中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5189-5196.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.018
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
公民逝世后器官捐献供肾移植术后应用卡泊芬净预防真菌感染的前瞻性研究
尚文俊,王志刚,索敬钧,李金锋,庞新路,丰永花,刘 磊,谢红昌,丰贵文
- (郑州大学第一附属医院肾移植科,河南省郑州市 450052)
Caspofungin for preventing fungal infection after kidney transplantation using donation after cardiac death donors: a prospective controlled trial
Shang Wen-jun, Wang Zhi-gang, Suo Jing-jun, Li Jin-feng, Pang Xin-lu, Feng Yong-hua, Liu Lei, Xie Hong-chang,Feng Gui-wen
- (Department of Kidney Transplantation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。
文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。
.jpg) 文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。
文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。摘要
背景:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物,研究表明其对深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当,但目前尚无肾移植术后应用卡泊芬净预防真菌感染的报道。
目的:分析公民逝世后器官捐献供肾肾移植与亲属活体肾移植术后真菌感染高危因素的差异,探讨应用卡泊芬净预防公民逝世后器官捐献供肾肾移植术后真菌感染的可行性和安全性。
方法:试验为前瞻性单中心临床试验,在中国河南省,郑州大学第一附属肾移植中心完成。选择2012年1月至2013年8月收治,移植前无明确真菌感染证据及无应用抗真菌类药物史的首次肾移植患者,其中公民逝世后器官捐献供肾肾移植102例为试验组,对照组为同期亲属活体肾移植86例。术前测定受者CYP3A5基因型,所有患者移植术后均采用他克莫司+吗替麦考酚酯+泼尼松三联免疫抑制方案。试验组术后采用卡泊芬净预防性抗真菌治疗2周,比较两组真菌感染的高危因素以及相同CYP3A5基因型受者术后1、2周及1,3,6个月卡泊芬净对他克莫司谷浓度、他克莫司谷浓度/剂量比值的影响,检测各随访时间点肝肾功能、记录不良事件及真菌感染情况。试验于2017年11月在中国临床试验注册中心注册(ChiCTR-OON-17013342)。
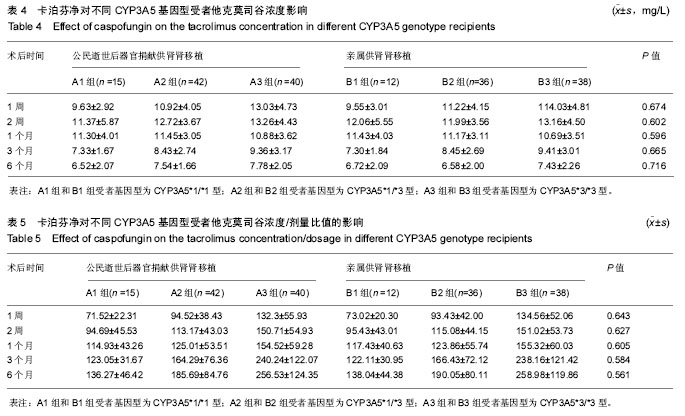
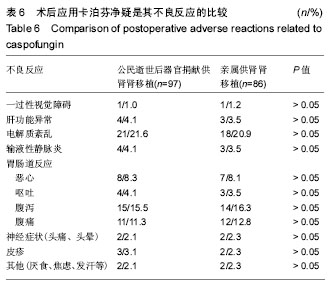
结果与结论:①受者随访6个月人/肾存活率分别为98.4%,97.3%,其中试验组102例,入组97例;对照组86例全部随访;②术前透析时间、血红蛋白值、冷缺血时间、热缺血时间、术中输血量、中心静脉导管留置时间、甲强龙用量、ATG用量、1周时血肌酐下降幅度、血小板减少症和术后体温> 38 ℃持续时间是试验组相对对照组术后真菌感染的极高危因素;③随访6个月时,试验组、对照组真菌感染率分别为0%、2.3%;④术后1周试验组血肌酐值高于对照组(P < 0.05),其他时间点两组无差异(P > 0.05);⑤移植术后应用卡泊芬净2周,对不同CYP3A5基因型受者他克莫司谷浓度和和他克莫司谷浓度/剂量比值各随访时间点比较均无差异(P > 0.05);⑥卡泊芬净可能相关不良反应以电解质紊乱发生率最高(21.6%),但两组比较均无差异(P > 0.05);⑦提示:公民逝世后器官捐献供肾肾移植相对亲属供肾肾移植存在众多术后真菌感染的极高危因素,应用卡泊芬净预防真菌感染,效果显著,且对他克莫司谷浓度无影响,安全性高,可作为预防肾移植术后真菌感染的新方案和有效途径。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-4534-6577(丰贵文)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。
文题释义:
卡泊芬净:卡泊芬净是新型棘白菌素类全身抗真菌药物。棘白菌素类药物作用于真菌细胞壁,与目前临床常用的抗真菌药物无交叉耐药。卡泊芬净适用于治疗侵袭性念珠菌病、当前抗真菌疗法无效或不能耐受患者的侵袭性曲霉菌病,以及持续粒细胞缺乏伴发热患者疑似真菌感染者的经验性治疗。
卡泊芬净对念珠菌和曲霉菌感染的作用:临床试验表明卡泊芬净对由念珠菌属和曲霉菌属引起的深部真菌感染有广谱抗菌作用,且对氟康唑和伊曲康唑耐药的念珠菌有很强的抗菌作用和耐受性,并无与剂量或作用持续时间相关的毒性,疗效优于或与两性霉素B的作用相当。