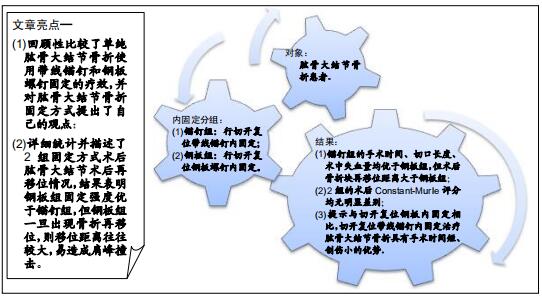
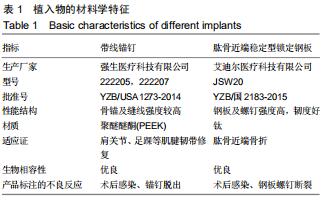
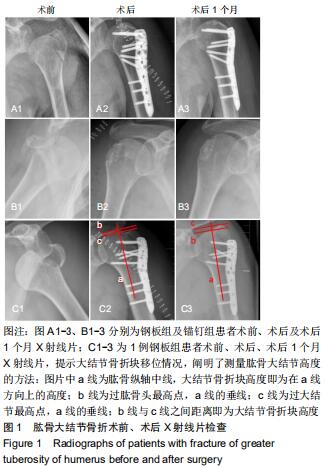
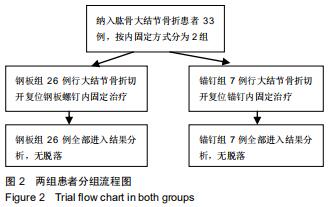
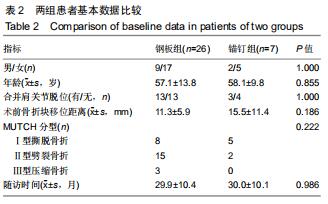
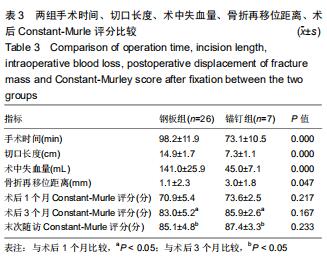
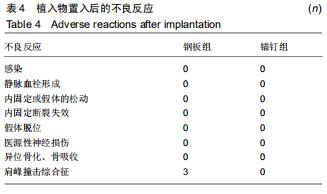
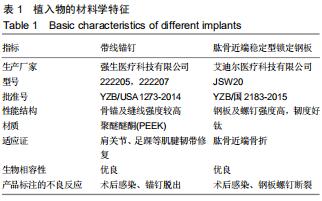
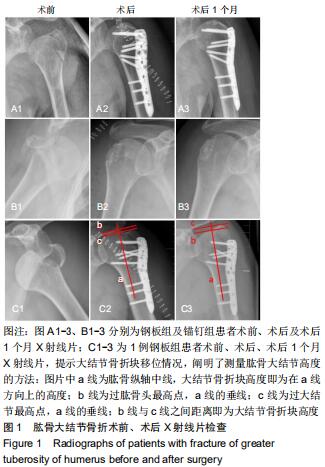
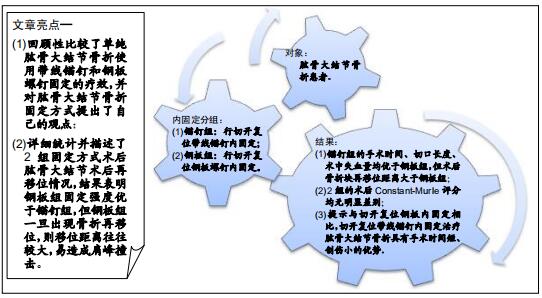
|
[1] VIJAYVARGIYA M, PATHAK A, GAUR S. Outcome analysis of locking plate fixation in proximal humerus fracture. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016; 10(8):RC01-RC05.
[2] KIM DR, NOH YM, LEE SY. Arthroscopic reduction and suture bridge fixation of a large displaced greater tuberosity fracture of the humerus. Arthrosc Tech. 2019;8(9):975-985.
[3] ROULEAU DM, MUTCH J, LAFLAMME GY. Surgical treatment of displaced greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24:46-56.
[4] MICHELE AV, DAVIDE A, ANDREA P, et al. Isolated fractures of the greater tuberosity in proximal humerus: does the direction of displacement influence functional outcome? Acta Biomed. 2013; 84: 219-228.
[5] GILLESPIE RJ, JOHNSTON PS, GORDON VA, et al. Using plate osteosynthesis to treat isolated greater tuberosity fractures. Am J Orthop. 2015;44(8):E248-E251.
[6] MUTCH J, LAFLAMME GY, HAGEMEISTER N, et al. A new morphological classification for greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B:646-651.
[7] CHEN YF, ZHANG W, CHEN Q, et al. AO X-shaped midfoot locking plate to treat displaced Isolated greater tuberosity fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):e995-e999.
[8] BOB Y, TODD CM, SCOTT AT, et al. Operative treatment of isolated greater tuberosity fractures: retrospective review of clinical and functional outcomes. Orthopedics. 2012;35(6):e807-e814.
[9] YIN B, MOEN TC, THOMPSON SA, et al. Operative treatment of isolated greater tuberosity fractures: retrospective review of clinical and functional outcomes. Orthopedics. 2012;35(6): e807-e814.
[10] JI JH, SHAFI M, SONG IS, et al. Arthroscopic fixation technique for comminuted, displaced greater tuberosity fracture. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(5):600-609.
[11] LEE SU, JEONG C, PARK IJ. Arthroscopic fixation of displaced greater tuberosity fracture of the proximal humerus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(2):378-380.
[12] MATTYASOVSZKY SG, BURKHART KJ, AHLERS C, et al. Isolated fractures of the greater tuberosity of the proximal humerus. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(6):714-720.
[13] CAO L, WENG W, SONG S, et al Comparison of effectiveness between minimally invasive cannulated screw and open reduction and plate fixation in treatment of humeral greater tuberosity fracture. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013;27(4):418-422.
[14] ALBERIO RL, RE MD, GRASSI FA. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for proximal humerus fractures: a retrospective study describing principles and advantages of the technique. Adv Orthop. 2018;5904028:1-10.
[15] DEBOTTIS D, ANAVIAN J, GREEN A. Surgical management of isolated greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus. Orthop Clin North (Am). 2014;45(2):207-218.
[16] 徐薇,许德荣,任志楠,等. 腰椎多节段内固定术中失血量准确评估的研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(7): 535-537.
[17] 叶庭均,王蕾. 肱骨近端骨折切开复位内固定术后撞击征原因分析[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2012,33(1):3-5.
[18] 白云鹏,沈燕国,曹师锋,等. 带线锚钉处理复杂肱骨近端骨折中粉碎性大结节的临床优势[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(10):920-924.
[19] 王光勇,杜俊生,钟兵. 钢板和空心螺钉置入修复劈裂型肱骨大结节骨折:肩关节功能比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(40): 6482-6487.
[20] LIN CL, SU FL, CHANG CH, et al. Effect of shoulder abduction on the fixation of humeral greater tuberosity fractures: a biomechanical study for three types of fixation constructs. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015; 24: 547-554.
[21] MUTCH J, ROULEAU DQ, LAFLAMME GY, et al. Accurate measurement of greater tuberosity displacement without computed tomography: validation of a method on plain radiography to guide surgical treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28(8): 445-451.
[22] BAHRS C, LINGENFELTER E, FISCHER F, et al. Mechanism of injury and morphology of the greater tuberosity fracture. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(2):140-147.
[23] 杨国勇,向明,陈杭,等.关节镜下中空螺钉和(或)锚钉缝线桥技术固定肱骨大结节骨折[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(21):1342-1348.
[24] HU CZ, ZHOU KH, PAN FG, et al. Application of pre-contoured anatomic locking plate for treatment of humerus split type greater tuberosity fractures: A prospective review of 68 cases with an average follow-up of 2.5 years. Injury. 2018;49:1108-1112.
[25] CLAVERT P, ADAM P, BEVORT A, et al. Pitfalls and complications with locking plate for proximal humerus fracture. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19:489-494.
[26] DANIEL D, JACK A, ANDREW G. Surgical management of isolated greater tuberosity fractures of the proximal humerus. Orthop Clin N Am. 2014;45:207-218.
[27] BURKHART SS, COLE BJ. Bridging Self-Reinforcing double-row rotator cuff repair: we really are doing better. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(5): 677-680.
[28] LIN CL, HONG CK, JOU IM, et al. Suture anchor versus screw fixation for greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus-a biomechanical study. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(3):423-428.
[29] GANG X, KAPIL C, THOU L, et al. Titanium mini locking plate with trans-osseous sutures for the treatment of humeral greater tuberosity fracture osteosynthesis versus PHILOS: a retrospective view. Int Orthop. 2018;42:2467-2473.
[30] DOMINIQUE M, MUTCH J, LAFLAMME GY. Surgical treatment of displaced greater tuberosity fractures of the humerus. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24:46-56.
|