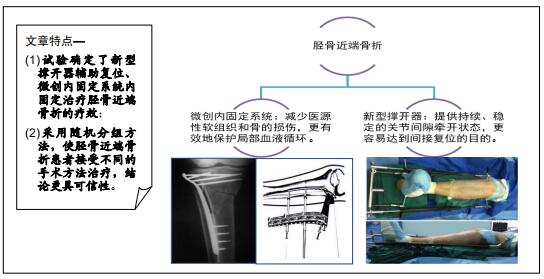
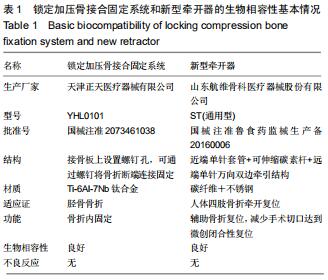
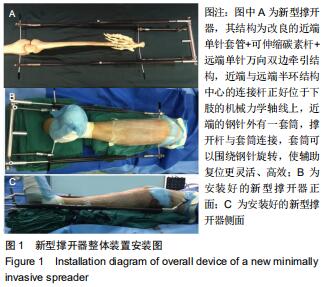
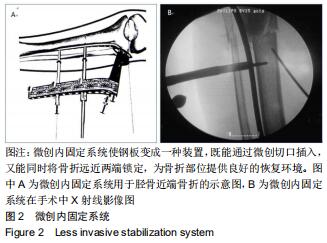
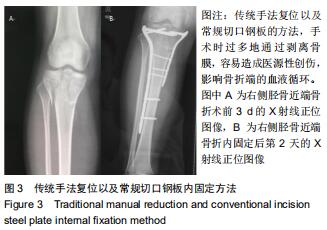
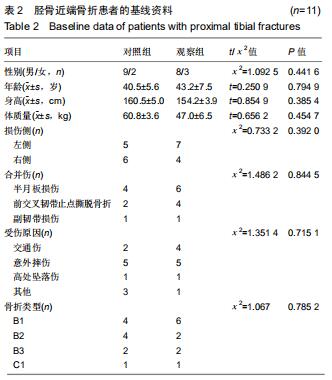
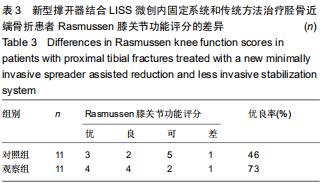
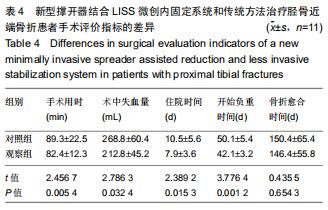
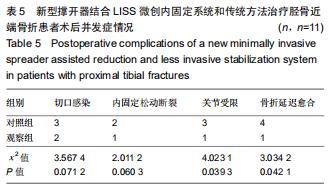
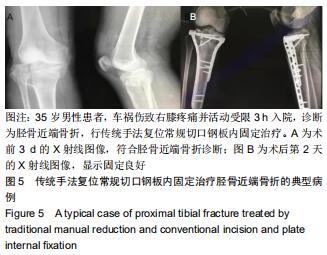
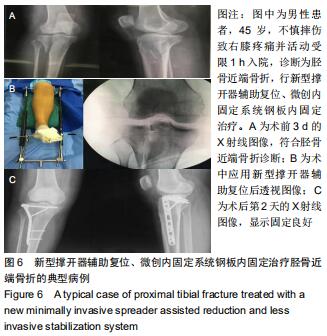
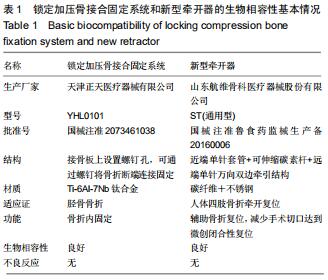
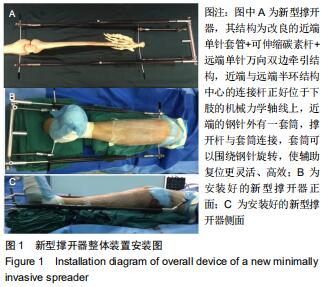
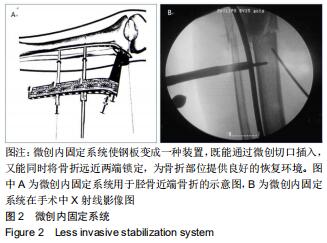
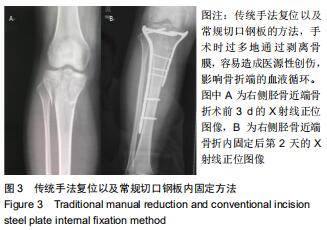
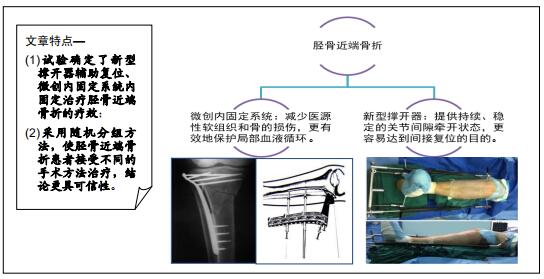
|
[1] MEHIN R, O'BRIEN P, BROEKHUYSE H, et al. Endstage arthritis following tibia plateau fractures: average 10-year follow-up. Can J Surg. 2012;55(2):87-94.
[2] 王建伟,杨星光,王韬,等,微创内固定系统治疗胫骨近端复杂骨折[J].中国临床医学,2007,14(4):554-557.
[3] 陈新宇.微创内固定技术与传统手术对胫骨平台骨折患者膝关节功能的影响对比[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(10)43-44.
[4] KRIEG JC. Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A2-A10.
[5] SCHANDELMAIER P, PARTENHEIMER A, KOENEMANN B, et al. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3: SC55-SC63.
[6] GOESLING T, FRENK A, APPENZELLER A, et al. LISS PLT: design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A11-A15.
[7] 李浩,徐龙伟,季卫平,等LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用[J].实用骨科杂志,2007,13(1):45-47.
[8] SCHÜTZ M, KÄÄB MJ, HAAS N. Stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the LIS-System: early clinical experience in Berlin. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A30-A35.
[9] STANNARD JP, WILSON TC, VOLGAS DA, et al. Fracture stabilization of proximal tibial fractures with the proximal tibial LISS: early experience in Birmingham, Alabama (USA). Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A36-A42.
[10] 骆锦强,袁权华,陈振宇,等.LISS钢板在胫骨近端骨折中的应用研究[J].中国医学创新,2009,6(22):25-26.
[11] GRALA P, TWARDOSZ W, TONDEL W, et al. Large bone distractor for open reconstruction of articular fractures of the calcaneus. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1283-1288.
[12] 吴煌,廖瑛,范伟杰,等.SchatzkerⅤⅥ型胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗与疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(12):891-893.
[13] RASMUSSEN PS. Tibial condylar fractures. Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(7):1331-1350.
[14] 胡超,张桃根,蔡林.胫骨平台骨折的治疗现状[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012,27(2):191-192.
[15] 王庆鹏,孙永明.胫骨平台骨折及其伴随损伤的诊断[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(11):953.
[16] BAREI DP, NORK SE, MILLS WJ, et al. Functional outcomes of severe bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with dual incisions and medial and lateral plates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1713-1721.
[17] 徐云钦,李强,申屠刚,等.三种手术方法在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(3):281-283.
[18] 王星华,姚振均,张庆华,等.带锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折38例报告[J].中国临床医学,2003,10(1):47-49.
[19] SAFRAN O, LIEBERGALL M, SEGAL D, et al. Proximal tibial fractures-should we nail them?. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001; 30(9):681-684.
[20] 曾庆敏,丁磊,张键.交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨近端骨折26例分析[J].中国临床医学,2008,15(4):545-546.
[21] 王海滨,卢旭华.有限内固定结合外固定架在胫骨骨折治疗中的应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,14(14):1074-1076.
[22] VEITCH SW, STROUD RM, TOMS AD. Compaction bone grafting in tibial plateau fracture fixation. J Trauma. 2010;68(4):980-983.
[23] 苏琦,陈芒.锁定钢板治疗胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2010, 13(6):654-655.
[24] 王亦.骨与关节损伤[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:736.
[25] 王永宏,戴守达,董小雄,等.双钢板支撑治疗Scliatzker V及VI型胫骨平台骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(2):157.
[26] 罗从风,陈云丰,高洪,等.改良双钢板法治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2004,24(6):326-329.
[27] WILSON W, VAN RIETBERGEN B, VAN DONKELAAR CC, et al. Pathways of load-induced cartilage damage causing cartilage degeneration in the knee after meniscectomy. J Biomech. 2003;36(6): 845-851.
[28] 胡超,蔡林,王建平等.复杂性胫骨平台骨折的手术治疗[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(8):749-750.
[29] 李翔,范卫民,刘锋,等.LISS在复杂胫骨平台骨折中的应用[J].江苏医药, 2007,33(2):140-142.
[30] 张经纬,何贤峰,朱李梅,等.股骨LISS钢板外固定治疗胫骨骨折116例体会[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):874-875.
[31] 姜新峰,陈华.股骨撑开器辅助复位治疗不稳定型胫骨平台骨折疗效分析[J].江苏医药,2016,7(2):1151-1152.
[32] 张志伟.长骨撑开器于胫骨平台骨折手术中的应用[J].中国医学工程,2015, 23(11):71-72.
|