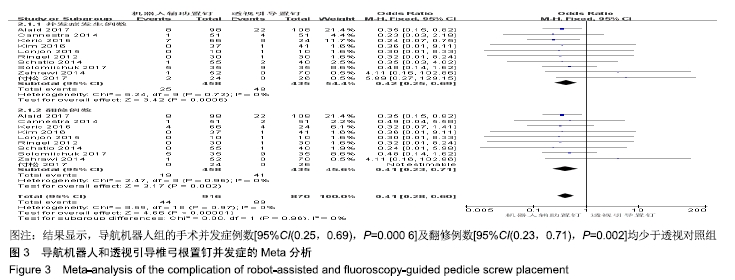
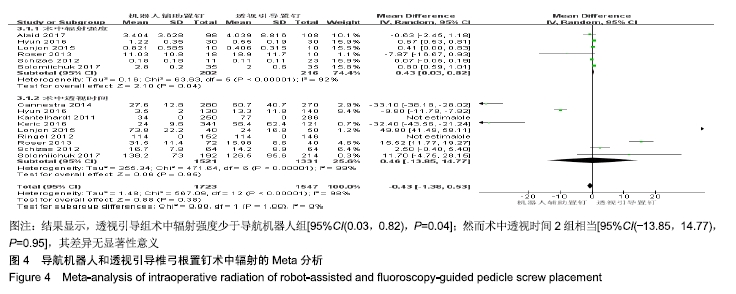
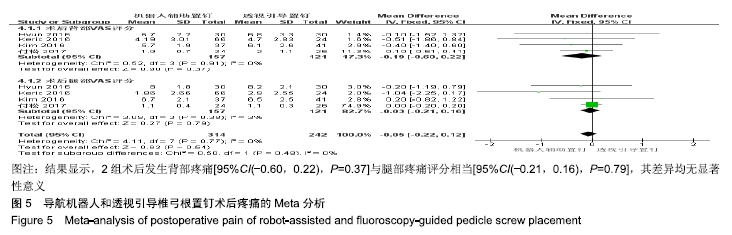
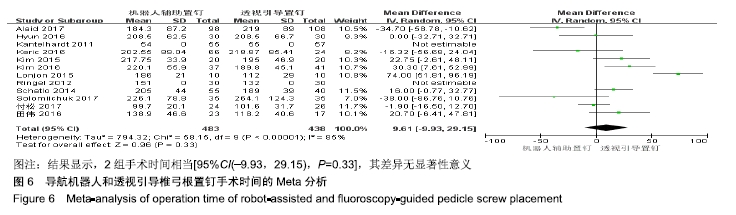
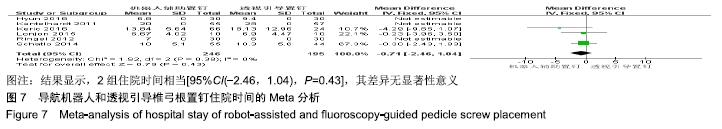
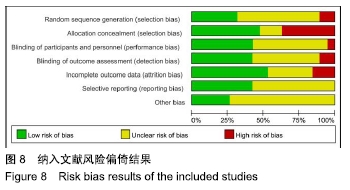
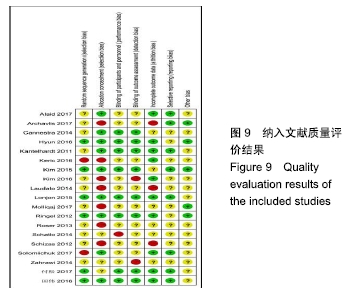
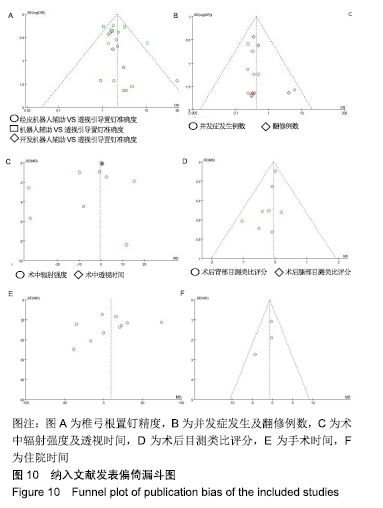
[1] 汤旭日,马安军,傅弛,等. 单侧与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定对行TLIF治疗的腰椎退行性病变患者的效果比较[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(6): 965-967.
[2] ELDER BD, LO SF, HOLMES C, et al. The biomechanics of pedicle screw augmentation with cement. Spine J. 2015; 15(6):1432-1445.
[3] GALBUSERA F, VOLKHEIMER D, REITMAIER S, et al. Pedicle screw loosening: a clinically relevant complication? Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(5): 1005-1016.
[4] VADALÀ G, ACCOTO D, RUSSO F, et al. A new surgical positioning system for robotic assisted minimally invasive spine surgery and transpedicular approach to the disc. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017; 31(4 suppl 1):159-165.
[5] MALHAM GM, PARKER RM. Early experience of placing image-guided minimally invasive pedicle screws without K-wires or bone-anchored trackers. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018; 28(4):357-363.
[6] ALAID A, VON ECKARDSTEIN K, SMOLL NR, et al. Robot guidance for percutaneous minimally invasive placement of pedicle screws for pyogenic spondylodiscitis is associated with lower rates of wound breakdown compared to conventional fluoroscopy-guided instrumentation. Neurosurg Rev. 2018; 41(2):489-496.
[7] ARCHAVLIS E, AMR N, KANTELHARDT SR, et al. Rates of upper facet joint violation in minimally invasive percutaneous and open instrumentation: a comparative cohort study of different insertion techniques. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018; 79(1):1-8.
[8] CANNESTRA AF. Significant decreased radiation exposure in percutaneous adult degenerative spinal instrumentation with robotic guidance. Spine J. 2014; 14(11):S171.
[9] HYUN SJ, KIM KJ, JAHNG TA, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus open fluoroscopic-guided spinal instrumented fusions: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(6):353-358.
[10] KANTELHARDT SR, MARTINEZ R, BAERWINKEL S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(6):860-868.
[11] KERIC N, EUM DJ, AFGHANYAR F, et al. Evaluation of surgical strategy of conventional vs. percutaneous robot-assisted spinal trans-pedicular instrumentation in spondylodiscitis. J Robot Surg. 2017; 11(1):17-25.
[12] KIM HJ, LEE SH, CHANG BS, et al. Monitoring the quality of robot-assisted pedicle screw fixation in the lumbar spine by using a cumulative summation test. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(2):87-94.
[13] KIM HJ, JUNG WI, CHANG BS, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery. Int J Med Robot. 2017; 13(3): 1-7.
[14] LAUDATO PA, PIERZCHALA K, SCHIZAS C. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy using o-arm, robotic guidance, or freehand technique: a comparative study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018; 43(6):E373-E378.
[15] LONJON N, CHAN-SENG E, COSTALAT V, et al. Robot-assisted spine surgery: feasibility study through a prospective case-matched analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(3):947-955.
[16] MOLLIQAJ G, SCHATLO B, ALAID A, et al. Accuracy of robot-guided versus freehand fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42(5):E14.
[17] RINGEL F, STÜER C, REINKE A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(8):E496-501.
[18] ROSER F, TATAGIBA M, MAIER G. Spinal robotics: current applications and future perspectives. Neurosurgery. 2013; 72 Suppl 1:12-18.
[19] SCHATLO B, MOLLIQAJ G, CUVINCIUC V, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine: a matched cohort comparison. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 20(6):636-643.
[20] SCHIZAS C, THEIN E, KWIATKOWSKI B, et al. Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012; 78(2):240-245.
[21] SOLOMIICHUK V, FLEISCHHAMMER J, MOLLIQAJ G, et al. Robotic versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for metastatic spinal disease: a matched-cohort comparison. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42(5): E13.
[22] ZAHRAWI F. Comparative analysis of robotic-guided pedicle screw placement accuracy and freehand controls in percutaneous adult degenerative spinal instrumentation. Spine J. 2014; 14(11):S63.
[23] 付松,邵诗泽,王龙强,等. Quadrant系统下椎间融合辅助机器人治疗老年单节段腰椎退变的临床研究[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017,3(2):70-76.
[24] 田伟,范明星,韩晓光,等. 机器人辅助与传统透视辅助脊柱椎弓根螺钉内固定的临床对比研究[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志, 2016,1(1): 4-10.
[25] XU YF, LE XF, TIAN W, et al. Computer-assisted, minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: One surgeon's learning curve A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(27): e11423.
[26] OVERLEY SC, CHO SK, MEHTA AI, et al. Navigation and Robotics in Spinal Surgery: Where Are We Now? Neurosurgery. 2017; 80(3S): S86-S99.
[27] ONEN MR, NADERI S. Robotic systems in spine surgery. Turk Neurosurg. 2014; 24(3):305-311.
[28] RINGEL F, VILLARD J, RYANG YM, et al. Navigation, robotics, and intraoperative imaging in spinal surgery. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2014; 41:3-22.
[29] 陈龙,海涌,关立,等.机器人辅助置入与徒手置入椎弓根螺钉的对比研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2017, 6(10): 730-736.
[30] 王洪伟. 微创椎弓根螺钉置入中脊柱手术机器人的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53): 8647.
|