中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (26): 4101-4105.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2758
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
髋部几何力学结合骨折风险预测简易工具预测中老年妇女的骨折风险
叶云金1,李健阳2,葛继荣1,许惠娟1,陈赛楠1,谢丽华1,李 莉2
1福建省中医药研究院,福建省福州市 350003;2福建中医药大学,福建省福州市 350122
Combination of hip geometry mechanics and fracture risk assessment tool to predict fracture risk in middle-aged and elderly women
Ye Yunjin1, Li Jianyang2, Ge Jirong1, Xu Huijuan1, Chen Sainan1, Xie Lihua1, Li Li2
1Fujian Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, Fujian Province, China; 2Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
FRAX工具:是世界卫生组织于2007年推荐的一种评估骨折风险的新型软件工具,其作用主要用于临床上,评估有哪些患者有接受骨质疏松诊断和治疗的需要。此软件可以预测患者10年内有多大可能会发生骨折,其主要依据是骨折密度和骨折危险因子的情况,通过一系列大样本循证医学原始数据,骨折部位也很广,包括髋骨骨折百分率,以及全身主要部位的骨折百分率。FRAX工具的使用方法也较为简单,只需要访问官网或用苹果手机下载FRAX应用,在其中录入患者的性别、年龄、身高以及体质量即可。
HSA分析软件:HSA分析软件是美国The Johns Hopkins University 大学 Thomas Beck教授多年来应用CT和双能X射线骨密度仪通过骨几何学特征及一些骨结构指标来研究髋关节近段骨强度,建立了相应的髋关节结构分析系统几何学模型,其作用主要用于了解骨几何力学特征,是用于科研和药物治疗研究的最领先的骨结构分析手段。美国The Johns Hopkins University 大学拥有其专利及商业注册,2006年2月美国Hologic公司与其签署协议在双能X射线数字化骨密度仪中独家使用HSA分析软件,透过骨密度扫描的髋部近端骨成像分析其几何力学的参数。
背景:髋部几何力学是基于双能X射线吸收测定法扫描的图像上进行分析髋部结构(皮质厚薄)的力学研究,可以更好地弥补骨密度的偏差。骨折风险预测简易工具(FRAX)可以将骨折概率与多种临床危险因子以及股骨颈的骨密度相结合,预测10年内髋骨骨折概率和10年内主要骨质疏松性骨折(脊椎、前臂、髋骨或肩部骨折)概率。
目的:分析中老年妇女髋部几何力学以及FRAX@工具与骨折的相关性,探讨两者结合对中老年妇女脆性骨折风险预测的临床意义。
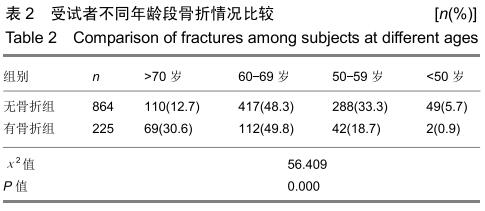
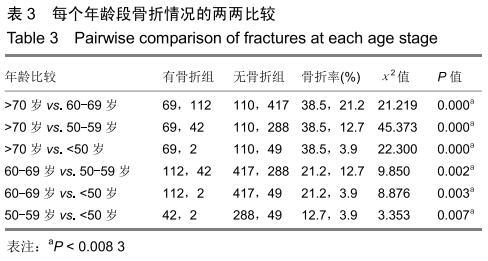
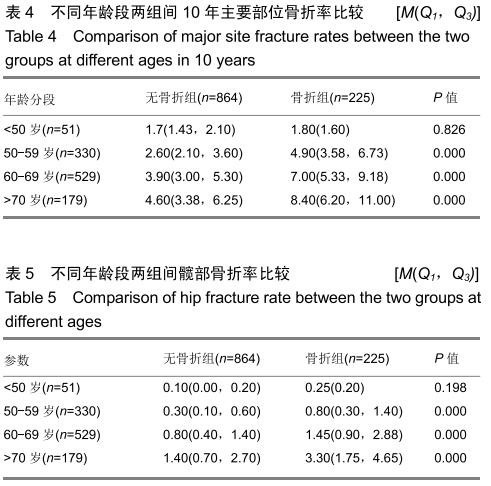
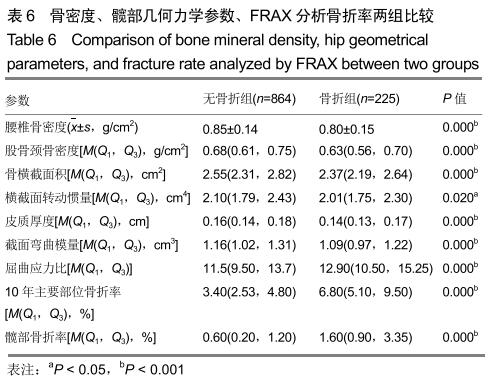
方法:回顾性研究1 089名中老年女性受试者,根据调查问卷分既往有骨折组225例和无骨折864例,双能X射线骨密度仪检测骨密度,HSA软件分析髋部几何力学参数:骨横截面积、横截面转动惯量、截面弯曲模量、皮质厚度和屈曲应力比数值;FRAX@工具计算未来10年主要部位骨折率和髋部骨折率。研究获得福建省中医药研究院伦理委员会审批。
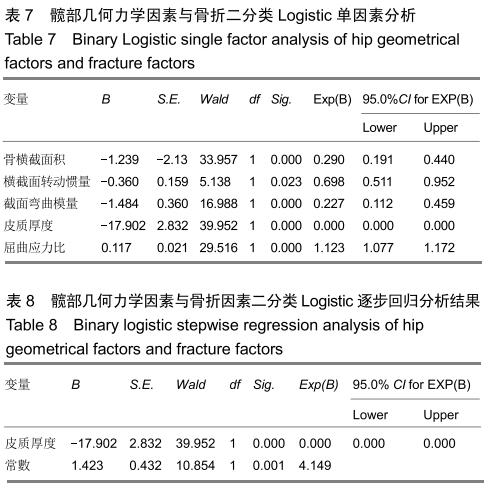
结果与结论:①骨折组的年龄明显高于无骨折组;②2组髋部几何力学参数比较:无骨折组的腰椎骨密度、股骨颈骨密度、骨横截面积、横截面转动惯量、皮质厚度、截面弯曲模量均明显高于骨折组,而屈曲应力比低于骨折组,经Logistic回归分析,显示皮质厚度是骨折的保护因素(OR=0.000,95%CI:0.000-0.000);③不同年龄段FRAX计算分析,骨折组的未来10年主要部位骨折率、髋部骨折率均明显高于无骨折组;④结果说明,髋部几何力学与骨折发生有明显关联性,股骨颈皮质厚度是骨折发生的保护因素,FRAX@分析对预测骨折发生具有临床指导价值,两者结合可以更好地预测骨质疏松性骨折的发生。
ORCID: 0000-0003-2135-2657(叶云金)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: