| [1] Ebert JR,Munsie C,Joss B, et al.Guidelines for the early restoration of active knee flexion after total knee arthroplasty: Implications for rehabilitation and early intervention.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(6): 1135-1140. [2] Seo JG,Moon YW,Park SH,et al. The comparative efficacies of intra-articular and IV tranexamicacid for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1869-1874. [3] Sabatini L, Atzori F. Topical intraarticular and intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Ann Transl Med.2015;3(S1): S18.doi: 10.3978/j.issn. 2305-5839. 2015.02.25.[4] Wayne TN, Nima M, Jason JD. Topical vs Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(5):1022-1026.[5] CRASH-2 trial collaborators,Shakur H,Robert I,et al.Effects of tranexamic acid ondeath, vascular occlusive events,and blood transfusion in trauma patients with significant Haemorrhage (CRASH-2): arandomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2010;376(9734):23-32.[6] Bagsby DT,Samujh CA,Vissing JL,et al.Tranexamic acid decreases incidence of blood transfusion in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12): 2106-2109.[7] Yang ZG,Chen WP,Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty:a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(13):1153-1159.[8] Bourke DL, Smith TC. Estimating allowable hemodihtion. Anaesthesiology. 1974;41:609-612.[9] Nadler SB, Hidalgo JU, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51:224-232.[10] 闵令田,翁文杰,邱勇,等. 关节腔内灌注氨甲环酸降低全膝关节置换手术出血的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华关节外科杂志, 2014,8(4):482-486.[11] Bidolegui F, Arce G, Lugones A, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion in patients undergoingtotal knee arthroplasty without tourniquet:a prospective randomized controlled trial. Orthop J. 2014;8(1): 250-254.[12] 席少华, 周朝波, 赵桂林.氨甲环酸在全膝关节置换术中局部应用和静脉应用的止血效果比较[J].实用药物和临床,2015,18(4):762-765.[13] Roche M,Law TY,Rosas S, et al. Transfusion requirements following total knee arthroplasty in patients with preexisting blood dyscrasia.Surg Technol Int. 2017;30:435-440. [14] 马金辉,孙伟,高福强,等.关节腔注射氨甲环酸单侧全膝关节置换者的失血量及肢体周径变化:随机对照[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(35): 5577-5582.[15] Balasubramanian N,Natarajan GB,Prakasam S.Prospective study to compare intra-articular versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing post-operative blood loss in staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty.Malays Orthop J. 2016;10(3):7-11.[16] Evangelista PJ,Aversano MW,Koli E,et al.Effect of of tranexamic acid on transfusion rates following total joint arthroplasty:A cost and comparative effectiveness analysis. Orthop Clin North Am. 2017;48(2):109-115.[17] Aydin BK,Durgut F,Erkocak öF,et al.Other benefits of intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty apart from reducing blood transfusion rates. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017;28(1):25-29.[18] Ralley FE, Berta D, Binns V, et al. One intraoperative dose of tranexamic acid for patients having primary hip of knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1905-1911.[19] Alshryda S, Sukeik M, Sarda P,et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(8): 1005-1015.[20] Zhang Y,Zhang JW,Wang BH.Efficacy of tranexamic acid plus drain-clamping to reduce blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Medicine. 2017;96(26):e7363.[21] Tian P,Liu WB,Li ZJ,et al.The efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in revision in total knee arthroplasty:a meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Discord.2017; 18(1):273.[22] Yu Z,Yao L,Yang Q.Tranexamic acid plus diluted-epinephrine venrsus tranexamic acid alone for blood loss in total joint arthroplasty:a meta-analysis.Medicine. 2017;96(24):e7095.[23] Soni A, Saini R, Gulati A, et al. Comparison between intravenous and intra-articular regimens of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1525-1527.[24] 王浩然,董金波,李江华,等. 全膝关节置换中静脉和局部应用氨甲环酸的止血效果对比[J].重庆医学,2016,45(30):4249-4251.[25] Goyal N,Chen DB,Harris IA,et al.Intravenous vs intra-articular tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty:a randomized double-blind trial.J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1):28-32.[26] Zhao-Yu C, Yan G, Wei C, et al.Reduced blood loss after intra-articular tranexamic acid injection during total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of the literature. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(12):3181-3190.[27] Loxano M,Basora M,Peidro L,et al.Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid administration during total knee arthroplasty. Vox Sanguinis. 2008;95(1):39-44.[28] Kim TK,Chang CB,Koh IJ.Pratical issues for the ues of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty:a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(8):1849-1858.[29] Molloy DO,Archbold HA,Ogonda L,et al.Comparison of topical fibrin spray and tranexamic acid on blood lose after total knee replacement:a prospective randomised controlled trial.J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2007;89(3):306-309.[30] 冯贵喜,刘军,张福江,等. 氨甲环酸局部应用对单侧全膝关节置换术后隐性失血量的影响[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016, 36(3): 151-155.[31] Mutsuzaki H,Ikeda K.Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid via a drain plus drain-clamping to reduce blood loss in cementless total knee arthroplasty.J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; (7):1-6.[32] Jiang B,Kao M,Bohm MT,et al.Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong). 2014;22(2):146-149.[33] Kosins AM,Schol T,Cetinkaya M,et al.Evidence-based value of subcutaneous surgical wound drainage: The largest systematic review and meta-analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132(2): 443-450.[34] Demirkale L,Tecimel O,Sesen H,et al. Nondrainage decreases blood transfusion need and infection rate in bilateral total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014;29(5): 993-997.[35] 董盼锋,陈跃平,康杰,等.人工膝关节置换的引流效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2649-2654.[36] 张纪,张洪. 人工膝关节置换术后放置引流与否的对比研究[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(12):1119-1122. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: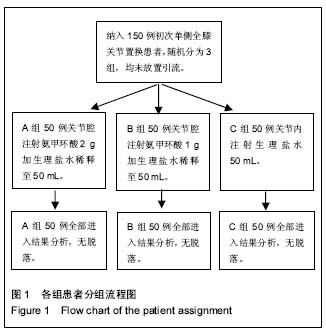
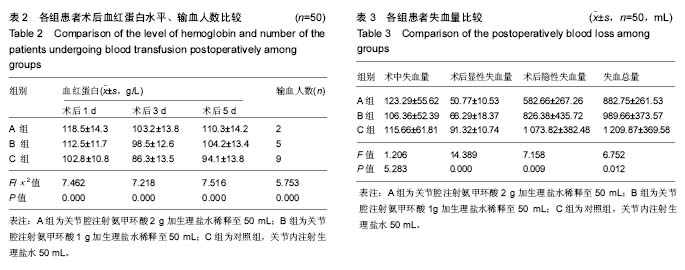
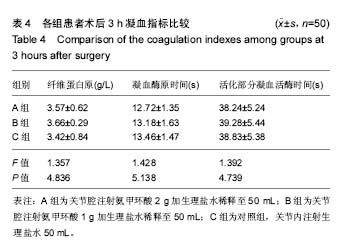
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: