中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5128-5133.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.008
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
脊髓半横断损伤对大鼠骨折愈合的影响
陈齐勇,林 煜,梁硅清,刘伯龄
- (厦门大学附属福州第二医院骨科,福建省福州市 350007)
Effect of spinal cord hemisection on bone fracture healing in rats
Chen Qi-yong, Lin Yu, Liang Gui-qing, Liu Bo-ling
- (Department of Orthopedics, Fuzhou No. 2 Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, Fuzhou 350007, Fujian Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。
文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。
文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。摘要
背景:研究证明,神经系统显著影响骨折的愈合过程,神经不同层面、不同成分对骨痂影响各不相同。
目的:制备脊髓半横断损伤并骨折的大鼠模型,观察神经完整性不同的骨折,愈合时骨痂量的不同和组织形态学变化,探讨其对骨痂生成的影响。
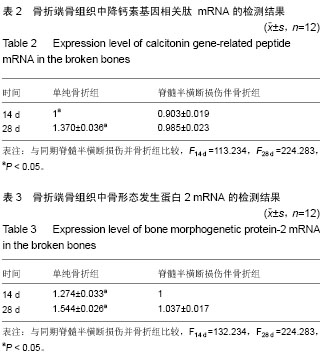
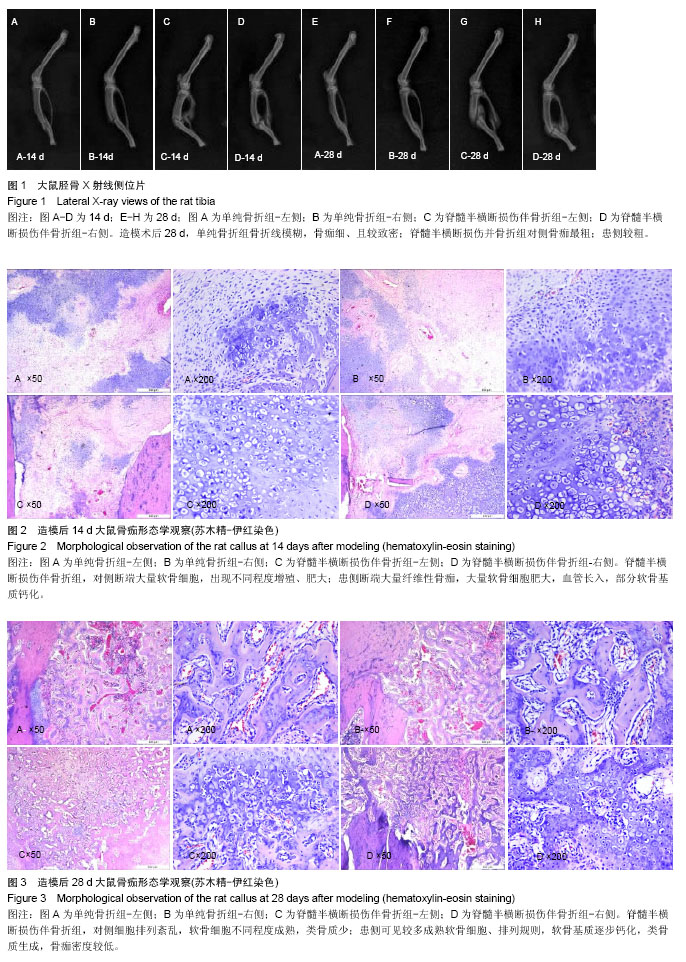
方法:雄性SD大鼠48只,分2组,制备单纯骨折模型及脊髓半横断损伤并骨折模型,切断右半侧脊髓。于术后14,28 d分批取材,取胫骨,称量湿质量,X射线观察骨折愈合情况,苏木精-伊红染色观察骨痂组织形态变化,qPCR SYBR GREEN法检测骨折断端骨组织降钙素基因相关肽、骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA的表达。
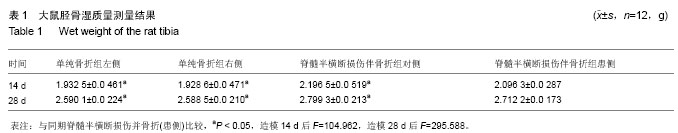
结果与结论:①脊髓半横断损伤并骨折组,对侧胫骨湿质量大于患侧(P < 0.05),均大于单纯骨折组(P < 0.05);②X射线显示脊髓半横断损伤并骨折,对侧骨痂最大,患侧次之,单纯骨折骨痂最小;③苏木精-伊红染色显示,28 d脊髓半横断损伤并骨折组,对侧细胞排列紊乱;患侧纤维骨痂为主,细胞排列较规则;单纯骨折,骨性骨痂为主,细胞排列规则。④qPCR SYBR GREEN法结果显示,单纯骨折组降钙素基因相关肽、骨形态发生蛋白2表达较脊髓半横断损伤并骨折组高(P < 0.05);⑤结果提示,完整神经支配是骨折愈合的必须因素。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-6894-7290(陈齐勇)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。
文题释义:
脊髓半横断损伤:双侧肢体神经通路完整性不同,临床表现为Brown Sequard综合征,病损平面以下患侧肢体上运动神经元瘫痪,深感觉消失,精细触觉障碍,血管舒缩运动障碍,对侧肢体痛温觉消失,而触觉保留。
降钙素基因相关肽:是广泛分布于神经系统的一种神经肽,其在外周及脊髓参与伤害性信息的传递及痛敏化的形成,并与P物质、兴奋性氨基酸、辣椒素1型受体、趋化因子、激活素、大麻素受体、阿片受体、神经生长因子、血管活性肠肽、5-羟色胺、糖皮质激素等生物活性物质或受体在痛觉调制过程中存在相互影响。它是一种具有强大舒血管作用和神经细胞保护作用的调节肽,对心脏具有正性变时、变力作用。1983年由Rosenfeld等应用分子生物学技术发现,由37个氨基酸组成。在体内主要分布于神经系统,亦广泛分布于心血管系统和肺组织内。在心脏,主要存在于心房、心室、室间隔、窦房结、乳头肌和冠状动脉壁的神经纤维内。