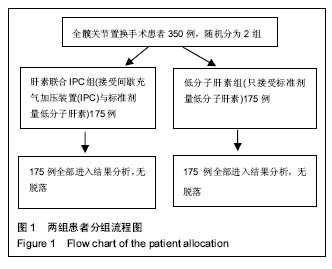
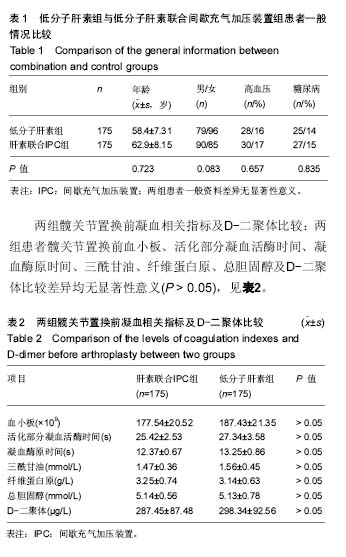
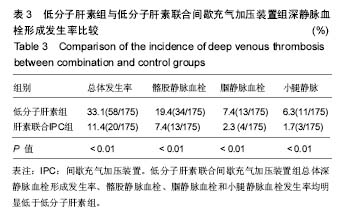
| [1] 董玉金,张铁,慧钟声,等.创伤骨折患者深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(11):1077-1083.[2] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2): 65-71.[3] Warwick D.New concepts in orthopaedic thromboprophylaxis.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2004;86(6):788-792.[4] Jameson SS,Charman SC,Gregg PJ,et al.The effect of aspirin and low-molecular-weight heparin on venous thromboembolism after hip replacement:a non-randomised comparison from information in the National Joint Registry.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93(11):1465-1470.[5] Kakkos SK,Caprini JA,Geroulakos G,et al.Combined intermittent pneumatic leg compression and pharmacological prophylaxis for prevention of venous thromboembolism in high-risk patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;8(4): CD005258.[6] Chen AH,Frangos SG,Kilarn S,et al.Intermittent pneumatic compression devices-physiological mechanisms of action.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg.2001;2l(5):383-392.[7] 马骊,王欣,蒋丽华.人工髋关节置换后的深静脉血栓形成:发生因素及其预防策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(9): 1677-1680.[8] Kim YH.The incidence of deep vein thrombosis after cementless and cemented knee replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1990;72(51):779-783.[9] 何文.下肢深静脉血栓形成的超声检查[J].中华医学杂志, 2003, 83(7):615-616.[10] 陆芸,马宝通,郭若霖,等.骨科创伤患者深静脉血栓危险因素的研究[J]中华骨科杂志,2007,27(9):693-698.[11] Kyyrle PA,Eichinger S.Deep vein thrombosis. Lancet. 2005; 365(9465):1163-1174.[12] 何斌, 倪增良, 徐增成. 低分子肝素联合压力泵预防老年髋部骨折深静脉血栓的临床观察[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2014, 34(10):839-842.[13] Freedman KB,Brokenthal KR,Fitzgerald RH,et al.A meta -analysis of thromboembolic prophylaxis following elective total hip arthoplasty.J Bone Joint Sung Am.2000;82(7):929-938.[14] Bashir R,Zack CJ,Zhao H,et al.Comparative outcomes of catheter—directed thrombolysis plus anticoagulation vsanticoagulation alone to treat lower-extremity proximal deep vein thrombosis.JAMA Intern Med.2014;174(9):1494-1501.[15] Hansson PO,Welin L,Tibblin G,et al,Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in the general population."The Study of Men Born in 1913.Arch Intern Med.1997;157(15):1665-1670.[16] Prandoni P, Bilora F, Marchiori A,et al. An association between atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis. New Eng J Med.2003;348:1435-1441.[17] 王震. 全髋关节置换术围手术期深静脉血栓防治的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4):350-353.[18] Landisch RM, Hanson SJ, Cassidy LD,et al. Evaluation of guidelines for injured children at high risk for venous thromboembolism: A prospective observational study.JTrauma Acute Care Surg.2017;82(5):836-844.[19] Ahmad J, Lynch MK, Maltenfort M,et al.Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolism After Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgery. Foot Ankle Spec. 2017;10(5):449-454.[20] Barco S, Corti M, Trinchero A, et al. Survival and recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with first proximal or isolated distal deep vein thrombosis and no pulmonaryembolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(7):1436-1442.[21] Yong BC,Jun DZ, Hui S, et al. Rivaroxaban Versus enoxaparin for hromboprophylaxi 8 after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysi s of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Pharnlacol. 2010,66(11):1099-1108.[22] 常国祥,骆彩霞,门琦华,等.低分子肝素钠预防骨科大手术术后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].中国现代药物应用, 2011,4(22):124-125.[23] 程丈俊,王俊文,任义军,等.利伐沙班与低分子量肝素在初次全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成防治中的比较研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012,6(14): 480-483.[24] 周健,刘忠达,林伟龙,等.髋关节置换术后利伐沙班预防下肢深静脉血栓的疗效与安全性[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2015,18(12): 1106-1108.[25] 靖光武,叶树楠,杨述华,等.髋关节置换后利伐沙班与低分子肝素预防下肢深静脉血栓的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(22):4028-4031.[26] 杨军,王毅.创伤患者深静脉血栓预防的监测与个体化治疗[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(11):1054-1056.[27] Lang KJ, Saha P, Roberts LN, et al. Changing paradigms in the management of deep vein thrombosis[J]. Br J Haematol, 2015,170(2):162-174.[28] 赵志刚,谢林,丁凡,等. 利伐沙班预防关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的临床前瞻性对照研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(7): 619-622.[29] 陆慧杰,庄汝杰,陈之青. 利伐沙班对比依诺肝素预防骨科大手术后深静脉血栓形成的疗效与安全性评价[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2015,31( 9) :693-695.[30] Ezelsoy M,Turunc G,Bayram M,et al.Early Outcomes of Pharmacomechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis Patients.Heart Surg Forum. 2015;18(6):222-225.[31] Napolitano M,Saccullo G,Malato A,et al.Optimal duration of low molecular weight heparin for the treatment of cancer-related deep vein thrombosis:the Cancer-DACUS Study.J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32(32):3607-3612.[32] 孙宁, 杨帆, 李宇能,等. 新鲜下肢骨折术前深静脉血栓形成危险程度评分量表初探[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2015, 53(2): 101-105.[33] Kanaan AO,Silva MA,Donovan JK,et al.Meta-analysis of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in medically ill patients. Clin Ther. 2007;29(11):2395-2405.[34] 农林. 利伐沙班预防人工全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓的临床分析[J].中国卫生产业,2011,12(8):63-64.[35] Geets WH,Bergqvist D,Pineo GF,et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines(8th edition).Chest.2008;133(6 Suppl):381S-453S.[36] 周筠,毕方刚,陈聚伍.利伐沙班与低分子肝素对骨折患者下肢深静脉血栓预防的疗效比较[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2015,32(12): 3187-3189.[37] 张晖,王东,孙海钰,等.髋关节置换后应用利伐沙班预防深静脉血栓疗效及安全性分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(30): 5440-5445.[38] Pitto RP, Hamer H, Heiss-Dunlop W, et al. Mechanical prophylaxis of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip replacement, a randomised clinical trial.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2004;86(5):639-642.[39] 张竞,张金庆,郭盛杰等.不同频次使用间歇式充气加压装置对预防关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的效果研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(4):335-338. [40] 赵宇驰,张树栋,于明伟,等. 药物联合间歇充气加压装置预防关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的随机对照研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2015,35(11):1091-1095.[41] 郑虹,高雨农,燕鑫,等.术后应用低分子肝素联合逐级加压弹力袜预防妇科恶性肿瘤患者静脉血栓栓塞性疾病[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2014,36(1):39-42.[42] 吴志刚, 谢军, 杨国谋. 血塞通联合利伐沙班预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的疗效及对患者血液流变学的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2015, 25(3):75-78.[43] 胡洪波,张苏斌,李玉民.人工髋关节置换术研究进展[J]. 包头医学院学报,2011,11(4):136-137.[44] 曹玉强,王鹏,邸鸿强.人工髋关节置换术在老年股骨颈骨折中的应用体会[J].中国老年保健医学,2012,10(1):48-49.[45] 邱贵兴,杨庆铭,余楠生,等. 低分子肝素预防髋、膝关节手术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的多中心研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26(12):819-822.[46] 简蔚泓, 廖学勤, 兰小勇,等.低分子肝素联合压力泵对髋部骨折围术期DVT临床疗效及凝血功能作用[J].中国生化药物杂志,2017,37(1):133-135.[47] Kakkos SK,Warwick D,Nicolaides AN,et a1. Combined (mechanical and pharmacologica1)modalities for the prevention of venous throm boem bolism in joint replacement surgery.J Bone Joint Surg (Br).2012;94(6):729-734.[48] Akins PT, Harris J, Alvarez JL, et al. Risk factors associated with 30-day readmissions after instrumented spine surgery in 14,939 patients. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2015;40:1022-1032.[49] Cook AD, Gross BW, Osler TM,et al.Vena Cava Filter Use in Trauma and Rates of Pulmonary Embolism, 2003-2015.JAMA Surg.2017;10(15):199-203. [50] Kiluk IE, Krajewska A, Kosacka U, et al. manifestations of pulmonary embolism in younger compared to older patients: Clinical presentation, prediction rules and long-term outcomes. Adv Med Sci.2017;62(2):254-258.[51] Koitabashi N,Niwamae N,Taguchi T,et al.Remarkable regression of massive deep vein thrombosis in response to intensive oral rivaroxaban treatment.Thromb J.2015;13:13. |
.jpg)
.jpg)