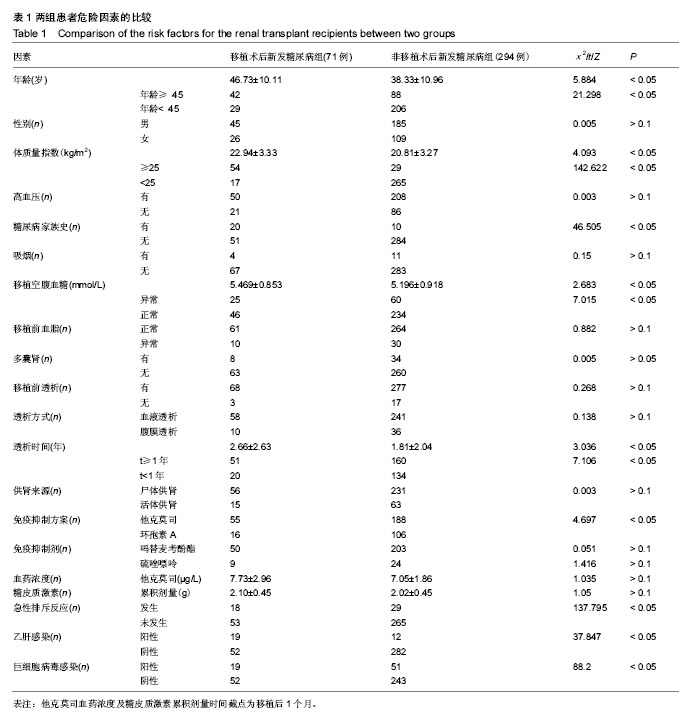
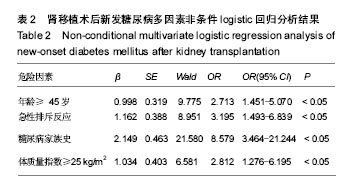
| [1] Sato T,InagakiA,UchidaK,etal.Diabetes mellitus after transplant: relationship to pretransplant glucose metabolism and tacrolimus or cyclosporine A-based therapy. Transplantation. 2003;76(9): 1320-1326.[2] Wiesbauer F, Heinze G, Regele H, et al.Glucose control is associated with patient survival in diabetic patients after renal transplantation. Transplantation. 2010; 89(5):612-619.[3] CosioFG,Pesavento TE, Kim S, et al.Patient survival after renal transplantation: IV. Impact of post-transplant diabetes.Kidney International.2002;62(4): 1440-1446.[4] Burroughs TE, Swindle J,Takemoto S, et al. Diabetic complications associated with new-onset diabetes mellitus in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007;83(8): 1027-1034.[5] Goldmannova D, Karasek D, Krystynik O, et al. New-onset diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation. Biomed Pap Med FacUnivPalacky Olomouc Czech Repub.2016;160(2): 195-200.[6] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(Suppl 1): S42-S47.[7] Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y,VanMeurs JB, et al. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 2004;338(2): 143-156.[8] 闫娜娜,姚斌,王宇,等. 中国人群肾移植术后糖尿病危险因素的Meta分析[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(10): 4395- 4404.[9] Maskey R. New-Onset Diabetes after Transplant (NODAT). Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2014;12(48):301-305. [10] 陈雄,姚斌,董婷婷,等.肾移植术后糖尿病临床特点及相关危险因素分析[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2009, 48(7):547-551.[11] Shah T, Kasravi A, Huang E, et al. Risk factors for development of new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation.Transplantation.2006; 82(12):1673-1676.[12] 余爱荣,范星,辛华雯,等.肾移植术后糖尿病发病率与危险因素[J].药物流行病学杂志, 2011(4):169-172.[13] Caillard S, Eprinchard L, Perrin P, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors of Glucose Metabolism Disorders in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Role of Systematic Screening by Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. Transplantation. 2011; 91(7): 757-764.[14] Chakkera HA, Hanson RL, Raza SM, et al. Pilot Study: Association of Traditional and Genetic Risk Factors and New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus Following Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation Proceedings. 2009;41(10): 4172-4177.[15] Kurzawski M, Dziewanowski K, Dro?dzik M. Analysis of type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk factors in relation to new onset diabetes after transplantation in renal transplant recipients medicated with tacrolimus. Pharmacological Reports Pr. 2013;65(1):1-11.[16] 贺春燕, 毕会民. 肾移植术后糖尿病的临床特点及危险因素分析[J].实用老年医学, 2012, 26(1):50-52.[17] 王英吉, 狄文佳, 孙勤,等. 肾移植术后糖尿病相关危险因素[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2015, 24(1):21-25.[18] HjelmesæthJ,HartmannA,KofstadJ,etal.Tapering off prednisolone and cyclosporin the first year after renal transplantation: the effect on glucose tolerance. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2001;16(4):829-835.[19] 黄正宇,李敏如,曾芳芳,等. 肾移植术后糖尿病的危险因素分析[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2008, 29(6):777-781.[20] Siraj ES, Abacan C, Chinnappa P, et al. Risk factors and outcomes associated with posttransplant diabetes mellitus in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation Proceedings. 2010;42(5):1685-1689.[21] 陈敏灵,张尧,于明香,等. 肾移植术后糖尿病的发病及其危险因素分析[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2013, 29(9):750-755.[22] Yu H, Kim H, Baek C H, et al. Risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus after living donor kidney transplantation in Korea - a retrospective single center study. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17(1):106.[23] Gaynor JJ, Ciancio G, Guerra G, et al. Multivariable risk of developing new onset diabetes after transplant results from a single center study of 481 adult, primary kidney transplant recipients. Clinical Transplantation.2015;29(4):301-310.[24] Mucha K,Foroncewicz B,Ryter M,et al. Weight gain in renal transplant recipients in a Polish single centre.AnnTransplant. 2015, 20:16-20.[25] Roland M,GataultP,Al-NaijjarA,et al.Early pulse pressure and low grade proteinuria as independent long-term risk factors for new-onset diabetes after kidney transplantation. Am Transplant.2008;8(8):1719-1728.[26] Prasad GV,Kim SJ,Huang M,etal.Reduced incidence of new-onset diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase inhibitors (statins).Am Transpl.2004;4(11):1897-1903.[27] Abbas MH, Ismail MI, El Deeb SA, et al. Effect of pretransplant hepatitis C virus on the development of new-onset diabetes mellitus after transplant in Egyptian living-donor renal allotransplant recipients at mansoura urology and nephrology center . Exp Clin Transplant. 2015; 13(1):26-34. [28] Fabrizio F, Paul M, Vivek D, et al. Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus and HCV Seropositive Status After Renal Transplantation: Meta-Analysis of Clinical Studies. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(10):2433-2440.[29] 卢一平. 肾移植受者糖尿病、高血压和血脂异常防治策略[J]. 中华移植杂志:电子版, 2010, 4(3):5-9.[30] Wissing KM, Pipeleers L. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus after renal transplantation: Prevention and treatment.Transplantation Reviews. 2014; 28(2):37-46.[31] 蒋婉洁,卢一平. KDIGO临床实践指南:肾移植受者的诊治[J]. 中华移植杂志:电子版, 2010, 4(2):156-164.[32] 倪雪峰,程东瑞. 肾移植术后糖尿病的诊治进展[J]. 肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2015, 24(3):284-288.[33] Knowler WC, Barrett-Connor E, Fowler SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of T2DM with lifestyle intervention or metformin. New Eng J Med.2002; 346(6):393-403.[34] Sharif A, Hecking M, de Vries AP, et al. Proceedings from an international consensus meeting on posttransplantation diabetes mellitus: recommendations and future directions.Am J Transplant.2014;14(9):1992-2000.[35] 詹珊珊,贾伟平. 生活方式与糖尿病[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2011, 27(8):692-695. |
.jpg)
.jpg)