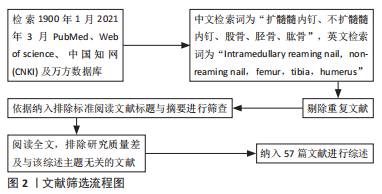
[1] 张经,王斌,吕欣.解剖型髓内钉在四肢管状骨骨折治疗中的应用:把持与抗旋转能力更强[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(6):917-922.
[2] BONG MR, KOVAL KJ, EGOL KA. The history of intramedullary nailing. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64(3-4):94-97.
[3] BEKOS A, SIOUTIS S, KOSTROGLOU A, et al. The history of intramedullary nailing. Int Orthop. 2021;45(5):1355-1361.
[4] ROSA N, MARTA M, VAZ M, et al. Intramedullary nailing biomechanics: Evolution and challenges. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(3):295-308.
[5] 黄正.扩髓治疗骨折不愈合的生物学机理研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007.
[6] 唐三元,杨辉.髓内钉治疗长骨骨折扩髓与不扩髓的争论[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2004,1(1):25-28.
[7] 任强.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉治疗成人胫骨干骨折的效果分析[D].张家口:河北北方学院,2018.
[8] 熊军,余斌,欧阳汉斌,等.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉固定治疗胫骨闭合性骨折的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(24):2025-2029.
[9] 许新忠,荆珏华,周云,等.髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折并发症分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(2):133-134.
[10] BRUMBACK RJ, VIRKUS WW. Intramedullary nailing of the femur: reamed versus nonreamed. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8(2):83-90.
[11] HEIM D, SCHLEGEL U, PERREN SM. Intramedullary pressure in reamed and unreamed nailing of the femur and tibia--an in vitro study in intact, human bones. Injury. 1993;24(1):S56-S63.
[12] MOUSAVI M, DAVID R, SCHWENDENWEIN I, et al. Influence of controlled reaming on fat intravasation after femoral osteotomy in sheep. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;394:263-270.
[13] 陈中伟, 张俊飞, 杜武军, 等. 脂肪栓塞综合征诊治的临床研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2021,23(1):78-81.
[14] KROPFL A, DAVIES J, BERGER U, et al. Intramedullary pressure and bone marrow fat extravasation in reamed and unreamed femoral nailing. J Orthop Res. 1999;17(2):261-268.
[15] BAIG MN, CURTIN W. A simple and easy intramedullary lavage method to prevent embolism during and after reamed long bone nailing. Cureus. 2017;9(8):e1609.
[16] WILLIS BH, CARDEN DL, SADASIVAN KK. Effect of femoral fracture and intramedullary fixation on lung capillary leak. J Trauma. 1999;46(4):687-692.
[17] AOKI S, YOKOYAMA K, ITOMAN M. Effects of reamed or unreamed intramedullary nailing under non-damaged conditions on pulmonary function in sheep. J Trauma. 2005;59(3):647.
[18] DEHGHAN N, SCHEMITSCH EH. Extended applications of the reamer-irrigator-aspirator (RIA) system. Injury. 2017;48(Suppl 1):S47-S51.
[19] CLAES L. Improvement of clinical fracture healing - What can be learned from mechano-biological research? J Biomech. 2021;115:110148.
[20] 徐绍勇.交锁髓内钉扩髓与否在治疗胫骨骨折中的临床比较研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2010.
[21] 孙林,刘兴华,王雪松,等.带锁髓内钉治疗新鲜四肢长骨干骨折1224例疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(3):129-135.
[22] 罗先正,张薇.髓内钉的生物力学设计[J].中华骨科杂志,1997, 16(4):57-61.
[23] KLEIN S. Reaming versus non-reaming in medullary nailing: interference with cortical circulation of the canine tibia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990; 109(6):314-316.
[24] SCHEMITSCH EH, KOWALSKI MJ, SWIONTKOWSKI MF, et al. Comparison of the effect of reamed and unreamed locked intramedullary nailing on blood flow in the callus and strength of union following fracture of the sheep tibia. J Orthop Res. 1995;13(3):382-389.
[25] KLEIN C, SPRECHER C, RAHN BA, et al. Unreamed or RIA reamed nailing: an experimental sheep study using comparative histological assessment of affected bone tissue in an acute fracture model. Injury. 2010;41(11): S32-S37.
[26] KALBAS Y, QIAO Z, HORST K, et al. Early local microcirculation is improved after intramedullary nailing in comparison to external fixation in a porcine model with a femur fracture. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018;44(5):689-696.
[27] GREKSA F, TÓTH K, BOROS M, et al. Experimental studies of microcirculatory changes in the bone. Magy Seb. 2012;65(4):178-183.
[28] 李云,肖景,张光明.不扩髓逆行交锁髓内钉治疗肱骨中段骨折[J].广州医药,2005,36(4):30-31.
[29] YOUNIS M, BARNHILL SW, MAGUIRE J, et al. Management of humeral impending or pathological fractures with intramedullary nailing: reaming versus non reaming technique-a retrospective comparative study. Musculoskelet Surg. 2020. doi:10.1007/s12306-020-00668-6.
[30] BALTOV A, MIHAIL R, DIAN E. Complications after interlocking intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures. Injury, 2013;45 (Suppl 1):S9-S15.
[31] 崔智勇,田耘,冯辉,等.顺行髓内钉固定治疗12-A型肱骨干骨折中医源性骨折的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(1):10-15.
[32] 赵宝成,马宝通,刘林涛,等.带锁髓内钉治疗526例长骨骨折疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(3):136-142.
[33] HUSEBYE EE, LYBERG T, OPDAHL H, et al. Intravasation of bone marrow content. Can its magnitude and effects be modulated by low pressure reaming in a porcine model? Injury. 2010;41:S9-S15.
[34] BAUR M, WEBER B, LACKNER I, et al. Structural alterations and inflammation in the heart after multiple trauma followed by reamed versus non-reamed femoral nailing. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0235220.
[35] LACKNER I, WEBER B, MICLAU T, et al. Reaming of femoral fractures with different reaming irrigator aspirator systems shows distinct effects on cardiac function after experimental polytrauma. J Orthop Res. 2020; 38(12):2608-2618.
[36] DUAN X, LI T, MOHAMMED AQ, et al. Reamed intramedullary nailing versus unreamed intramedullary nailing for shaft fracture of femur: a systematic literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(10): 1445-1452.
[37] 王雄,戴七一,李书振.扩髓与不扩髓条件下髓内钉置入内固定治疗成人股骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26): 4812-4816.
[38] 张广申.对比分析髓内钉扩髓、不扩髓治疗老年股骨干骨折的效果[J].中国伤残医学,2017,25(8):34-36.
[39] 徐九峰,李冬梅,李玉祥,等.老年股骨干骨折患者采用髓内钉扩髓与不扩髓治疗的比较[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(13):3596-3597.
[40] 吴克俭,汤俊君.成人股骨干骨折髓内钉治疗需要关注的问题[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(11):921-926.
[41] 窦连荣,窦帮,朱玮,等.老年粗隆间骨折中亚洲型PFNA使用导针扩髓与否的疗效比较[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2015,11(5): 327-330.
[42] 孙晓望,梁凡,邓明.股骨近端防旋髓内钉扩髓与否对老年股骨转子间骨折的疗效影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(6):854-857.
[43] 陆洲,孙奇,裘晓冬,等.无牵引床仰卧位不扩髓与扩髓股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的比较研究[J].中医正骨,2017, 29(9):15-18.
[44] 韦怀籍,周建飞,徐攀峰.股骨近端防旋髓内钉术中扩髓对手术失血量的影响[J].中国医药导报,2016,13(12):81-84.
[45] WISS DA, STETSON WB. Unstable fractures of the tibia treated with a reamed intramedullary interlocking nail. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (315):56-63.
[46] LIN CA, SWIONTKOWSKI M, BHANDARI M, et al. Reaming does not affect functional outcomes after open and closed tibial shaft fractures: the results of a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30(3):142-148.
[47] BRIEL M, SPRAGUE S, HEELS-ANSDELL D, et al. Economic evaluation of reamed versus unreamed intramedullary nailing in patients with closed and open tibial fractures: results from the study to prospectively evaluate reamed intramedullary nails in patients with tibial fractures (SPRINT). Value Health. 2011;14(4):450-457.
[48] 万云华.扩髓与不扩髓交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折的比较分析[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(14):49-50.
[49] LI CX, ZHAO HJ, ZHAO WQ, et al. System evaluation on reamed and non-reamed intramedullary nailing in the treatment of closed tibial fracture. Acta Cir Bras. 2013;28(10):744-750.
[50] 努尔哈那提·沙依兰别克,金格勒,杨毅,等.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉修复成人胫骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(39):5912-5918.
[51] 郝同玉.扩髓与非扩髓型交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨干骨折患者的疗效[J].医疗装备,2017,30(1):136-137.
[52] GAEBLER C, MCQUEEN MM, VÉCSEI V, et al. Reamed versus minimally reamed nailing: a prospectively randomised study of 100 patients with closed fractures of the tibia. Injury. 2011;42(suppl 4):S17-S21.
[53] 郑军贤,程迅生,郑国海,等.扩髓交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折的疗效[J].安徽医学,2015,36(7):862-864.
[54] LARSEN LB, MADSEN JE, HOINESS PR, et al. Should insertion of intramedullary nails for tibial fractures be with or without reaming? a prospective, randomized study with 3.8 years’ follow-up. J Trauma. 2004;18(3):144-149.
[55] 田晓华,赵敏,闫红旗,等.扩髓产物留取装置的研制与临床应用初步报告[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(22):1915-1917.
[56] HALVACHIZADEH S, TEUBEN M, LEMPERT M, et al. Protective effects of new femoral reaming techniques (Reamer irrigator aspirator, RIA I and II) on pulmonary function and posttraumatic contusion (CT morphology) - results from a standardized large animal model. Injury. 2021;52(1):26-31.
[57] JAKMA TS, RÖLING MA, PUNT B, et al. More adverse events than expected in the outcome after use of the reamer-irrigator-aspirator. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2014;40(3):337-341. |
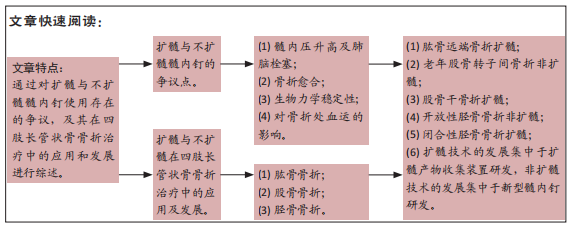
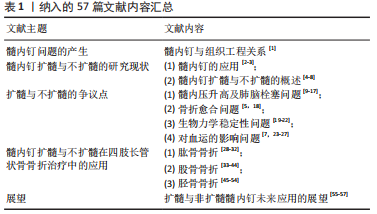
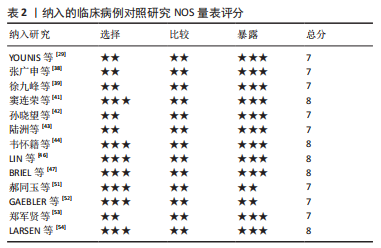
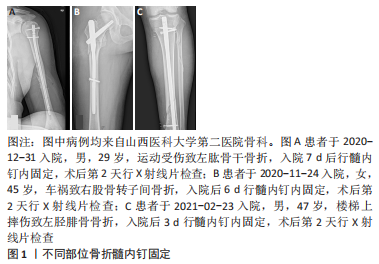 从生物力学角度看,与非扩髓相比,扩髓可置入较粗的髓内钉,增加钉-骨接触面积,提高了骨折固定的力学稳定性。扩髓还可将产生的骨碎屑带到骨折部位,起到内植骨的作用,进一步提高骨折愈合率。同时,扩髓也存在破坏内侧皮质骨血运、髓内压升高增加患者肺损伤概率、降低骨结构强度等风险。随着目前髓内钉设计和锻造工艺的进步,已逐渐研发出了直径相对较小,但更坚固的髓内钉。这类髓内钉的生产应用,加上对扩髓潜在风险的担忧,导致长管状骨骨折髓内固定时非扩髓髓内钉使用的逐渐增多。
从生物力学角度看,与非扩髓相比,扩髓可置入较粗的髓内钉,增加钉-骨接触面积,提高了骨折固定的力学稳定性。扩髓还可将产生的骨碎屑带到骨折部位,起到内植骨的作用,进一步提高骨折愈合率。同时,扩髓也存在破坏内侧皮质骨血运、髓内压升高增加患者肺损伤概率、降低骨结构强度等风险。随着目前髓内钉设计和锻造工艺的进步,已逐渐研发出了直径相对较小,但更坚固的髓内钉。这类髓内钉的生产应用,加上对扩髓潜在风险的担忧,导致长管状骨骨折髓内固定时非扩髓髓内钉使用的逐渐增多。