| [1]Boucard N, Viton C, Agay D, et al. The use of physical hydrogels of chitosan for skin regeneration following third-degree burns. Biomaterials. 2007;28(24):3478-3488.[2]Gupta B, Agarwal R, Alam MS. Textile-based smart wound dressings. Indian J Fibre Text. 2010;35(2):174-187.[3]Choudhury AJ, Gogoi D, Chutia J, et al. Controlled antibiotic-releasing Antheraea assama silk fibroin suture for infection prevention and fast wound healing. Surgery. 2016; 159(2):539-547.[4]Obermeier A, Schneider J, Wehner S, et al. Novel high efficient coatings for anti-microbial surgical sutures using chlorhexidine in fatty acid slow-release carrier systems. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101426.[5]Schreml S, Szeimies RM, Prantl L,et al. Wound healing in the 21st century. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;63(5):866-881.[6]Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Zhang M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010; 62(1):83-99.[7]符旭东,郭家平.壳聚糖类水凝胶在组织工程领域的研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2010,30(15):1308-1310.[8]Amsden B. Novel biodegradable polymers for local growth factor delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97(Pt B): 318-328.[9]Tessmar JK, Göpferich AM. Matrices and scaffolds for protein delivery in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007; 59(4-5):274-291.[10]Lee KY, Mooney DJ. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem Rev. 2001;101(7):1869-1879.[11]Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Sudheesh Kumar PT, et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(3):322-337.[12]Elviri L, Bianchera A, Bergonzi C, et al. Controlled local drug delivery strategies from chitosan hydrogels for wound healing. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][13]Archana D, Dutta J, Dutta PK. Evaluation of chitosan nano dressing for wound healing: characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;57:193-203.[14]Dai T, Tanaka M, Huang YY, et al.Chitosan preparations for wounds and burns: antimicrobial and wound-healing effects (vol 9, pg 857, 2011). Expert Rev Anti-Infe. 2013; 11(8):866.[15]Pérez RA, Won JE, Knowles JC, et al. Naturally and synthetic smart composite biomaterials for tissue regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):471-496.[16]Ferreira MO, Leite LL, de Lima IS, et al. Chitosan Hydrogel in combination with Nerolidol for healing wounds. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;152:409-418.[17]Li M, Ke QF, Tao SC, et al. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/ chitosan composite hydrogels loaded with exosomes derived from miR-126-3p overexpressed synovium mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic chronic wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(42):6830-6841.[18]Zubair M, Malik A, Ahmad J. Clinico-microbiological study and antimicrobial drug resistance profile of diabetic foot infections in North India. Foot (Edinb). 2011;21(1):6-14.[19]Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Zhang M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010; 62(1):83-99.[20]Jayakumar R, Prabaharan M, Sudheesh Kumar PT, et al. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2011;29(3):322-337.[21]Amidi M, Mastrobattista E, Jiskoot W, et al. Chitosan-based delivery systems for protein therapeutics and antigens. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(1):59-82.[22]Borderud SP, Li Y, Burkhalter JE, et al. Electronic cigarette use among patients with cancer: Characteristics of electronic cigarette users and their smoking cessation outcomes (vol 120, pg 3527, 2014). Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 2015;121(5): 800-801.[23]王冰洋,牛广明,杜华,等.不同敷料在糖尿病足溃疡伤口治疗中的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(34): 5155-5162.[24]Moura LI, Dias AM, Carvalho E, et al. Recent advances on the development of wound dressings for diabetic foot ulcer treatment--a review. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7093-7114.[25]Hennink WE, van Nostrum CF. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54(1):13-36.[26]Doyle JS, Buising KL, Thursky KA, et al. Epidemiology of infections acquired in intensive care units. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;32(2):115-138.[27]Yousafzai MT, Siddiqui AR, Rozi S, et al. Determinants of Compliance with Universal Precautions at First Level Care Facilities in North West Frontier Province of Pakistan. Am J Epidemiol. 2010;171:120-137.[28]Gao G, Lange D, Hilpert K, et al. The biocompatibility and biofilm resistance of implant coatings based on hydrophilic polymer brushes conjugated with antimicrobial peptides. Biomaterials. 2011;32(16):3899-3909.[29]Flores CY, Diaz C, Rubert A, et al. Spontaneous adsorption of silver nanoparticles on Ti/TiO2 surfaces. Antibacterial effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010; 350(2):402-408.[30]El-Naggar MY, Gohar YM, Sorour MA, et al. Hydrogel Dressing with a Nano-Formula against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diabetic Foot Bacteria. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016; 26(2): 408-420.[31]Heunis TD, Smith C, Dicks LM. Evaluation of a nisin-eluting nanofiber scaffold to treat Staphylococcus aureus-induced skin infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013; 57(8):3928-3935.[32]Nimal TR, Baranwal G, Bavya MC, et al. Anti-staphylococcal Activity of Injectable Nano Tigecycline/Chitosan-PRP Composite Hydrogel Using Drosophila melanogaster Model for Infectious Wounds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(34):22074-22083.[33]Anjum S, Arora A, Alam MS, et al. Development of antimicrobial and scar preventive chitosan hydrogel wound dressings. Int J Pharm. 2016;508(1-2):92-101.[34]Sung JH, Hwang MR, Kim JO, et al. Gel characterisation and in vivo evaluation of minocycline-loaded wound dressing with enhanced wound healing using polyvinyl alcohol and chitosan. Int J Pharm. 2010;392(1-2):232-240.[35]Pulat M, Kahraman AS, Tan N, et al. Sequential antibiotic and growth factor releasing chitosan-PAAm semi-IPN hydrogel as a novel wound dressing. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(7): 807-819.[36]El-Naggar MY, Gohar YM, Sorour MA, et al. Hydrogel Dressing with a Nano-Formula against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Diabetic Foot Bacteria. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;26(2): 408-420.[37]Zhang D, Zhou W, Wei B, et al. Carboxyl-modified poly(vinyl alcohol)-crosslinked chitosan hydrogel films for potential wound dressing. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;125:189-199.[38]Ngadaonye JI, Geever LM, McEvoy KE, et al. Evaluation of Novel Antibiotic-Eluting Thermoresponsive Chitosan-PDEAAm Based Wound Dressings. Int J Polym Mater. 2014;63(17):873-883.[39]Sinha M, Banik RM, Haldar C, et al. Development of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride loaded poly(ethylene glycol)/chitosan scaffold as wound dressing. J Porous Mat. 2012;20(4):799-807.[40]Radhakumary C, Antonty M, Sreenivasan K. Drug loaded thermoresponsive and cytocompatible chitosan based hydrogel as a potential wound dressing. Carbohyd polym. 2011;83(2):705-713.[41]Mahmoud AA, Salama AH. Norfloxacin-loaded collagen/chitosan scaffolds for skin reconstruction: Preparation, evaluation and in-vivo wound healing assessment. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016;83:155-165.[42]Ong SY, Wu J, Moochhala SM, et al. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials. 2008;29(32): 4323-4332.[43]Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27(1): 76-83.[44]Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, et al. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10): 499-511.[45]Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, et al. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles - nanoparticle or silver ion. Toxicol Lett. 2012; 208(3):286-292.[46]Xiu ZM, Zhang QB, Puppala HL, et al. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012;12(8):4271-4275.[47]Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2007;3(1):95-101. [48]Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27(1): 76-83.[49]Anisha BS, Biswas R, Chennazhi KP, et al. Chitosan-hyaluronic acid/nano silver composite sponges for drug resistant bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;62:310-320.[50]Jaiswal M, Koul V, Dinda AK. In vitro and in vivo investigational studies of a nanocomposite-hydrogel-based dressing with a silver-coated chitosan wafer for full-thickness skin wounds. J Appl Polym Sci. 2016;133(21):43472.[51]Martins AF, Monteiro JP, Bonafe EG, et al. Bactericidal activity of hydrogel beads based on N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan/alginate complexes loaded with silver nanoparticles. Chinese Chem Lett. 2015;26(9):1129-1132.[52]Yadollahi M, Farhoudian S, Namazi H. One-pot synthesis of antibacterial chitosan/silver bio-nanocomposite hydrogel beads as drug delivery systems. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015; 79:37-43.[53]Sacco P, Travan A, Borgogna M, et al. Silver-containing antimicrobial membrane based on chitosan-TPP hydrogel for the treatment of wounds. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(3): 128.[54]Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, et al. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10): 499-511.[55]Coleman NJ. Aspects of the in vitro bioactivity and antimicrobial properties of Ag(+)- and Zn (2+)-exchanged 11 A tobermorites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(6): 1347-1355.[56]Iyigundogdu ZU, Demirci S, Bac N, et al. Development of durable antimicrobial surfaces containing silver- and zinc-ion-exchanged zeolites. Turk J Biol. 2014;38(3): 420-427.[57]Pelgrift RY, Friedman AJ. Nanotechnology as a therapeutic tool to combat microbial resistance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(13-14):1803-1815.[58]Kocbek P, Teskac K, Kreft ME, et al. Toxicological aspects of long-term treatment of keratinocytes with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Small. 2010;6(17):1908-1917.[59]Ng KW, Khoo SP, Heng BC, et al. The role of the tumor suppressor p53 pathway in the cellular DNA damage response to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32(32):8218-8225.[60]Sharma V, Singh SK, Anderson D, et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced genotoxicity in primary human epidermal keratinocytes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(5): 3782-3788.[61]Nair S, Sasidharan A, Divya Rani VV, et al. Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20 Suppl 1:S235-241.[62]Monteiro-Riviere NA, Wiench K, Landsiedel R, et al. Safety evaluation of sunscreen formulations containing titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in UVB sunburned skin: an in vitro and in vivo study. Toxicol Sci. 2011;123(1):264-280.[63]Hackenberg S, Kleinsasser N. Dermal toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles: a worrying feature of sunscreen. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012;7(4):461-463.[64]Kumar PT, Lakshmanan VK, Anilkumar TV, et al. Flexible and microporous chitosan hydrogel/nano ZnO composite bandages for wound dressing: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(5):2618-2629.[65]P T SK, Lakshmanan VK, Raj M, et al. Evaluation of wound healing potential of β-chitin hydrogel/nano zinc oxide composite bandage. Pharm Res. 2013;30(2):523-537.[66]Jayakumar R, Ramachandran R, Divyarani VV, et al. Fabrication of chitin-chitosan/nano TiO2-composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;48(2):336-344.[67]Archana D, Singh BK, Dutta J, et al. In vivo evaluation of chitosan-PVP-titanium dioxide nanocomposite as wound dressing material. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;95(1):530-539.[68]Grassian VH, O'shaughnessy PT, Adamcakova-Dodd A, et al. Inhalation exposure study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environ Health Perspect. 2007;115(3):397-402.[69]Lieder R, Darai M, Thor MB, et al. In vitro bioactivity of different degree of deacetylation chitosan, a potential coating material for titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012; 100(12):3392-3399.[70]Martins AF, Facchi SP, Monteiro JP, et al. Preparation and cytotoxicity of N,N,N-trimethyl chitosan/alginate beads containing gold nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72: 466-471.[71]Khan AU. Medicine at nanoscale: a new horizon. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:2997-2998.[72]Jiang W, Mashayekhi H, Xing B. Bacterial toxicity comparison between nano- and micro-scaled oxide particles. Environ Pollut. 2009;157(5):1619-1625.[73]Ruparelia JP, Chatterjee AK, Duttagupta SP, et al. Strain specificity in antimicrobial activity of silver and copper nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(3):707-716.[74]Gajjar P, Pettee B, Britt DW, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of Commercial Nanoparticles. Adv Mater Nanotechno Proceed. 2009;1151:130-132.[75]Wu B, Huang R, Sahu M, et al. Bacterial responses to Cu-doped TiO(2) nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ. 2010; 408(7):1755-1758.[76]Wang Z, Lee YH, Wu B, et al. Anti-microbial activities of aerosolized transition metal oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere. 2010;80(5):525-529. |
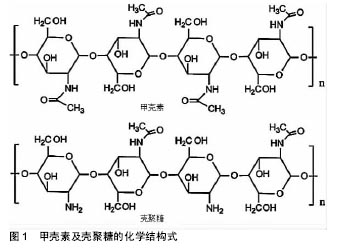
.jpg)
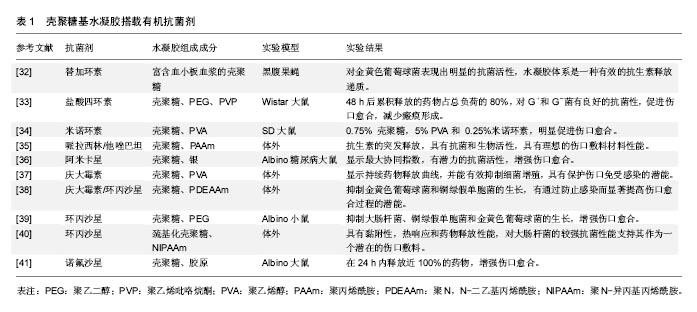
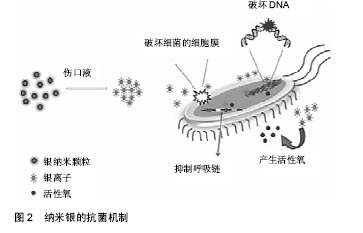
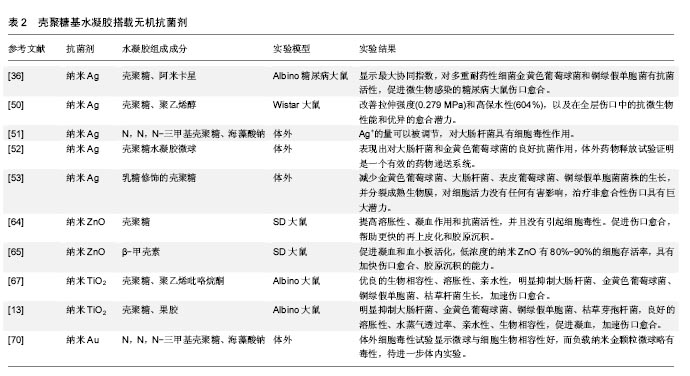
.jpg)