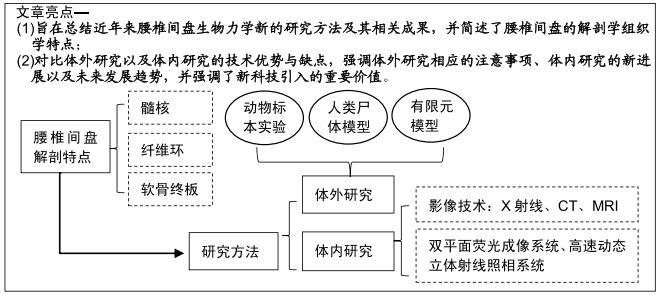
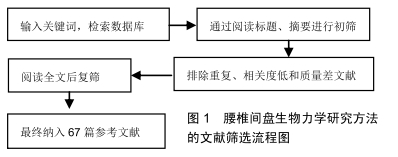
[1] ŁEBKOWSKI WJ. Autopsy evaluation of the extent of degeneration of the lumbar intervertebral discs. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002;13(75):188-190.
[2] RAJ PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology- pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 2008;8(1):18-44.
[3] ZHU Q, GAO X, BROWN MD, et al. Simulation of water content distributions in degenerated human intervertebral discs. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(1):147-153.
[4] IATRIDIS JC, MICHALEK AJ, PURMESSUR D, et al. Localized intervertebral disc injury leads to organ level changes in structure, cellularity, and biosynthesis. Cell Mol Bioeng, 2009;2(3):437-447.
[5] NEDRESKY D, SINGH G. Anatomy, Back, Nucleus Pulposus. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019.
[6] NEWELL N, LITTLE JP, CHRISTOU A, et al. Biomechanics of the human intervertebral disc: A review of testing techniques and results. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;69(Complete): 420-434.
[7] MELROSE J, SMITH SM, APPLEYARD RC, et al. Aggrecan, versican and type VI collagen are components of annular translamellar crossbridges in the intervertebral disc. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(2):314-324.
[8] BOREM R, MADELINE A, WALTERS J, et al. Angle-ply biomaterial scaffold for annulus fibrosus repair replicates native tissue mechanical properties, restores spinal kinematics, and supports cell viability. Acta Biomater. 2017; 58:254-268.
[9] BOREM R, MADELINE A, VELA RJ, et al. Multi-laminate annulus fibrosus repair scaffold with an interlamellar matrix enhances impact resistance, prevents herniation and assists in restoring spinal kinematics. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;95:41-52.
[10] MCGUIRE R, BOREM R, MERCURI J. The fabrication and characterization of a multi-laminate, angle-ply collagen patch for annulus fibrosus repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017; 11(12):3488-3493.
[11] ZHAO FD, POLLINTINE P, HOLE BD, et al. Vertebral fractures usually affect the cranial endplate because it is thinner and supported by less-dense trabecular bone. Bone. 2009;44(2):372-379.
[12] ADAMS MA, LAMA P, ZEHRA U, et al. Why do some intervertebral discs degenerate, when others (in the same spine) do not? Clin Anat. 2015 Mar;28(2):195-204
[13] GIERS MB, MUNTER BT, EYSTER KJ, et al. Biomechanical and endplate effects on nutrient transport in the intervertebral disc. World Neurosurg. 2017;99:395-402.
[14] ZEHRA U, FLOWER L, ROBSON-BROWN K, et al. Defects of the vertebral end plate: implications for disc degeneration depend on size. Spine J. 2017;17(5):727-737.
[15] CHEN S, FU P, WU H, et al. Meniscus, articular cartilage and nucleus pulposus: a comparative review of cartilage-like tissues in anatomy, development and function. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;370(1):53-70.
[16] GERSING AS, WOERTLER K, JUNGMANN PM, et al. Vertebrae, Vertebral End Plates, and Disks: Concepts and Specific Pathologies. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2019; 23(5):489-496.
[17] RAJ PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology- pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract. 2008;8(1):18-44.
[18] RAOUL S, FAURE A, ROBERT R, et al. Role of the sinu- vertebral nerve in low back pain and anatomical basis of therapeutic implications.Surg Radiol Anat.2003;24(6):366-371.
[19] WILKE HJ, KETTLER A, WENGER KH, et al. Anatomy of the sheep spine and its comparison to the human spine. Anat Rec. 1997;247(4):542-555.
[20] KUMAR N, KUKRETI S, ISHAQUE M, et al. Anatomy of deer spine and its comparison to the human spine. Anat Rec. 2000; 260(2):189-203.
[21] HOWARTH SJ, GALLAGHER KM, CALLAGHAN JP. Postural influence on the neutral zone of the porcine cervical spine under anterior-posterior shear load. Med Eng Phys. 2013; 35(7):910-918.
[22] BERGER-ROSCHER N, CASAROLI G, RASCHE V, et al. Influence of complex loading conditions on intervertebral disc failure. Spine. 2017;42(2):E78-E85.
[23] JAUMARD NV, LEUNG J, GOKHALE AJ, et al. Relevant anatomic and morphological measurements of the rat spine. Spine. 2015;40(20):E1084-E1092.
[24] MOSLEY GE, HOY RC, NASSER P, et al. Sex differences in rat intervertebral disc structure and function following annular puncture injury. Spine. 2019;44(18):1257-1269.
[25] CHOI H, TESSIER S, SILAGI ES, et al. A novel mouse model of intervertebral disc degeneration shows altered cell fateand matrix homeostasis. Matrix Biol. 2018;70:102-122.
[26] FU M, YE Q, JIANG C, et al. The segment-dependent changes in lumbar intervertebral space height during flexion-extension motion. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(4):245-252.
[27] COSTI JJ, STOKES IA, GARDNER-MORSE M, et al. Direct measurement of intervertebral disc maximum shear strain in six degrees of freedom: Motions that place disc tissue at risk of injury. J Biomech. 2007;40(11):2457-2466.
[28] DMITRIEV AE, GILL NW, KUKLO TR, et al. Effect of multilevel lumbar disc arthroplasty on the operative- and adjacent-level kinematics and intradiscal pressures: an in vitro human cadaveric assessment. Spine J. 2008;8(6): 918-925.
[29] KETTLER A, ROHLMANN F, RING C, et al. Do early stages of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration really cause instability? Evaluation of an in vitro database. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(4):578-584.
[30] SUNNI N, ASKIN GN, LABROM RD, et al. The effect of repeated loading and freeze-thaw cycling on immature bovinethoracic motion segment stiffness. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228(10):1100-1107.
[31] HU B, LV X, CHEN S, et al. Application of finite element analysis for investigation of intervertebral disc degeneration: from laboratory to clinic. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39(1):7-15.
[32] 冯其金,赵玲娟,郑昆仑,等. 有限元分析法在腰椎生物力学中的研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2018,24(2):255-258.
[33] NATARAJAN RN, WILLIAMS JR, ANDERSSON GBJ. Modeling changes in intervertebral disc mechanics with degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:36.
[34] 张振军,李阳,廖振华,等.有限元法在腰椎生物力学应用中的研究进展和展望[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2016,33(6):1196-1202.
[35] BASHKUEV M, REITMAIER S, SCHMIDT H. Effect of disc degeneration on the mechanical behavior of the human lumbar spine:a probabilistic finite element study. Spine J. 2018;18(10):1910-1920.
[36] MASNI-AZIAN, TANAKA M. Biomechanical investigation on the influence of the regional material degeneration of an intervertebral disc in a lower lumbar spinal unit: A finite element study. Comput Biol Med. 2018;98:26-38.
[37] NATARAJAN RN. Modeling changes in intervertebral disc mechanics with degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(suppl_2):36.
[38] SCHMIDT H, GALBUSERA F, ROHLMANN A, et al. What have we learned from finite element model studies of lumbar intervertebral discs in the past four decades? J Biomech. 2013;46(14):2342-2355.
[39] SCHMIDT H, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Temporal and spatial variations of pressure within intervertebral disc nuclei. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;79:309-313.
[40] AUERBACH JD, WILLS BPD, MCINTOSH TC, et al. Evaluation of spinal kinematics following lumbar total disc replacement and circumferential fusion using in vivo fluoroscopy. Spine. 2007;32(5):527-536.
[41] AUERBACH JD, JONES KJ, MILBY AH, et al. Segmental contribution toward total lumbar range of motion in disc replacement and fusions. Spine. 2009;34(23):2510-2517.
[42] WONG KWN, LUK KDK, LEONG JCY, et al. Continuous dynamic spinal motion analysis. Spine. 2006;31(4):414-419.
[43] TAKAYANAGI K, TAKAHASHI K, YAMAGATA M, et al. Using cineradiography for continuous dynamic-motion analysis of the lumbar spine. Spine. 2001;26(17):1858-1865.
[44] 孟悛非,范淼.重视CT检查中的辐射剂量[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2008,42(10):1015-1017.
[45] GRIVAS TB, SAVVIDOU O, BINOS S, et al. Morphometric characteristics of the thoracοlumbar and lumbar vertebrae in the Greek population: a computed tomography-based study on 900 vertebrae-“Hellenic Spine Society (HSS) 2017 Award Winner”. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2019;14:2.
[46] GULEC A, KACIRA BK, KUTAHYA H, et al. Morphometric analysis of the lumbar vertebrae in the Turkish population using three-dimensional computed tomography: correlation with sex, age, and height. Folia Morphologica. 2017;76(3):433-439.
[47] OCHIA RS, INOUE N, RENNER SM, et al. Three-dimensional in vivo measurement of lumbar spine segmental motion. Spine. 2006;31(18):2073-2078.
[48] OCHIA RS, INOUE N, TAKATORI R, et al. In vivo measurements of lumbar segmental motion during axial rotation in asymptomatic and chronic low back pain male subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(13):1394-1399.
[49] GODA Y, SAKAI T, HARADA T, et al. Degenerative Changes of the Facet Joints in Adults With Lumbar Spondylolysis. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(6):E738-E742.
[50] ZHONG W, DRISCOLL SJ, WU M, et al. In vivo morphological features of human lumbar discs. Medicine. 2014;93(28):e333.
[51] MCGREGOR AH, ANDERTON L, GEDROYC WMW, et al. The use of interventional open MRI to assess the kinematics of the lumbar spinein patients with spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002;27(14):1582-1586.
[52] POWERS CM, KULIG K, HARRISON J, et al. Segmental mobility of the lumbar spine during a posterior to anterior mobilization: assessment using dynamic MRI. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(1):80-83.
[53] KULIG K, LANDEL R, POWERS CM. Assessment of lumbar spine kinematics using dynamic MRI: a proposed mechanism of sagittal plane motion induced by manual posterior-to-anterior mobilization. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2004;34(2):57.
[54] SABNIS AB, CHAMOLI U, DIWAN AD. Is L5–S1 motion segment different from the rest? A radiographic kinematic assessment of 72 patients with chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(5):1127-1135.
[55] WALTER BA, MAGESWARAN P, MO X, et al. MR elastography-derived stiffness: a biomarker for intervertebral disc degeneration. Radiology. 2017;285(1):167-175.
[56] BEAUCHEMIN PF, BAYLY PV, GARBOW JR, et al. Frequency-dependent shear properties of annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus by magnetic resonance elastography. NMR Biomed. 2018;31(10):e3918.
[57] SHELDRICK K, CHAMOLI U, MASUDA K, et al. A novel magnetic resonance imaging postprocessing technique for the assessment of intervertebral disc degeneration-Correlation with histological grading in arabbit disc degeneration model. JOR Spine. 2019;2(3):e1060.
[58] LAWRENCE RL, ELLINGSON AM, LUDEWIG PM. Validation of single-plane fluoroscopy and 2D/3D shape-matching for quantifyingshoulder complex kinematics. Med Eng Phys. 2018;52:69-75.
[59] BAI J, HU Y, DU L, et al. Assessing validation of dual fluoroscopic image matching method for measurement of in vivo spine kinematics. Chin Med J. 2011;124(11):1689-1694.
[60] WANG S, XIA Q, PASSIAS P, et al. Measurement of geometric deformation of lumbar intervertebral discs under in-vivo weightbearing condition. J Biomech. 2009;42(6): 705-711.
[61] LI G, WANG S, PASSIAS P, et al. Segmental in vivo vertebral motion during functional human lumbar spine activities. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(7):1013-1021.
[62] WANG S, PASSIAS P, LI G, et al. Measurement of vertebral kinematics using noninvasive image matching method- validation and application. Spine. 2008;33(11):E355-E361.
[63] WU M, WANG S, DRISCOLL SJ, et al. Dynamic motion characteristics of the lower lumbar spine: implication to lumbarpathology and surgical treatment. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23(11):2350-2358.
[64] LIU Z, TSAI T, WANG S, et al. Sagittal plane rotation center of lower lumbar spine during a dynamicweight-lifting activity. J Biomech. 2016;49(3):371-375.
[65] AIYANGAR AK, ZHENG L, TASHMAN S, et al. Capturing three-dimensional in vivo lumbar intervertebral joint kinematics using dynamic stereo-X-ray imaging. J Biomech Eng. 2014;136(1):11004.
[66] AIYANGAR A, ZHENG L, ANDERST W, et al. Apportionment of lumbar L2-S1 rotation across individual motion segments during adynamic lifting task. J BiomechM 2015;48(13): 3709-3715.
[67] BYRNE RM, AIYANGAR AK, ZHANG X. A dynamic radiographic imaging study of lumbar intervertebral disc morphometryand deformation in vivo. Sci Rep.2019;9(1): 15490.
|