| [1] Kasir R, Vernekar VN, Laurencin CT. Regenerative Engineering of Cartilage Using Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2015;1(1):42-49.[2] Wankhade UD, Shen M, Kolhe R, et al. Advances in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Isolation, Characterization, and Application in Regenerative Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3206807.[3] Naderi N, Wilde C, Haque T, et al. Adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells in 3-dimensional spheroid cultures (microtissue): implications for the reconstructive surgeon. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67(12):1726-1734.[4] Li H, Han Z, Liu D, et al. Autologous platelet-rich plasma promotes neurogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Int J Neurosci. 2013;123(3):184-190.[5] Marx C, Silveira MD, Beyer Nardi N. Adipose-derived stem cells in veterinary medicine: characterization and therapeutic applications. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(7):803-813.[6] Banyard DA, Salibian AA, Widgerow AD, et al. Implications for human adipose-derived stem cells in plastic surgery. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(1):21-30.[7] Mantovani C, Terenghi G, Magnaghi V. Senescence in adipose-derived stem cells and its implications in nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(1):10-15.[8] Xu FT, Li HM, Yin QS, et al. Effect of activated autologous platelet-rich plasma on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(2):257-270.[9] Xu FT, Li HM, Zhao CY, et al. Characterization of Chondrogenic Gene Expression and Cartilage Phenotype Differentiation in Human Breast Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promoted by Ginsenoside Rg1 In Vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(5):1890-1902.[10] Konno M, Hamazaki TS, Fukuda S, et al. Efficiently differentiating vascular endothelial cells from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in serum-free culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;400(4):461-465.[11] Sahar DE, Walker JA, Wang HT, et al. Effect of endothelial differentiated adipose-derived stem cells on vascularity and osteogenesis in poly(D,L-lactide) scaffolds in vivo.J Craniofac Surg. 2012;23(3):913-918.[12] Deveza L, Choi J, Imanbayev G, et al. Paracrine release from nonviral engineered adipose-derived stem cells promotes endothelial cell survival and migration in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(3):483-491.[13] Berardi GR, Rebelatto CK, Tavares HF, et al. Transplantation of SNAP-treated adipose tissue-derived stem cells improves cardiac function and induces neovascularization after myocardium infarct in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011;90(2): 149-156.[14] Park IS, Chung PS, Ahn JC. Adipose-derived stromal cell cluster with light therapy enhance angiogenesis and skin wound healing in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;462(3):171-177.[15] Brown CF, Yan J, Han TT, et al. Effect of decellularized adipose tissue particle size and cell density on adipose-derived stem cell proliferation and adipogenic differentiation in composite methacrylated chondroitin sulphate hydrogels. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):045010. [16] Murdolo G, Piroddi M, Tortoioli C, et al. Free Radical-derived Oxysterols: Novel Adipokines Modulating Adipogenic Differentiation of Adipose Precursor Cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(12):4974-4983.[17] Chen CC, Hsu LW, Nakano T, et al. DHL-HisZn, a novel antioxidant, enhances adipogenic differentiation and antioxidative response in adipose-derived stem cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:1601-1609.[18] Morandi EM, Verstappen R, Zwierzina ME, et al. ITGAV and ITGA5 diversely regulate proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016 ;6:28889.[19] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[20] Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA, et al. Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2001;189(1):54-63.[21] Festy F, Hoareau L, Bes-Houtmann S, et al. Surface protein expression between human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and mature adipocytes. Histochem Cell Biol. 2005; 124(2):113-121.[22] Feng X, Liu X, Cai X, et al. The Influence of Tetracycline Inducible Targeting Rat PPARγ Gene Silencing on the Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(41):6330-6338. |
.jpg)
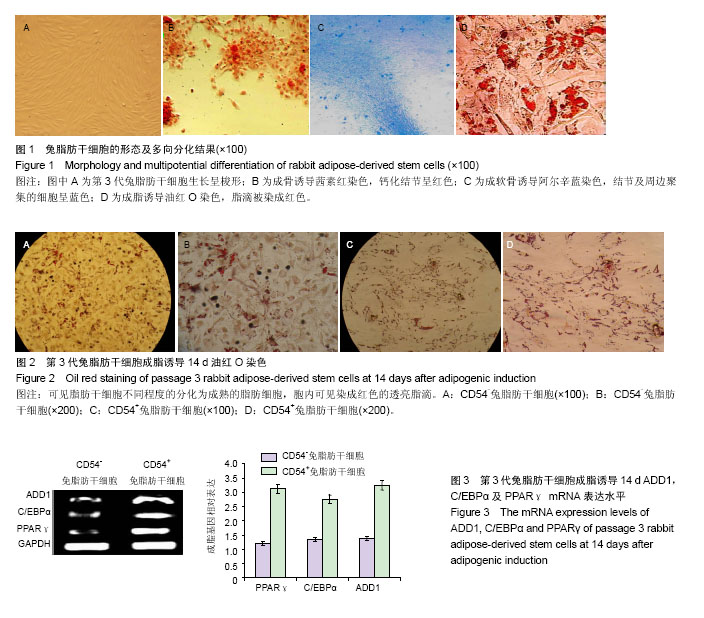
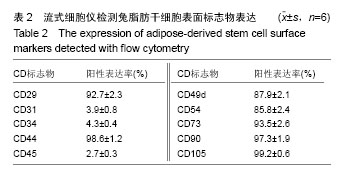
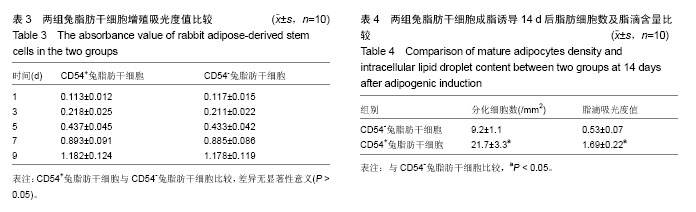
.jpg)
.jpg)