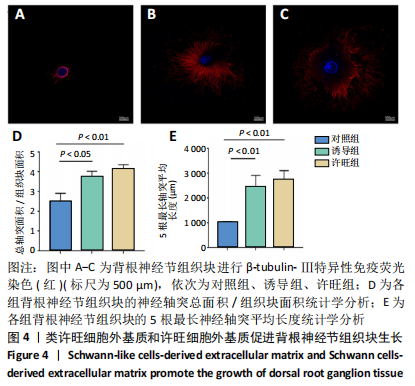
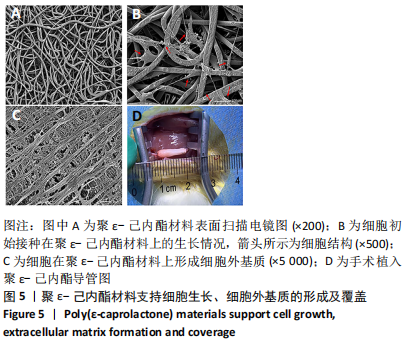
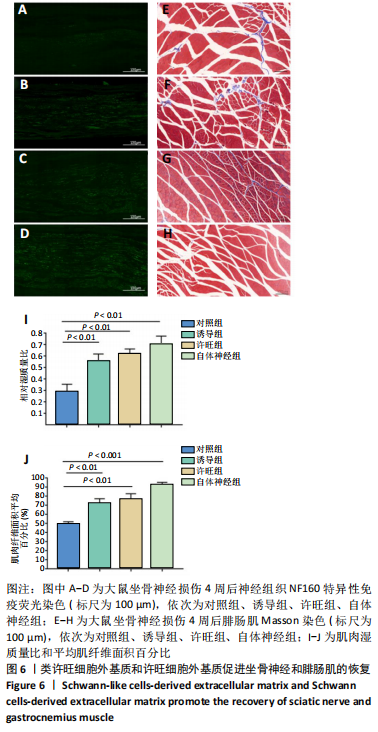
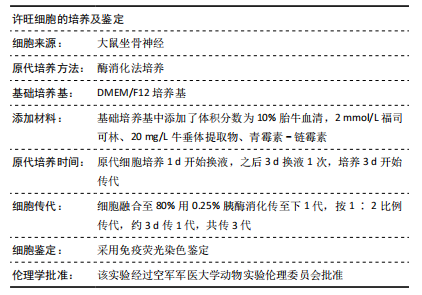
[1] FEINBERG JH, NADLER SF, KRIVICKAS LS. Peripheral nerve injuries in the athlete. Sports Med. 1997;24(6):385-408.
[2] GU X, DING F, YANG Y, et al. Construction of tissue engineered nerve grafts and their application in peripheral nerve regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93(2):204-230.
[3] NOBLE J, MUNRO CA, PRASAD VS, et al. Analysis of upper and lower extremity peripheral nerve injuries in a population of patients with multiple injuries. J Trauma. 1998;45(1):116-122.
[4] GUTMANN E, GUTTMANN L, MEDAWAR PB, et al. The rate of regeneration of nerve. Exp Biol. 1942;19:14-44.
[5] LEE SK, WOLFE SW. Peripheral nerve injury and repair. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8(4):243-252.
[6] LI R, LIU Z, PAN Y, et al. Peripheral nerve injuries treatment: a systematic review. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(3):449-454.
[7] MATSUYAMA T, MACKAY M, MIDHA R. Peripheral nerve repair and grafting techniques: a review. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2000;40(4): 187-199.
[8] FLORES AJ, LAVERNIA CJ, OWENS PW. Anatomy and physiology of peripheral nerve injury and repair. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2000; 29(3):167-173.
[9] SIEMIONOW M, BRZEZICKI G. Chapter 8: Current techniques and concepts in peripheral nerve repair. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2009;87: 141-172.
[10] JIANG X, LIM SH, MAO HQ, et al. Current applications and future perspectives of artificial nerve conduits. Exp Neurol. 2010;223(1): 86-101.
[11] MILLESI H. Techniques for nerve grafting. Hand Clin. 2000;16(1):73-91.
[12] MILLESI H, MEISSL G, BERGER A. The interfascicular nerve-grafting of the median and ulnar nerves. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(4): 727-750.
[13] MILLESI H, MEISSL G, BERGER A. Further experience with interfascicular grafting of the median, ulnar, and radial nerves. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(2):209-218.
[14] MOZAFARI R, KYRYLENKO S, CASTRO MV, et al. Combination of heterologous fibrin sealant and bioengineered human embryonic stem cells to improve regeneration following autogenous sciatic nerve grafting repair. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2018;24:11.
[15] 高红伟,安荣泽,王兆杰.周围神经损伤修复功能评价方法的研究进展[J].中国医学创新,2014,11(6):146-148.
[16] 郭英,范艳茹,周慧芳,等.雪旺细胞对周围神经损伤修复的研究进展[J].继续医学教育,2019,33(1):113-115.
[17] JESSEN KR, MIRSKY R, LLOYD AC. Schwann Cells: Development and Role in Nerve Repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(7):a020487.
[18] 曲巍,蒋华军,李登军,等.成年鼠坐骨神经雪旺细胞体外培养的实验研究[J].实用手外科杂志,2008,22(1):30-32.
[19] CHEN CJ, OU YC, LIAO SL, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells for peripheral nerve repair. Exp Neurol. 2007;204(1):443-453.
[20] MAHAY D, TERENGHI G, SHAWCROSS SG. Growth factors in mesenchymal stem cells following glial-cell differentiation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2008;51(Pt 4):167-176.
[21] KEILHOFF G, GOIHL A, STANG F, et al. Peripheral nerve tissue engineering: autologous Schwann cells vs. transdifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1451-1465.
[22] SHIMIZU S, KITADA M, ISHIKAWA H, et al. Peripheral nerve regeneration by the in vitro differentiated-human bone marrow stromal cells with Schwann cell property. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359(4): 915-920.
[23] HOU SY, ZHANG HY, QUAN DP, et al. Tissue-engineered peripheral nerve grafting by differentiated bone marrow stromal cells. Neuroscience. 2006;140(1):101-110.
[24] GU Y, ZHU J, XUE C, et al. Chitosan/silk fibroin-based, Schwann cell-derived extracellular matrix-modified scaffolds for bridging rat sciatic nerve gaps. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2253-2263.
[25] 邹多宏,刘衍钊,邓立方.局部微环境、干细胞及生物支架材料之间相互影响在再生医学中的作用[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2015, 21(5):387-393.
[26] KWOK JC, DICK G, WANG D, et al. Extracellular matrix and perineuronal nets in CNS repair. Dev Neurobiol. 2011;71(11):1073-1089.
[27] 宗海斌,李爱国,董玉珍.骨髓间充质干细胞分化的类施万细胞对大鼠脊髓损伤的作用[J].广东医学,2012,33(22):3384-3386.
[28] 赵宝辉. Triton X-100制备去细胞神经移植体的实验研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2005.
[29] 姜南,张志雄,李俊莹,等.大鼠坐骨神经离断后细胞增殖、迁移与凋亡在近远端神经片段的表达研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2019, 23(8):1430-1433.
[30] 何新泽,王维,呼铁民,等.周围神经损伤的修复:理论研究与技术应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(7):1044-1050.
[31] 蒋沛然,王志萍.模式生物神经轴突再生的研究进展[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2020,49(4):500-507.
[32] DAS KK, SRIVASTAVA AK. Nerve conduits as replacements of autografts in peripheral nerve surgery: Still a work in progress. Neurol India. 2019; 67(Supplement):S115-S117.
[33] FANG X, ZHANG C, ZHANG C, et al. Reactivation of Denervated Schwann Cells by Embryonic Spinal Cord Neurons to Promote Axon Regeneration and Remyelination. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7378594.
[34] XING H, LEE H, LUO L, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived biomaterials in engineering cell function. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;42:107421.
[35] YU WM, YU H, CHEN ZL. Laminins in peripheral nerve development and muscular dystrophy. Mol Neurobiol. 2007;35(3):288-297.
[36] CHEN TJ, KUKLEY M. Glutamate receptors and glutamatergic signalling in the peripheral nerves. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(3):438-447.
[37] CHEN ZL, STRICKLAND S. Laminin gamma1 is critical for Schwann cell differentiation, axon myelination, and regeneration in the peripheral nerve. J Cell Biol. 2003;163(4):889-899.
[38] ZURINA IM, PRESNIAKOVA VS, BUTNARU DV, et al. Tissue engineering using a combined cell sheet technology and scaffolding approach. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:63-83.
[39] 余一凡,王婷,金石峰,等.细胞膜片技术在组织修复中的研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2020,31(5):318-321.
[40] KHALILI M, ASADI M, KAHROBA H, et al. Corneal endothelium tissue engineering: An evolution of signaling molecules, cells, and scaffolds toward 3D bioprinting and cell sheets. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5): 3275-3303.
[41] YI S, XU L, GU X. Scaffolds for peripheral nerve repair and reconstruction. Exp Neurol. 2019;319:112761.
[42] CARVALHO MS, SILVA JC, UDANGAWA RN, et al. Co-culture cell-derived extracellular matrix loaded electrospun microfibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;99:479-490.
|