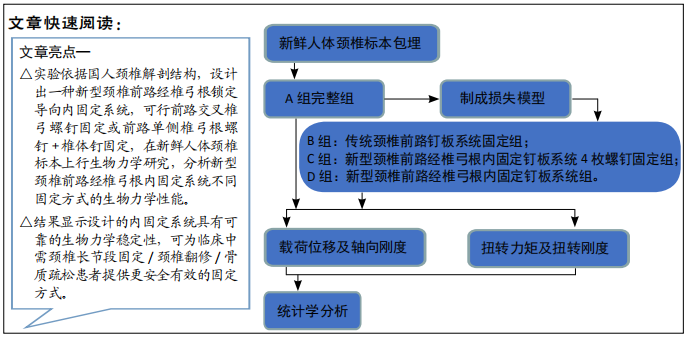
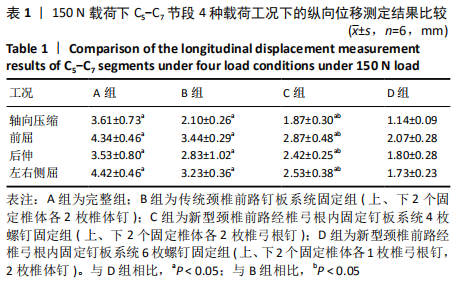
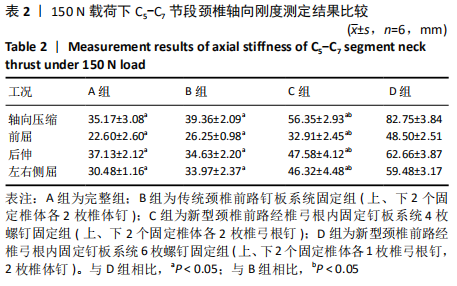
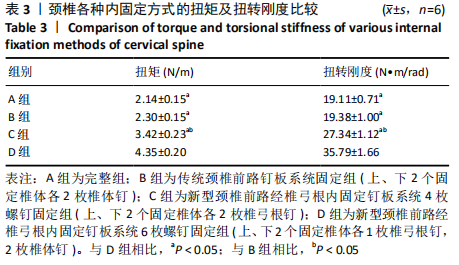
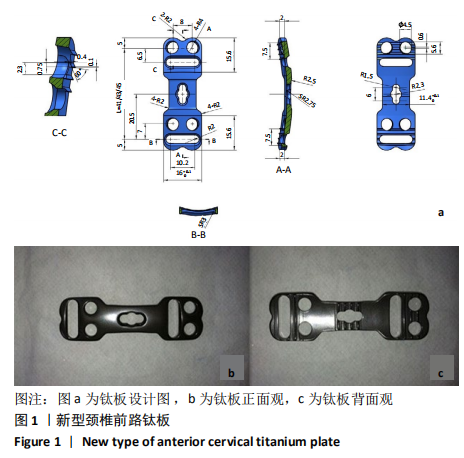
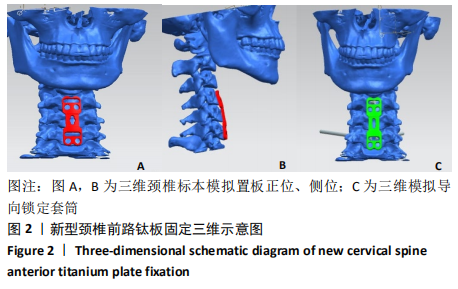
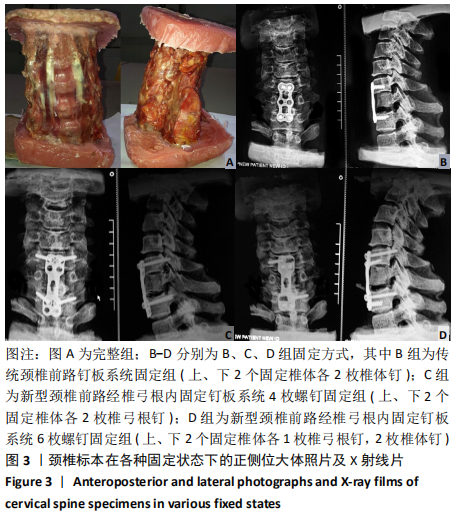
[1] AKULA M, TAHA M, MATHEW B, et al. The Plate cage Benezech implant as an alter- native to autologous bone graft in the treatment of cervical spondylosis:clinical and functional outcome. Br J Neurosurg. 2008;22(4):542-545.
[2] ARTS MP, BRAND K, VAN DEN AKKER E, et al. NE therlands Cervical Kinematics(NECK) Trial. Cost-effectiveness of anterior cervical discectomy with or without interbody fusion and arthroplasty in the treatment of cervical disc herniation;a double-blind randomised multicenter study. BMC Museuloskelet Disord. 2010;16(11):122.
[3] AYDOGAN M, OZTURK C, KARATOPRAK O, et al. The pedicle screw fixation with vertebroplasty augmentation in the surgical treatment of the severe osteoporotic spines. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(6):444-447.
[4] BARNES AH, EGUIZABAL JH, ACOSTA FJ, et al. Biomechanical pullout strength and stability of the cervical artificial pedicle screw.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(1):E16-20.
[5] BECKER S, CHAVANNE A, SPITALER R, et al. Assessment of different screwaugmentation techniques and screw designs in osteoporotic spines. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(11):1462-1469.
[6] BELKOFF SM, MATHIS JM, ERBE EM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of a new bone cement for use in vertebroplasty. Spine. 2000;25(9):1061-1064.
[7] KOILER H, HEMPFINNG A, ACOSTA F, et al. Cervical anterior transpedicular screw fixation. Part I: Study on morphological feasibility,indications and technical prerequisites. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(4):523-538.
[8] EINSIEDEL T, SCHMELZ A, ARAND M, et al. Injuries of the cervical spine in patients with 24 ankylosing spondylitis: experience at two trauma centers. Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5:33-45.
[9] KOLLER H, ACOSTA F, HEMPFING A, et al. Cervical anterior transpedicular screw Fixation. Part I: Study on morphological feasibility ,indications, and technical prerequisites. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:523-538.
[10] 赵刘军,徐荣明,夏华杰,等.两种下颈椎经关节螺钉植入方法的比较研究[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(8):590-592.
[11] 丁宁. 颈前路反向椎弓根固定技术的应用研究[D].徐州:徐州医学院,2011.
[12] 朱青安,胡庆茂,钟世镇,等. 脊柱三维运动分析系统及其在腰椎稳定性分析中的应用[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1995,5(4):253-156 .
[13] VAECARO AR, BALDERSTON RA. Anterior Plate in strimuentation for disorders of the subaxial cervical spine. Clin Orhtop Relat Res. 1997;325:112-121.
[14] HE S, FENG H, LAN Z, et al. A Randomized Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes Between Zero-Profile and Traditional Multi-Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery for Cervical Myelopathy. Spine. 2018;43(5):E259-E266.
[15] DONNARUMMA P, BOZZINI V, RIZZI G, et al. Surgical management of C-type subaxial cervical fractures using eervical traction followed by anterior cervical diseeetomy and fusion within 12 h after the trauma. J Cranio Vertebral Junction Spine. 2017;8(4):338-341.
[16] MCCLELLAND S 3RD, PASSIAS PG, ERRICO TJ, et al. Inpatient versus Outpatient Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion:A Perioperative Complication Analysis of 259,414 Patients From the Heahhcare Cost and Utilization Project Databases. Int J Spine Surg. 2017;11:11.
[17] KOLLERH, ACOSTA F, TAUBER M, et al. Cervical anterior transpedicular screw fixation (ATPS)-PartⅡ,Accuracy of manual insenion and pull-out strength of ATPs. Eur spine J. 2008;17(4):539-555.
[18] BRAZENOR GA. Comparison of multisegment anterior cervical fixationusing bone strut graft versus atitanium rod and buttress prosthesis: analysis ofoutcome with long term follow-up and interview by independent physician. Spine. 2007;32(1):63-71.
[19] 王远致,刘洋,邓忠良,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉置入的实验研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2012,34(18):1839-1843.
[20] KOLLER H, SCHMIDT R, MAYER M, et al. The stabilizing potential of anteriorposterior and combined techniques for the reconstraction of a 2-level cervical corpectomy model: biomechanical study and first results of ATPS prototyping. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(12):2137-2148.
[21] SHAHROKNI M, ZHU Q, LIU J, et al. Design and biomechanical evaluation of a rodent spinal 6xation device. J Spinal Cord. 2012;50(7):543-547.
[22] WANG CS, LIU MJ, LIN JH, et al. One stage anterior-posterior approach for traumatic atlantoaxial instability combined with subaxial cervical spinal cordinjury. Chin J Traumatol. 2011;14(3):137-142.
[23] HUSSAIN M, NASSR A, NATARAJAN RN, et al. Biomechanical effects of anterior, posterior, and combined anterior-posterior instrumentation techniques on the stability of amultilevel cervical corpectomy construct: a finite element model analysis. Spine J. 2011;11(4):324-330.
[24] ONIBOKUN A, KHOO LT, BISTAZZONI S, et al. Anatomical considerations for cervical pediclescrew insertion the use of multiplanar computerized tomography measurements in 122 consecutive clinical cases. Spine J. 2009;9(9):729-734.
[25] 邓斌,袁峰,郭开今,等. 下颈椎颈前路反向椎弓根螺钉内固定的解剖学研究[J].徐州医学院学报,2010,30(8):520-523.
[26] 吴雪晖,李起鸿,杨柳,等. 锥状点式接触钢板内固定对局部皮质骨微循环影响的实验研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2000,20(2):237-241.
[27] PATTON AG, MORRIS RP, KUO YF, et al. Accuracy of fluoroscopy versus computer—assisted navigation for the placement of anterior cervical pedicle screws.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(7):E404-E410.
[28] 王力冉,赵刘军,顾勇杰,等.3D打印导航模板引导双侧下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉置钉的可行性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(11):1012-1017.
[29] 盛晓磊,袁峰,李智多,等. 3D打印组合式导板辅助下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉置人与徒手置钉的准确性对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):406-411. |