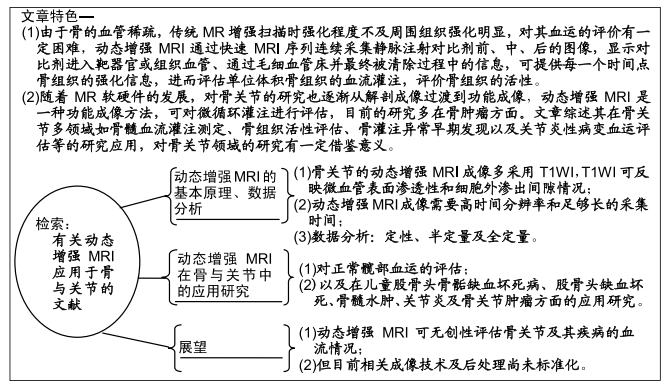
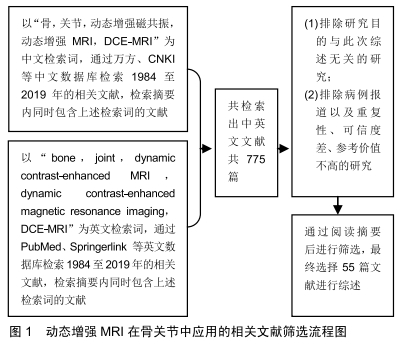
[1] FAYAD LM, JACOBS MA, WANG X, et al. Musculoskeletal tumors: how to use anatomic, functional, and metabolic MR techniques. Radiology. 2012;265:340-356.
[2] JAIN R. Measurements of tumor vascular leakiness using DCE in brain tumors: clinical applications. NMR Biomed. 2013; 26(8): 1042-1049.
[3] VENKATASUBRAMANIAN R, ARENAS RB, HENSON MA, et al. Mechanistic modelling of dynamic MRI data predicts that tumour heterogeneity decreases therapeutic response. Br J Cancer. 2010; 103(4):486-497.
[4] MEYER HJ, WIENKE A, SUROV A. Correlation between Ktrans and microvessel density in different tumors: a Meta-analysis. Anticancer Res. 2018;38(5):2945-2950.
[5] SHI C, LIU D, XIAO Z, et al. Monitoring tumor response to antivascular therapy using non-contrast intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI. Cancer Res. 2017;77(13): 3491-3501.
[6] SEAH S, WHEATON D, LI L, et al. The relationship of tibial bone perfusion to pain in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2012;20: 1527-1533.
[7] LEE JH, DYKE JP, BALLON D,et al. Assessment of bone perfusion with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonanceimaging. Orthop Clin North Am. 2009;40:249-257.
[8] BREAULT SR, HEYE T, BASHIR MR, et al. Quantitative dynamic contrastenhanced MRI of pelvic and lumbar bone marrow: Effect of age and marrow fat content on pharmacokinetic parameter values. Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200:297-303.
[9] MÜLLER GM, MÅNSSON S, MÜLLER MF, et al. Assessment of perfusion in normal carpal bones with dynamic gadolinium- enhanced MRI at 3 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging.2013;38(1):168-172.
[10] FAYAD LM, MUGERA C, SOLDATOS T, et al. Technical innovation in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of musculoskeletal tumors: an MR angiographic sequence using a sparse k-space sampling strategy. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42: 993-1000.
[11] RUNGE VM, CLANTON JA, HERZER WA, et al. Intravascular contrast agents suitable for magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology.1984;153(1):171-176.
[12] 程少容. 动态增强MRI评估股骨头血流灌注状态及激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的机制研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学, 2007.
[13] 卢光明.动态对比增强MRI的应用与进展[J].中华放射学杂志,2015, 49(6):406-409.
[14] DUTOIT JC, VERSTRAETE KL. Whole-body MRI, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, and diffusion-weighted imaging for the staging of multiple myeloma.Skeletal Radiol. 2017;46(6):733-750.
[15] BARNES SL, WHISENANT JG, LOVELESS ME, et al. Practical dynamic contrast enhanced mri in small animal models of cancer: data acquisition, data analysis, and interpretation. Pharmaceutics. 2012;4(3):442-478.
[16] EI KHOULI RH, JACOBS MA, MEZBAN SD, et al. Diffusion- weighted Imaging Improves the Diagnostic Accuracy of Conventional 3.0-T Breast MR Imaging. Radiology. 2010;256(1):64-73.
[17] 李佳璐,李鹍,丁莹莹.定量动态增强磁共振成像在骨与软组织肿瘤中的应用[J].放射学实践,2018,33(3):324-328.
[18] DYKE JP, AARON RK. Noninvasive methods of measuring bone blood perfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192(1):95-102.
[19] POOT DHJ, VAN DEHEIJDEN RA, VANMIDDELKOOP M, et al. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of the patellar bone: How to quantify perfusion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47(3)848-858.
[20] BUDZIK JF, LEFEBVRE G, FORZY G, et al. Study of proximal femoral bone perfusion with 3D T1 dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a feasibility study. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(12):3217-3223.
[21] 牛金亮,王峻,冯敢生,等. MR动态增强扫描评估髋部骨髓血流灌注的初步研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2008,24(10):1493-1496.
[22] WANG YXJ, GRIFFITH JF, KWOK AWL, et al. Reduced bone perfusion in proximal femur of subjects with decreased bone mineral density preferentially affects the femoral neck. Bone. 2009;45(4):711-715.
[23] 程立明,李子荣,王冉东,等.股骨头不同部位血流测定的实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2008,2(1):33-36.
[24] BUDZIK JF, LEFEBVRE G, BEHAL H, et al. Assessment of the zonal variation of perfusion parameters in the femoral head: a 3-T dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI pilot study. Skeletal Radiol. 2017;47:261-270.
[25] GRACIA G, BAUNIN C, VIAL J, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI for outcome prediction in early Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: Medium-term radiographic correlations. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105 (3):547-550.
[26] DILLMAN JR, HERNANDEZ RJ. MRI of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. AJR. 2009; 193(5):1394-1407.
[27] SUJLANA P, SKROK J, FAYAD LM. Review of dynamic contrast- enhanced MRI: Technical aspects and applications in the musculoskeletal system. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47(4): 875-890.
[28] COVA M, KANG YS, TSUKAMOTO H, et al. Bone marrow perfusion evaluated with gadolinium-enhanced dynamic fast MR imaging in a dog model. Radiology. 1991;179(2):535-539.
[29] 程少容,王仁法,高小玲,等. 动态增强MRI评价股骨头血流灌注状态的实验研究[J].中国临床医学影像杂志,2007,18(2):110-114.
[30] CHAN WP, LIU YJ, HUANG GS, et al. Relationship of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head to perfusion changes in the proximal femur by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(3):637-643.
[31] AARON RK, DYKE JP, CIOMBOR DM, et al. Perfusion abnormalities in subchondral bone associated with marrow edema, osteoarthritis, and avascular necrosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1117(1):124-137.
[32] BERG BCV, LECOUVET FE, KOUTAISSOFF S, et al. Bone marrow edema of the femoral head and transient osteoporosis of the hip. Eur J Radiol. 2008;67(1):68-77.
[33] MUELLER D, SCHAEFFELER C, BAUM T, et al. Magnetic resonance perfusion and diffusion imaging characteristics of transient bone marrow edema, avascular necrosis and subchondral insufficiency fractures of the proximal femur. Eur J Radiol.2014;83(10):1862-1869.
[34] GEITH T, NIETHAMMER T, MILZ S, et al. Transient bone marrow edema syndrome versus osteonecrosis: perfusion patterns at dynamic contrast-enhanced mr imaging with high temporal resolution can allow differentiation. Radiology. 2017;283(2):478-485.
[35] HIRATA T, KONISHIIKE T, KAWAI A, et al. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head perfusion in femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):294-301.
[36] KAMANO M, NARITA S, HONDA Y, et al. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;350(350):179-186.
[37] KONISHIIKE E, MAKIHATA H, TAGO T, et al. Acute fracture of the neck of the femur. An assessment of perfusion of the head by dynamic MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(4):596-599.
[38] DYKE JP, LAZARO LE, HETTRICH CM, et al. Regional analysis of femoral head perfusion following displaced fractures of the femoral neck. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41(2):550-554.
[39] LEE JH, DYKE JP, BALLON D, et al. Subchondral fluid dynamics in a model of osteoarthritis: use of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009; 17(10):1350-1355.
[40] KIM EY, KWACK KS, CHO JH, et al. Usefulness of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in differentiating between septic arthritis and transient synovitis in the hip joint. Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198(2):428-433.
[41] MCGILL M, MOLYNEAUX L, BOLTON T, et al. Response of Charcot's arthropathy to contact casting: assessment by quantitative techniques. Diabetologia. 2000;43(4):481-484.
[42] ZAMPA V, BARGELLINI I, RIZZO L, et al. Role of dynamic MRI in the follow-up of acute Charcot foot in patients with diabetes mellitus. Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40(8):991-999.
[43] 陈基明,翟建,张峥嵘,等. 动态增强MRI对早期类风湿性关节炎的诊断价值[J].临床放射学杂志,2014,33(3):415-419.
[44] 孙雁,张炳,季涛. 动态增强MRI对手部类风湿性关节炎活动性的诊断价值[J].中国临床医学影像杂志,2017,28(3):208-211.
[45] 曾伟科,莫颖倩,张翔,等.动态增强MRI定量评价类风湿性关节炎腕关节炎症活动度的价值[J]. 磁共振成像,2015,6(6):4555-461.
[46] 傅丽晖,张瑾,梁良. MRI动态增强技术对活动性类风湿性关节炎疗效判断的应用价值[J]. 医学影像学杂志,2019,29(5):828-832.
[47] 初广宇,张孟超,杨海山,等.动态对比增强MRI判断强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节炎活动性的临床初步研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2015,49(12): 895-899.
[48] 王娟,张家雄,周守国.扩散加权成像及动态增强MRI在强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节炎疗效评估中的价值[J]. 放射学实践,2019,34(1):60-64.
[49] OH E, YOON YC, KIM JH, et al. Multiparametric approach with diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI: a comparison study for differentiating between benign and malignant bone lesions in adults. Clin Radiol. 2017; 72(7): 552-559.
[50] 张晶,左盼莉,程克斌,等. 动态增强磁共振成像用于肌骨系统肿瘤定性诊断的可行性[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2):287-291.
[51] ZHA Y, LI M, YANG J. Dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of diffuse spinal bone marrow infiltration in patients with hematological malignancies. Korean J Radiol. 2010;11(2): 187-194.
[52] SHIH TT, HOU HA, LIU CY, et al. Bone marrow angiogenesis magnetic resonance imaging in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: peak enhancement ratio is an independent predictor for overall survival. Blood. 2009;113(14):3161-3167.
[53] MERZ M, MOEHLER TM, RITSCH J, et al. Prognostic significance of increased bone marrow microcirculation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: results of a prospective DCE-MRI study. Eur Radiol. 2016; 26(5):1404-1411.
[54] AMIT P, PATRO DK, BASU D, et al. Role of dynamic MRI and clinical assessment in predicting histologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bone sarcomas.Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;37(4):384-390.
[55] ANZIDEI M, NAPOLI A, SACCONI B, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound for the treatment of painful bone metastases: role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MRI in the assessment of clinical outcome. Radiol Med. 2016;121(12):905-915.
|