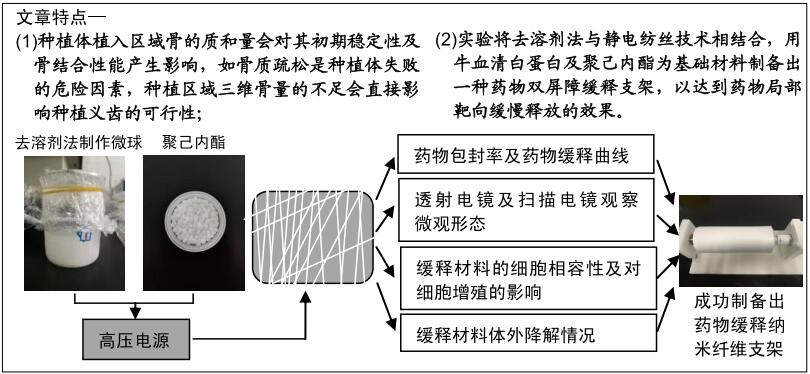
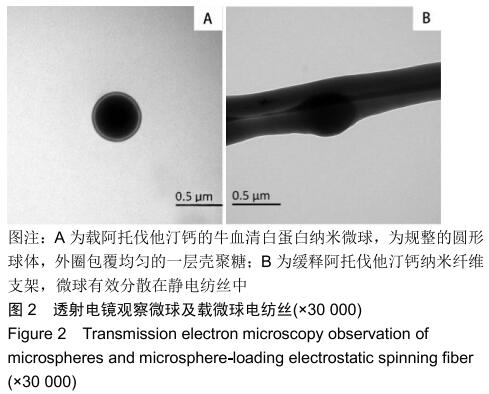
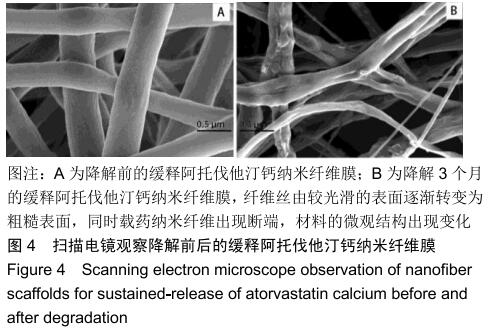
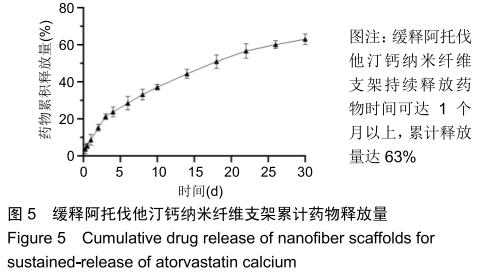
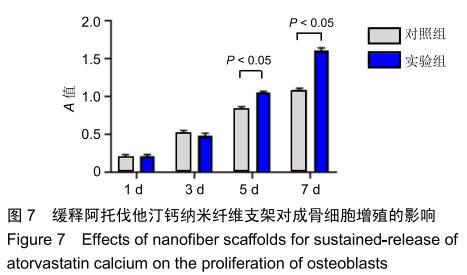
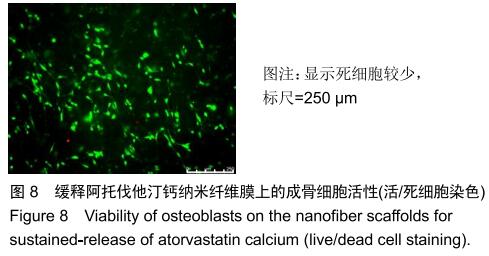
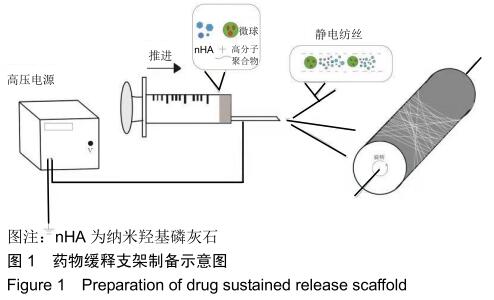
|
[1] 李莺,尤亚鹏,李宝娥,等.纯钛表面TiO_2纳米管结合Ⅰ型胶原促进成骨细胞黏附和骨结合[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(14): 2169-2176.
[2] 杨玉鹏,赵海静,谷建琦,等.钛芯与骨形成蛋白复合材料修复即刻种植牙槽骨缺陷的评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(22): 3536-3540.
[3] SEVIMAY M, TURHAN F, KILIÇARSLAN MA, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown.J Prosthet Dent. 2005;93(3): 227-234.
[4] LEE S, GANTES B, RIGGS M, et al. Bone density assessments of dental implant sites: 3. Bone quality evaluation during osteotomy and implant placement.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2007;22(2):208-212.
[5] OFFERMANNS V, ZOFFMANN ANDERSEN O, RIEDE G, et al. Bone regenerating effect of surface-functionalized titanium implants with sustained-release characteristics of strontium in ovariectomized rats.Int J Nanomed.2016;11:2431-2442.
[6] CORCUERA-FLORES JR, ALONSO-DOMÍNGUEZ AM, SERRERA-FIGALLO MÁ, et al. Relationship Between Osteoporosis and Marginal Bone Loss in Osseointegrated Implants: A 2-Year Retrospective Study. J Periodontol. 2016; 87(1):14-20.
[7] WANG M, LAN L, LI T, et al. The effect of oxytocin on osseointegration of titanium implant in ovariectomized rats. Connect Tissue Res.2016;57(3):220-225.
[8] SANTOS PL,GULINELLI JL, TELLES CS, et al. Bone substitutes for peri-implant defects of postextraction implants. Int J Biomater.2013;2013:307136.
[9] WANG Z, LI Y, ZHOU F, et al. Effects of Statins on Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk. Medicine. 2016;95(22):e3042.
[10] TSARTSALIS AN, DOKOS C, KAIAFA GD, et al. Statins, bone formation and osteoporosis: hope or hype?Hormones(Athens, Greece).2012;11(2):126.
[11] ORYAN A, ALIDADI S, MOSHIRI A, et al. Bone regenerative medicine: classic options, novel strategies, and future directions. J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9(1):18.
[12] GUTIERREZ GE, LALKA D, GARRETT IR, et al. Transdermal application of lovastatin to rats causes profound increases in bone formation and plasma concentrations.Osteoporosis Int. 2006;17(7):1033-1042.
[13] ZHENG IC, LI CC. Multiblock copolymers composed of poly (butylenes succinate)and poly(1,2-propylenesuccinate): Effect of molar ratio of diisocyanate to polyester diols oncrosslink densities, thermal properties, mechanical properties and biodegradability.Polym Degrad Stabil. 2010; 9(95):1-8.
[14] ZENG JB, LI YD. A novel biodegradable multiblock poly(ester urethane)containing poly(L-lactic acid)and poly(butylene sue-cinate)blocks.Polymer.2009;(50):1178-1186.
[15] DASH TK, KONKIMALLA VB. Poly-є-caprolactone based formulations for drug delivery and tissue engineering: A review. J Control Release.2012;158(1):15-33.
[16] YOSHIMOTO H, SHIN YM, TERAI H, et al. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2003;24(12):2077-2082.
[17] EICHHORN SJ, SAMPSON WW. Statistical geometry of pores and statistics of porous nanofibrous assemblies.J R Soc Interface.2005;2(4):309-318.
[18] FU R, LI C, YU C, et al. A novel electrospun membrane based on moxifloxacin hydrochloride/poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate for antibacterial wound dressings in practical application. Drug Delivery.2014;23(3):818-829.
[19] WENG L, XIE J. Smart electrospun nanofibers for controlled drug release: recent advances and new perspectives.Curr Pharm Design.2015;21(15):1944.
[20] HAN D, STECKL AJ. Triaxial Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Controlled Dual Release of Functional Molecules.ACS Appl Mater Inter.2013;5(16):8241-8245.
[21] WADE RJ, BASSIN EJ, GRAMLICH WM, et al. Nanofibrous Hydrogels with Spatially Patterned Biochemical Signals to Control Cell Behavior.Adv Mater.2015;27(8):1356-1362.
[22] SANTANA-MELO GF, RODRIGUES BVM, DA SILVA E, et al. Electrospun ultrathin PBAT/nHAp fibers influenced the in vitro and in vivo osteogenesis and improved the mechanical properties of neoformed bone.Colloid Surface B. 2017;155: 544-552.
[23] LI L, ZHOU G, WANG Y, et al. Controlled dual delivery of BMP-2 and dexamethasone by nanoparticle-embedded electrospun nanofibers for the efficient repair of critical-sized rat calvarial defect.Biomaterials.2015;37:218-229.
[24] LI D, SUN H, JIANG L, et al. Enhanced Biocompatibility of PLGA Nanofibers with Gelatin/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Bone Biomimetics Incorporation.ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2014;6(12): 9402-9410.
[25] WANG J, SUN B, TIAN L, et al. Evaluation of the potential of rhTGF- β3 encapsulated P(LLA-CL)/collagen nanofibers for tracheal cartilage regeneration using mesenchymal stems cells derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord[J]. Mat Sci Eng C.2017;70:637-645.
[26] ZHANG X, REAGAN MR, KAPLAN DL. Electrospun silk biomaterial scaffolds for regenerative medicine.Adv Drug Deliver Rev.2009;61(12):988-1006.
[27] KIM K, LUU YK, CHANG C, et al. Incorporation and controlled release of a hydrophilic antibiotic using poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds.J Control Release.2004;98(1):47-56.
[28] KHALF A, SINGARAPU K, MADIHALLY SV. Influence of solvent characteristics in triaxial electrospun fiber formation. React Funct Polym.2015;90:36-46.
[29] GAUTAM S, DINDA AK, MISHRA NC. Fabrication and characterization of PCL/gelatin composite nanofibrous scaffold for tissue engineering applications by electrospinning method.Mat Sci Eng C.2013;33(3):1228-1235.
|