中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3931-3936.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1265
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
首次单侧全髋关节置换中静滴与局部使用氨甲环酸效果比较的Meta分析
鹿 战1,史俊龙1,刘沛东1,雷宏伟1,杨自权2
- 1山西医科大学第二临床医学院骨科,山西省太原市 030000;2山西医科大学第二医院骨关节科,山西省太原市 030000
Intravenous infusion versus local application of tranexamic acid in primary unilateral total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
Lu Zhan1, Shi Junlong1, Liu Peidong1, Lei Hongwei1, Yang Ziquan2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Second Clinical Medical College, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
氨甲环酸:其结构与赖氨酸高度相似,与纤维蛋白溶酶原赖氨酸结合位点有很强的亲和力,从而抑制纤溶酶作用的发挥,发挥止血作用。
人工髋关节:仿照人体髋关节设计而成,假体柄与股骨髓腔嵌合,假体头在人体关节臼或假体髋臼杯中旋转,实现股骨的前屈、后伸及外展等运动。
摘要
背景:氨甲环酸在全髋关节置换术中的止血效果得到越来越多学者的认可,然而其安全而有效的应用方式一直存在争议。
目的:对比静滴和局部使用氨甲环酸在首次单侧全髋关节置换中的疗效。
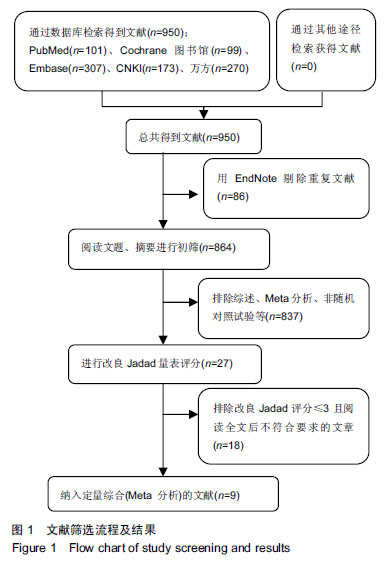
方法:检索相关数据库,如Cochrane Library、PubMed、Embase、中国知网、万方数据库等,时间截至2018年11月,所有相关文献均被查找,且查阅纳入文献的参考文献,以求查全。按照纳入及排除标准评价各个研究与此次课题符合程度及其质量,最后对合格的研究行Meta分析。
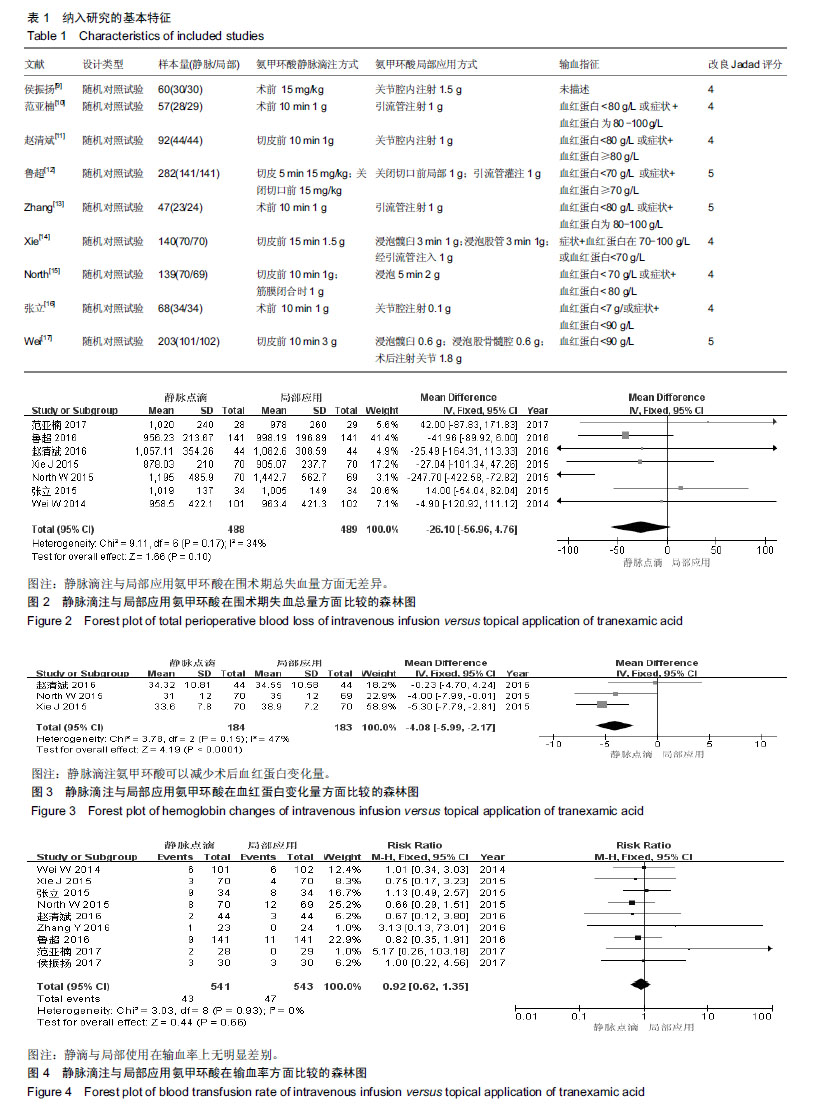
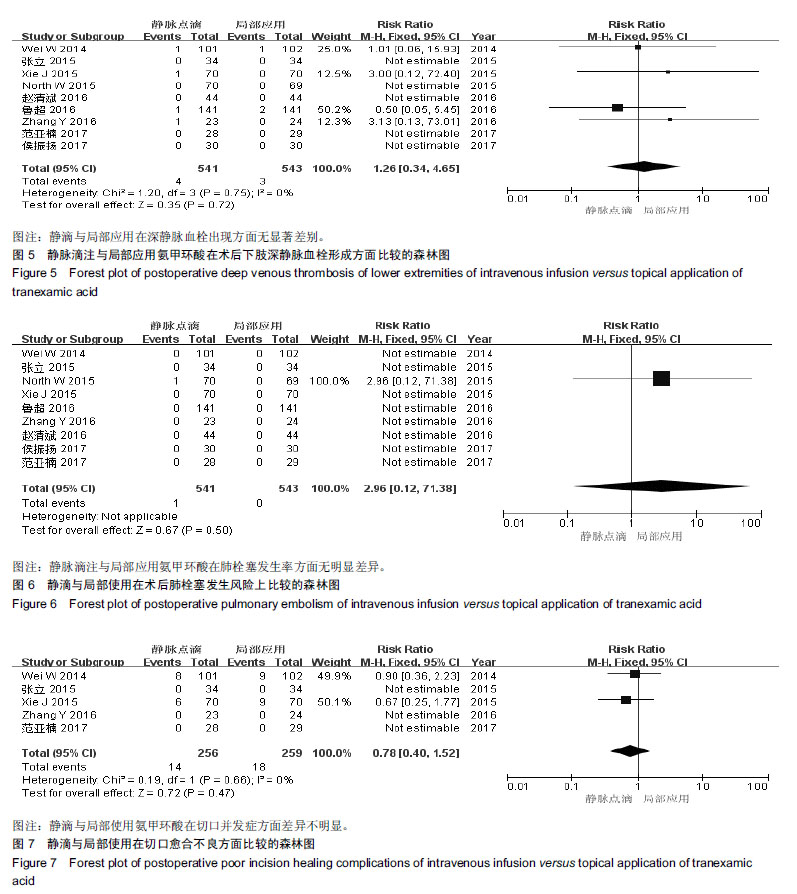
结果与结论:①经过3名评估者讨论,9篇符合要求的研究(改良Jadad 评分≥ 4)被纳入;②分析后可知,氨甲环酸在降低术后血红蛋白变化量方面,静滴较局部使用有优势[WMD=-4.08,95%CI(-5.99,-2.17),P < 0.01];③静滴与局部应用在围术期总失血量[WMD=-26.10,95%CI(-56.96,4.76),P=0.10]、输血率[RR=0.92,95%CI(0.62,1.35),P=0.66]、术后下肢深静脉血栓形成风险[RR=1.26,95%CI(0.34,4.65),P=0.72]、术后肺栓塞发生风险[RR=2.96,95%CI(0.12,71.38),P=0.50]及切口愈合不良发生率[RR=0.78,95%CI(0.40,1.52),P=0.47]等方面差异均无显著性意义;④提示相对于局部使用,静滴氨甲环酸能够降低血红蛋白围术期变化量,且不增加术后下肢深静脉形成、肺栓塞及切口愈合不良等风险。因此行首次单侧全髋关节置换时,推荐静滴氨甲环酸的方式。
ORCID: 0000-0003-3156-2607(鹿战)
中图分类号:
R459.9
.jpg)