[1] OHASHI K, SHIBATA R, MUROHARA T, et al. Role of anti-inflammatory adipokines in obesity-related diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014;25(7):348-355.
[2] BHASKARAN K, DOUGLAS I, FORBES H, et al. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers: a population-based cohort study of 5•24 million UK adults. Lancet.2014;384(9945):755-765.
[3] NCD RISK FACTOR COLLABORATION (NCD-RISC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19•2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387 (10026):1377-1396.
[4] HAMAD N, TRAVIS SP. Weight loss at high altitude: pathophysiology and practical implications. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18(1):5-10.
[5] LING Q, SAILAN W, RAN J, et al. The effect of intermittent hypoxia on bodyweight, serum glucose and cholesterol in obesity mice. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008;11(6):869-875.
[6] MORTOLA JP. Implications of hypoxic hypometabolism during mammalian ontogenesis. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004; 141(3):345-356.
[7] COSTALAT G, LEMAITRE F, TOBIN B, et al. Intermittent hypoxia revisited: a promising non-pharmaceutical strategy to reduce cardio-metabolic risk factors? Sleep Breath. 2018; 22(1): 267-271.
[8] KONG Z, ZANG Y, HU Y. Normobaric hypoxia training causes more weight loss than normoxia training after a 4-week residential camp for obese young adults. Sleep Breath. 2014; 18(3):591-597.
[9] KOJIMA M, HOSODA H, DATE Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth- hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402(6762):656-660.
[10] KAMEGAI J, TAMURA H, SHIMIZU T, et al. Chronic central infusion of ghrelin increases hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and Agouti-related protein mRNA levels and body weight in rats. Diabetes. 2001;50(11):2438-2443.
[11] 付鹏宇,龚丽景,朱镕鑫,等.Ghrelin-GHSR通路在急性低氧暴露大鼠胃炎症反应中的调节作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018,34(10):1103-1110.
[12] ALIPARASTI MR, ALIPOUR MR, ALMASI S, et al. Ghrelin Administration Increases the Bax/Bcl-2 Gene Expression Ratio in the Heart of Chronic Hypoxic Rats. Adv Pharm Bull. 2015;5(2):195-199.
[13] OH-I S, SHIMIZU H, SATOH T, et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature. 2006;443 (7112):709-712.
[14] STENGEL A, TACHÉ Y. Nesfatin-1--role as possible new potent regulator of food intake. Regul Pept. 2010;163(1-3):18-23.
[15] ZHANG T, WANG M, LIU L, et al. Hypothalamic nesfatin-1 mediates feeding behavior via MC3/4R-ERK signaling pathway after weight loss in obese Sprague-Dawley rats. Peptides. 2019;119:170080.
[16] ÖZTÜRK ÖZKAN G. Effects of Nesfatin-1 on Food Intake and Hyperglycemia. J Am Coll Nutr. 2019 Aug 1:1-7.
[17] 冯连世,张漓,高炳宏,等.不同环境下有氧运动对超重和肥胖青少年体重与体脂含量的影响[J].体育科学,2013,33(11):58-65.
[18] DE GROOTE E, BRITTO FA, BULLOCK L, et al. Hypoxic Training Improves Normoxic Glucose Tolerance in Adolescents with Obesity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(11):2200-2208.
[19] 吴娜娜,管延飞,朱欢,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年血浆食欲调节激素的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2015,31(3):281-283.
[20] 王茹,刘冬梅,吴娜娜,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年内源性大麻素及相关食欲调节激素的影响[J].体育科学,2016,36(2):51-57,71.
[21] URDAMPILLETA A, GONZÁLEZ-MUNIESA P, PORTILLO MP, et al. Usefulness of combining intermittent hypoxia and physical exercise in the treatment of obesity. J Physiol Biochem. 2012;68(2):289-304.
[22] 王茹,王红霞,许亚丽,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年形态学指标和糖脂代谢的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(9):81-87.
[23] 陈瑜文,林文弢,邱烈峰,等.间歇低氧运动对肥胖大鼠食欲的影响及其机制分析[J].体育学刊,2011,18(4):133-136.
[24] WASSE LK, SUNDERLAND C, KING JA, et al. Influence of rest and exercise at a simulated altitude of 4,000 m on appetite, energy intake, and plasma concentrations of acylated ghrelin and peptide YY. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012; 112(4):552-559.
[25] 吴菊花,杨亚南,翁锡全,等.低氧运动对营养性肥胖大鼠骨骼肌PGC-1α及其下游因子的影响[J].体育学刊, 2016,23(3) : 130-136.
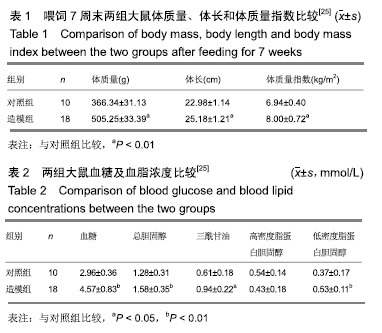
[26] 上官若男,苏全生,尚画雨,等.运动负荷强度与运动疲劳程度量化分级研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2013, 28(2): 188-192.
[27] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.
[28] HØYDAL MA, WISLØFF U, KEMI OJ, et al. Running speed and maximal oxygen uptake in rats and mice: practical implications for exercise training. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14(6):753-760.
[29] 何明,涂长春,黄起壬,等. Lee's 指数用于评价成年大鼠肥胖程度的探讨[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学杂志,1997,2(3):177-179.
[30] 张静,沙继斌,张林,等.有氧运动与多糖干预对肥胖大鼠的血脂调节及抗炎作用[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2016,35(2):86-91.
[31] 谢宜轩,李帅.持续和间歇低氧运动对肥胖大鼠体重及相关代谢指标的影响[J].扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2016,37(1): 31-34.
[32] TAN BK, HALLSCHMID M, KERN W, et al. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid/plasma ratio of the novel satiety molecule, nesfatin-1/NUCB-2, in obese humans: evidence of nesfatin-1/NUCB-2 resistance and implications for obesity treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96(4):E669-673.
[33] 孙文娟,于普艳,戴红艳,等.肥胖症病人血浆nesfatin-1水平变化及与BMI关系[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2013,28(3):235-236,240.
[34] 李娜,田字彬,孙桂荣,等.Nesfatin-1对肥胖大鼠胃排空及胃平滑肌条收缩性的影响[J].世界华人消化杂志,2012,20(8): 631-637.
[35] CUI H, SOHN JW, GAUTRON L, et al. Neuroanatomy of melanocortin-4 receptor pathway in the lateral hypothalamic area. J Comp Neurol. 2012;520(18):4168-4183.
[36] 习燕华,刘建英. Nesfatin-1在肥胖及血糖调节中的作用[J].生理科学进展,2013,44(3):220-222.
[37] CHAOLU H, ASAKAWA A, USHIKAI M, et al. Effect of exercise and high-fat diet on plasma adiponectin and nesfatin levels in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2011;2(2):369-373.
[38] HAGHSHENAS R, JAFARI M, RAVASI A, et al. The effect of eight weeks endurance training and high-fat diet on appetite-regulating hormones in rat plasma. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014;17(4):237-243.
[39] TSCHÖP M, SMILEY DL, HEIMAN ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407(6806):908-913.
[40] 汪军,田吉明. 8周跑台运动对肥胖大鼠下丘脑ghrelin 和obestatin 的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2009,32(4):57-60.
[41] 唐光旭,汪军.急性运动对肥胖大鼠下丘脑ghrelin和obestatin的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2010,29(5):551-555.
[42] 王宁琦,胡扬,官余凌,等.4周低氧运动结合饮食控制对肥胖青年体重、血脂及胰岛素抵抗的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2012, 31(4):289-294.
|