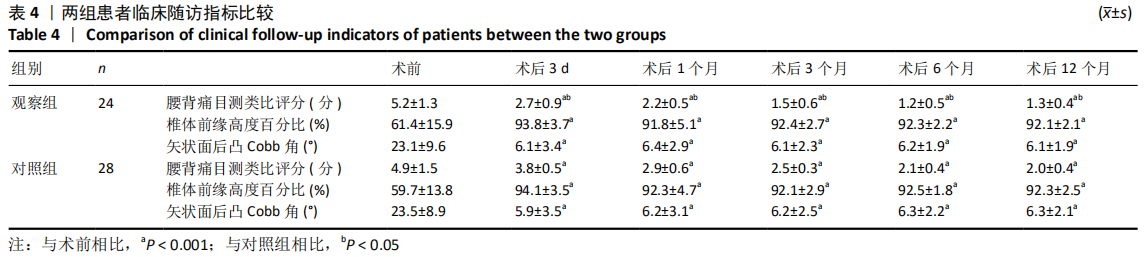
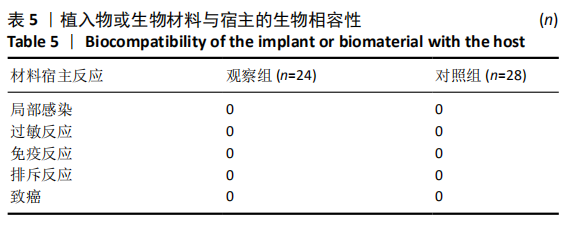
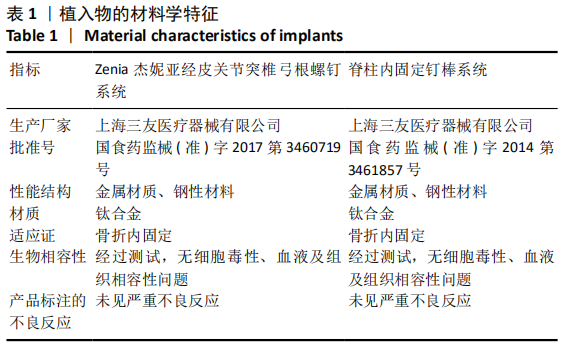
[1] 袁景, 王建峰, 杨平, 等.经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎AO-A1型骨折[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):345-347.
[2] 徐海栋. 脊柱胸腰椎骨折的外科治疗[J]. 医学研究生学报,2019,32(2): 113-118.
[3] DAHDALEH NS, SMITH ZA, HITCHON PW. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2014;25(2):337-346.
[4] OH HS, SEO HY. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation in Thoracolumbar Fractures: Comparison of Results According to Implant Removal Time. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):291-296.
[5] 王庆, 陈泰祥, 李章献, 等.微创经皮手术与开放手术椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效对比[J].中南医学科学杂志,2020,48(3): 297-300,319.
[6] SAHAI N, FALOON MJ, DUNN CJ, et al. Short-Segment Fixation With Percutaneous Pedicle Screws in the Treatment of Unstable Thoracolumbar Vertebral Body Fractures. Orthopedics. 2018;41(6):e802-e806.
[7] 谢鹏, 贺西京, 吕游, 等.微创经皮入路对无神经症状胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的有效性和安全性研究[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2017,20(3): 120-123.
[8] YANG M, ZHAO Q, HAO D, et al. Comparison of clinical results between novel percutaneous pedicle screw and traditional open pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures without neurological deficit. Int Orthop. 2019;43(7):1749-1754.
[9] 孟磊,王和洪,刘宏滨.经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定选择性治疗胸腰椎骨折的效果观察[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2015,18(11):74-76.
[10] LI L, DONG Y, HE Y, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar fractures by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation technique combined with three-step reduction. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2017;78(3):231-237.
[11] 傅扬, 李旭, 段丽群, 等. 经皮邻椎单平面螺钉联合伤椎万向钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效评价[J].颈腰痛杂志,2020,41(3):272-276.
[12] 赖伟强, 陈楚群, 殷炜聪, 等.肌间隙椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的效果及其对术后神经损伤和炎性反应的影响[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2018,21(5):64-68.
[13] YANG WE, NG ZX, KOH KM, et al.Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Singapore Experience.Singapore Med J. 2012;53(9):577-581.
[14] 张贤锋, 梁昌凡, 徐应林. 经伤椎置钉6钉与4钉内固定治疗A1型胸腰椎骨折临床疗效比较[J].安徽医药,2020,24(7):1325-1328.
[15] 杨建伟, 富灵杰, 张蒲. Wiltse入路伤椎椎弓根置钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(3):341-344.
[16] PHAN K, RAO PJ, MOBBS RJ. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2015;135:85-92.
[17] CUI S, BUSEL GA, PURYEAR AS. Temporary Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Stabilization Without Fusion of Adolescent Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2016;36(7):701-708.
[18] NI WF, HUANG YX, CHI YL, et al. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurologic intact thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23(8):530-537.
[19] LI C, PAN J, GU Y, et al. Minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture. Int J Surg. 2016;36(Pt A):255-260.
[20] 周晓, 胡旭琪, 陆惠根, 等.骨科机器人辅助与传统手术治疗胸腰椎骨折的对比研究[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(3):138-142.
[21] 韩明远, 贺振年, 郭剑, 等.经皮与肌间隙入路椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗A1型胸腰段椎体骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(2):161-164.
[22] WANG H, ZHOU Y, LI C, et al. Comparison of open versus percutaneous pedicle screw fixation using the sextant system in the treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(3):E239-E246.
[23] KOCIS J, KELBL M, KOCIS T, et al. Percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation for treatment of type A thoracolumbar fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(1):147-152.
[24] KANNO H, AIZAWA T, HASHIMOTO K, et al. Enhancing percutaneous pedicle screw fixation with hydroxyapatite granules: A biomechanical study using an osteoporotic bone model. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0223106.
[25] WANG H, ZHOU Y, LI C, et al.Comparison of Open Versus Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation Using the Sextant System in the Treatment of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Fractures. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(3):E239-E246.
[26] YANG M, ZHAO Q, HAO D, et al. Comparison of clinical results between novel percutaneous pedicle screw and traditional open pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures without neurological deficit. Int Orthop. 2019;43(7):1749-1754.
[27] WANG B, FAN Y, DONG J,et al.A retrospective study comparing percutaneous and open pedicle screw fixation for thoracolumbar fractures with spinal injuries. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(38):e8104.
[28] GAZZERI R. Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Fixation Technique in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine-Tips and Tricks. Surg Technol Int. 2016;28:303-310.
|