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(5):778-783.
[16] BAUWENS K, MATTHES G, WICH M, et al. Navigated total knee replacement. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2):261-269.
[17] 肖建林,刘潼,秦彦国,等.基于CT图像三维重建测量股骨外翻角[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(12):2041-2043.
[18] LI P, TSAI TY, LI JS, et al. Morphological measurement of the knee: race and sex effects.Acta Orthop Belg. 2014;80(2): 260-268.
[19] 董纪元,张健,王岩.国人人工膝关节几何外形尺寸的初步探讨[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(8):28-31,193.
[20] MISIR A, YILDIZ KI, KIZKAPAN TB. Wider femoral and mediolaterally narrower tibial components are required for total knee arthroplasty in Turkish patients.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2019;27(7):2155-2166.
[21] SEEDHOM BB, LONGTON EB, WRIGHT V, et al. Dimensions of the knee. Radiographic and autopsy study of sizes required by a knee prosthesis.Ann Rheum Dis.1972;31(1):54-58.
[22] SIDLER-MAIER CC, WADDELL JP. Incidence and predisposing factors of periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures: a literature review.International Orthopaedics. 2015; 39(9):1673-1682.
[23] HAFEZ MA, SHEIKHEDREES SM, SAWEERES ES. Anthropometry of Arabian Arthritic Knees: Comparison to Other Ethnic Groups and Implant Dimensions.J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(5):1109-1116.
[24] LOURES FB, DE ARAUJO GOES RF, DA PALMA IM, et al. Anthropometric study of the knee and its correlation with the size of three implants available for arthroplasty.Rev Bras Ortop. 2016;51(3):282-289.
|