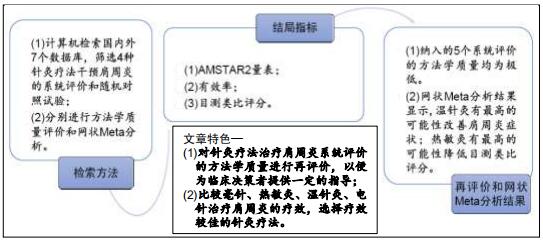
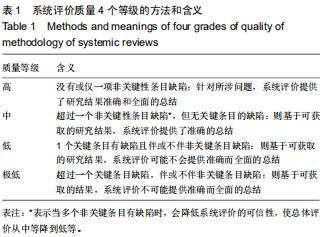
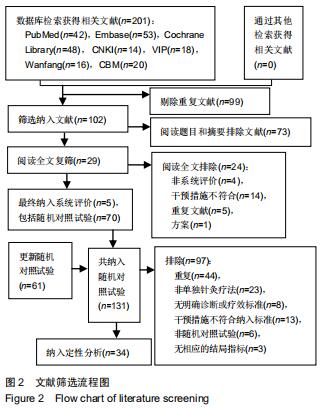
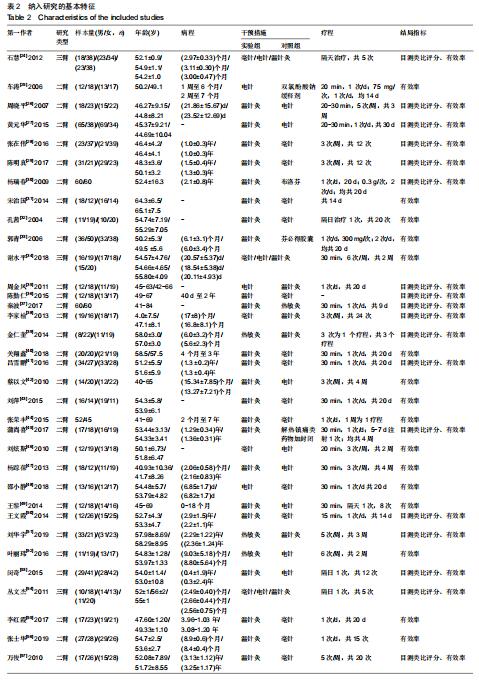
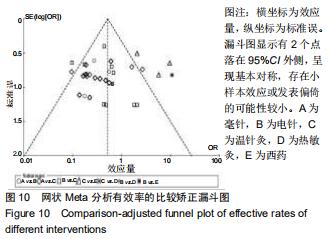
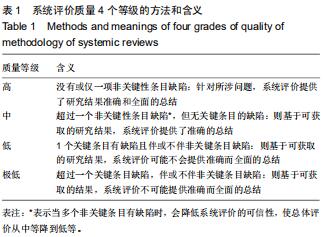
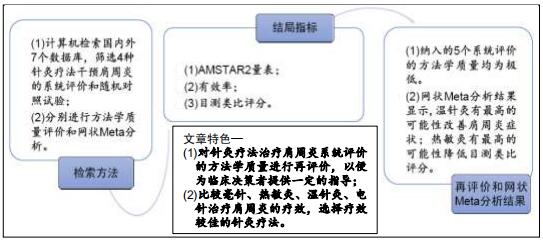
|
[1] LUNDBERG J. The frozen shoulder. Clinical and radiographical observations. The effect of manipulation under general anesthesia. Structure and glycosaminoglycan content of the joint capsule. Local bone metabolism. Acta Orthop Scand. 1969;119:1-59.
[2] 郭前进,刘志宏,崔周敏.肩周炎与肩周痛[J].实用疼痛学杂志, 1996,4(4): 187-190.
[3] HUANG C, XIE L, LIN Y, et al. Effectiveness and safety of fire needle on periarthritis of shoulder: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019;98(20): e15673.
[4] DAWSON J, SHEPPERD S, CARR A. An overview of factors relevant to undertaking research and reviews on the effectiveness of treatment for frozen shoulder. Shoulder Elbow. 2010; 2:232-237.
[5] PAREEK A, CHANDURKAR N, AMBADE R, et al. Efficacy and safety of etodolac-paracetamol fixed dose combination in patients with knee osteoarthritis flareup: a randomized, double-blind comparative evaluation. Clin J Pain. 2010; 26:561-566.
[6] GODWIN M, DAWES M. Intra-articular steroid injections for painful knees. Systematic review with meta-analysis. Can Fam Physician 2004; 50:241-248.
[7] GRILLET B, DEQUEKER J. Intra-articular steroid injection. A risk-benefit assessment. Drug Saf.1990;5(3):205-211.
[8] 梁繁荣,吴曦,李瑛,等.循证针灸学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009.
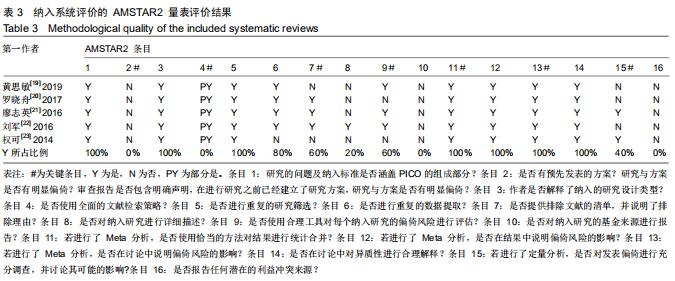
[9] 熊俊,陈日新,李万瑶.针灸治疗颈椎病系统评价/Meta分析文献质量多元评价研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(4):1064-1068.
[10] HIGGINS JP, GREEN S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. 4th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
[11] BEVERLEY JS, BARNABY CR, GEORGE W, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017; 358: j4008.
[12] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343: d5928.
[13] HIGGINS JP, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557-560.
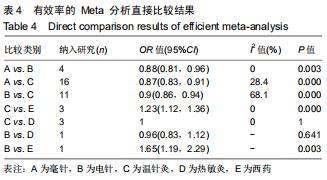
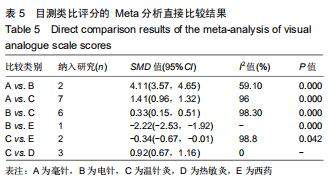
[14] WHITE IR. Network meta-analysis. Stata J.2015;15(4):951-985.
[15] BUCHER HC, GUYATT GH, GRIFFITH LE, et al. The results of direct and indirect treatment comparisons in meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Epidemiol.1997;50(6):683-691.
[16] HIGGINS JP, JACKSON D, BARRETT JK, et al. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res Synth Methods.2012;3(2):98-110.
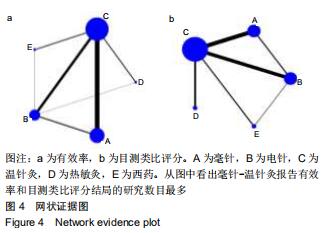
[17] SALANTI G, ADES AE, IOANNIDIS JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64(2): 163-171.
[18] VAN VALKENHOEF G, DIAS S, ADES AE, et al. Automated generation of node-splitting models for assessment of inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods.2016;7(1):80-93.
[19] 黄思敏,叶欣欣,吴宇欣,等.艾灸治疗肩周炎疼痛的Meta分析[J].全科护理, 2019, 17(14):1700-1705.
[20] 罗晓舟,唐纯志,杨雪捷,等. 针灸治疗肩周炎有效性Meta分析[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2017, 23(4): 586-591.
[21] 廖志英,陈婉蓉. 温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎的临床效果Meta分析[J].海南医学, 2016, 27(14):2382-2384.
[22] 刘军. 针刺治疗肩周炎的系统评价[D].济南:山东中医药大学, 2016.
[23] 权可,靳鹏超,权海霞,等.温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎随机对照临床研究文献Meta分析[J].河南中医, 2014,34(11): 2277-2279.
[24] 石慧,方剑乔,李邦伟,等.不同针灸疗法治疗肩周炎疗效评价(英文)[J].世界针灸杂志, 2012,22(2):6-11.
[25] 车涛,裘敏雷,忻志平,等.电针肩髃穴治疗肩关节周围炎疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志, 2006,25(1):21-22.
[26] 周晓平.温针灸对肩周炎的镇痛作用研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2007,23(1): 127-128.
[27] 黄元华.温针灸与电针治疗肩周炎的疗效比较分析[J].内蒙古中医药, 2015,34(5): 110,111.
[28] 张在伟.温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎的临床疗效[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2016,9(3): 125-126.
[29] 陈明真.温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎的临床疗效观察[J].中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2017,5(29):174-176.
[30] 杨瑞春.温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎的临床研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2009,11(6): 181-182.
[31] 宋治国,代亮,胡永春,等.温针灸治疗肩周炎疗效观察[J].实用中医药杂志, 2014, 30(6):542-543.
[32] 孔茜.温针治疗肩周炎的临床疗效观察[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学, 2004.
[33] 郭青.滞针法加温针灸阿是穴治疗肩周炎临床观察[J]. 光明中医, 2006, 21(08):33-34.
[34] 谢水平.不同针灸方法治疗急性期肩周炎的临床疗效对照研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2018.
[35] 周金凤,赵军超,倪凌凯,等. 电针治疗肩周炎30例临床观察[J].江苏中医药, 2011, 43(8):70.
[36] 陈勤仁.肩三针温针灸治疗肩周炎的临床研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2015.
[37] 李家榆.平衡针治疗肩周炎临床疗效观察[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2013.
[38] 金仁奎,吴永昌,郑英,等.热敏灸与温针灸治疗肩周炎临床疗效比较研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2014,48(5):86-88.
[39] 关翔鑫.温针灸法治疗肩周炎临床疗效观察[J].中国实用医药, 2018, 13(15):76-77.
[40] 吕雪鹏.温针灸与电针治疗肩周炎的疗效比较[J].中西医结合研究,2016, 8(4):185-187.
[41] 蔡以文.温针灸与电针治疗肩周炎的临床对照研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2010.
[42] 刘萍.温针灸治疗肩关节周围炎的疗效观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2015,34(9): 48-49.
[43] 张荣丰.温针灸治疗肩周炎的临床方法及效果分析[J].黑龙江医药, 2015, 28(2):379-380.
[44] 蒲尚喜. 温针灸治疗肩周炎随机平行对照研究[J].实用中医内科杂志, 2017,31(11): 60-62.
[45] 刘炫斯针刺患侧中平单穴治疗肩关节周围炎临床研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2010.
[46] 杨踪葆.郑氏“温通针法”治疗风寒湿型肩周炎的临床观察[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2013.
[47] 邵小静.电针疗法治疗风寒湿型肩周炎的临床体会[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2018,9(13): 23-24.
[48] 王黎,张心开.齐刺温针疗法治疗肩周炎临床疗效观察[J].新中医, 2014, 46(7):157-159.
[49] 王文霞,欧阳玲.温针灸治疗肩周炎38例疗效观察[J].中医药导报, 2014, 20(8): 104-106.
[50] 秦波.肩周炎患者应用热敏灸与温针灸治疗的临床效果对比分析[J].中医临床研究, 2017, 9(9):105-107.
[51] 刘华宇.热敏灸对肩周炎患者肩关节功能及前屈活动度的影响[J].中国民间疗法,2019, 27(16):9-10.
[52] 叶丽玮. 热敏灸治疗肩周炎(风寒湿型)临床疗效观察[D]. 济南:山东中医药大学, 2016.
[53] 闵奇.温针治疗对肩关节周围炎患者临床探究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2015,17(5): 124-125.
[54] 丛文杰,方剑乔,王晨瑶,等.毫针的不同针灸疗法治疗肩关节周围炎疗效比较[J].上海针灸杂志,2010,29(11):713-715.
[55] 李红霞. 温针灸治疗肩周炎的疗效观察[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2017, 8(20): 34-35.
[56] 张士华,于金婵,丁婷,等.温针灸疗法治疗肩周炎的效果评价[J].当代医药论丛, 2019,17(5):198-199.
[57] 万俊. 温针灸治疗肩周炎43例[J].湖南中医杂志, 2010, 26(5): 56-58.
[58] GREEN S, BUCHBINDER R, HETRICK S. Acupuncture for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;(2):CD005319.
[59] KUBO K, YAJIMA H, TAKAYAMA M, IKEBUKURO T, et al. Effects of acupuncture and heating on blood volume and oxygen saturation of human Achilles tendon in vivo. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2010; 109(3): 545-550.
[60] KUBO K, YAJIMA H, TAKAYAMA M, et al. Changes in blood circulation of the contralateral Achilles tendon during and after acupuncture and heating. Int J Sports Med. 2011; 32(10):807-813.
[61] YAJIMA H, TAKAKURA N, TAKAYAMA M, et al. Inhibitory effect of acupuncture on vibration-induced finger flexion reflex in human- Comparison between radial, median, ulnar nerve stimulation. Med Acupunct.2013; 25(4):269-274.
[62] CHEING GL, SO EM, CHAO CY. Effectiveness of electroacupuncture and interferential eloctrotherapy in the management of frozen shoulder. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(3):166-170.
[63] 吕海兵,张宏如,段佳强,等.功能解剖视角下肩周炎常用穴位新解[J].时珍国医国药, 2019,30(2):417-419.
[64] 纪鹏程,乔宇,李梅梅,等. 热敏灸治疗肩周炎的研究现状及探析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019, 19(71): 80-81.
[65] 郭长青,马惠芳,李晓芳.温针灸治疗痹证的临床研究[J].针灸临床杂志, 2003,19(4):49-52.
[66] 李忠爽.温针灸加理疗治疗肩周炎疗效观察[J].按摩与康复医学, 2010, 11(33):106-107.
[67] 周晓平.温针灸对肩周炎的镇痛作用研究[J].实用医学杂志, 2007,23(1): 127-128.
[68] 岳萍,高亮,陈默,等.温针灸对膝骨性关节炎兔行为学及关节软骨肿瘤坏死因子-α、基质金属蛋白酶-3 含量的影响[J].针刺研究, 2016,41(3): 235-239.
[69] 洪金标,彭宏,易受乡,等.艾灸对机体产生的多重效应及其机理探讨[J].中华中医药学刊,2010,28(2):277-280.
[70] 唐照亮,宋小鸽,王宁新,等.艾灸活血化瘀作用机制的研究[J].安徽中医学院学报,2004,23(2):24-28.
[71] 陈日新,康明非.腧穴热敏化及其临床意义[J].中医杂志, 2006,47(12): 905-906.
[72] MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
[73] LI J, LIU Z, CHEN R, et al. The quality of reports of randomized clinical trials on traditional Chinese medicine treatments: a systematic review of articles indexed in the China National Knowledge Infrastructure database from 2005 to 2012. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014; 14:362.
[74] PAGE MJ, HIGGINS JP, CLAYTON G, et al. Empirical Evidence of Study Design Biases in Randomized Trials: Systematic Review of Meta-Epidemiological Studies. PLoS One. 2016;11(7): e0159267.
[75] SCHULZ KF, ALTMAN DG, MOHER D, et al. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int J Surg. 2011;9(8):672-677.
[76] FAVEJEE MM, HUISSTEDE BM, KOES BW. Frozen shoulder: the effectiveness of conservative and surgical interventions--systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(1):49-56.
[77] MAUND E, CRAIG D, SUEKARRAN S, et al. Management of frozen shoulder: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2012;16(11):1-264.
[78] 郑江.冻结肩[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2014,2(3):191-195.
|