中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (24): 3792-3796.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2745
• 数字化骨科Digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
半自动脊柱手术机器人系统在脊柱外科治疗中的应用
林云志,方国芳,李修往,吴家昌,吴铭杰,谭 亮,赖国华,叶灼烽,桑宏勋
- 南方医科大学深圳医院骨科,广东省深圳市 518100
Application of semi-automatic spinal surgery robot system in spinal surgery
Lin Yunzhi, Fang Guofang, Li Xiuwang, Wu Jiachang, Wu
Mingjie, Tan Liang, Lai Guohua, Ye Zhuofeng, Sang Hongxun
- Department of Orthopedics, Shenzhen Hospital, Southern Medical University, Shenzhen 518100, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
医学机器人:是多学科研究和发展的成果,是指被应用在诊断、治疗、康复、护理和功能辅助等诸多医学领域的机器人,目前主要被分为手术机器人、康复机器人、辅助机器人、服务机器人。
自动化程度:可分为医师完全直接控制、医师机器人协同控制、医师监督下半自动及机器人全自动4个等级。医师监督下半自动即在医师监督下,手术机器人有一定的自主性执行手术任务,医师主要起到巡视监督的作用,在执行的过程中参与较少,例如肿瘤放射治疗的赛博刀系统。术中或术前医师负责手术规划,执行工作交付于手术机器人,医师在术中可调整手术计划,确保手术过程的安全执行。
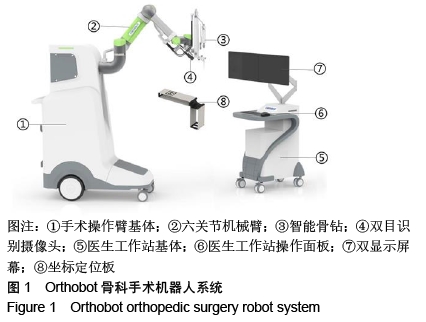
背景:临床常用的手术机器人主要依赖进口,自动化程度不高,核心技术无法突破,国产机器人方兴未艾,手术机器人造价昂贵,手术费用居高不下。课题组及深圳鑫君特智能医疗器械有限公司协同开发了Orthobot脊柱外科专用手术机器人系统,对国产手术机器人的发展意义重大。
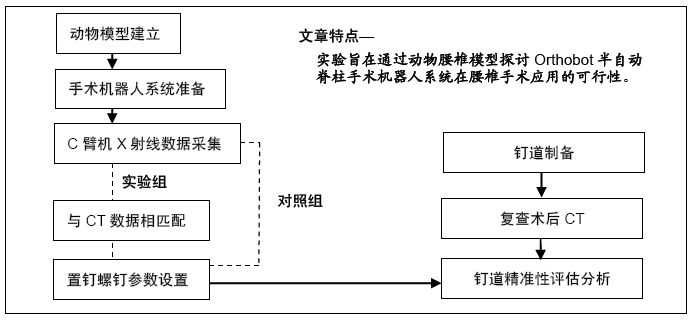
目的:通过动物腰椎模型探讨Orthobot半自动脊柱手术机器人系统在腰椎手术的应用可行性,验证其安全性及有效性,优化手术流程。
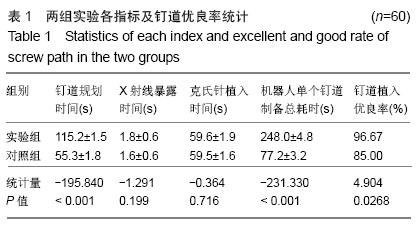
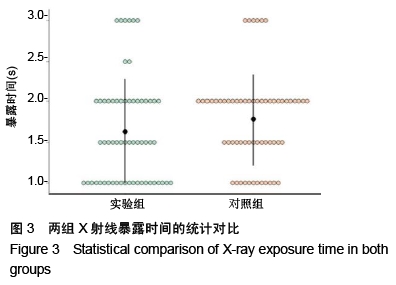
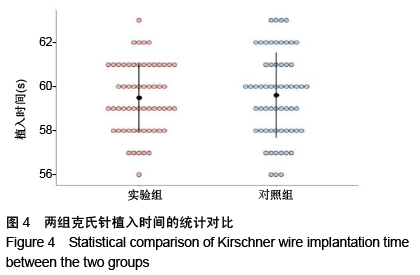
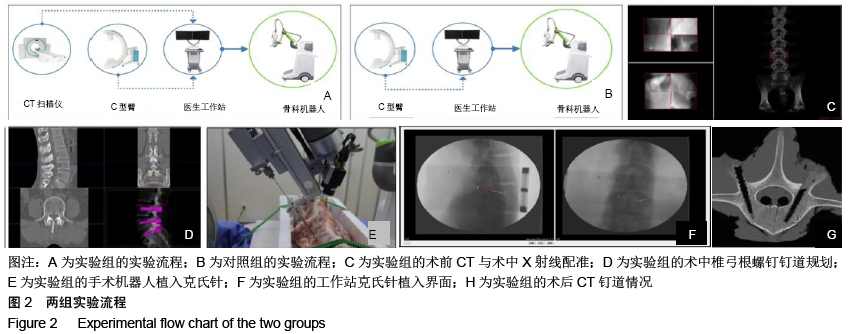
方法:将12具实验猪腰椎标本(L1-L6)随机分成2组,实验组(6具)采用术前CT扫描数据结合术中C臂机X射线透视进行配准,在三维CT数据下规划钉道,应用Orthobot机器人系统进行腰椎标本椎弓根定位,克氏针钻孔,沿克氏针攻丝,制备钉道;对照组(6具)直接采用术中C臂机X射线透视数据,在二维X射线数据下规划钉道。记录术中钉道规划时间、克氏针植入时间、射线暴露时间及机器人单个钉道制备总耗时。复查CT扫描,参照Abul-Kasimhierarchy分级系统评估植入椎弓根螺钉钉道的准确性与优良率。
结果与结论:①实验组钉道规划时间、单个钉道制备总耗时长于对照组(P < 0.001),两组射线暴露时间、克氏针植入时间比较无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②复查CT评估显示,实验组制备60个腰椎椎弓根螺钉钉道的优良率为96.7%(58/60),明显优于对照组的优良率85.0%(51/60)(P < 0.05);③结果表明对比单纯采用术中C臂,应用半自动Orthobot脊柱手术机器人系统结合术前CT与术中C臂置钉的准确率高、安全有效,但术中系统注册匹配时间增加、手术总耗时更长。
ORCID: 0000-0002-6549-7973(林云志)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: