中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (15): 2453-2460.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.15.027
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
微创与开放经椎间孔椎体间融合治疗腰椎滑脱的Meta分析
闫兵山1, 2,徐宝山2,刘 越2,杨 强2
- 1天津医科大学研究生院,天津市 300070;2天津市天津医院,天津市 300211
Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis
Yan Bing-shan1, 2, Xu Bao-shan2, Liu Yue2, Yang Qiang2
- 1Graduate School of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脊柱融合术:脊柱融合术的发展有近百年的历史,1911年Albee等采用脊柱融合术治疗脊柱结核,以达到阻止结核感染播散的目的,同年,Hibbs等采用脊柱融合术控制脊柱侧凸患者畸形的发展,1959年Boucher等做了第一例椎弓根螺钉腰椎关节固定。自20世纪80年代以来,椎弓根螺钉技术得到广泛应用。融合术应用增加最多的是因为椎管狭窄而实施椎板切除术的老年患者,麻醉技术和围绕脊柱成像技术的进步也促使这种手术在老年人群中迅速增加。
微创手术:是电子显示系统与高科技手术器械以及传统外科手术相结合的前沿技术。随着科学技术的发展进步,“微创”这一概念已深入到外科手术的各种领域,如脑外、泌尿外科、骨科,手术方式多种多样,手术器械都很多,监控系统也不仅限于内窥镜,比如骨关节镜、胸腔镜、介入治疗;更多是采用介入的方式,如脊柱外科、骨科;还有其他方式,如显微外科广泛应用于手外科等。甲状腺手术既是美容手术,也是最为简单的微创手术。
摘要
背景:微创经椎间孔椎间融合治疗腰椎滑脱具有组织损伤小、术中出血少、术后住院时间短等优势,但其与开放经椎间孔椎体间融合治疗腰椎滑脱的疗效比较没有经过严格的循证医学检验。
目的:系统性评价微创经椎间孔椎体间融合和开放经椎间孔椎体间融合治疗腰椎滑脱的临床疗效及安全性。
方法:计算机检索万方数据库、CNKI、PubMed、Cochrane Library等数据库,以腰椎滑脱、微创、开放、经椎间孔椎体间融合术、minimally invasive、open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion、微创经椎间孔椎体间融合、开放经椎间孔椎体间融合等为检索词。由2名作者独立对纳入的文献进行质量评价及数据提取,用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析。
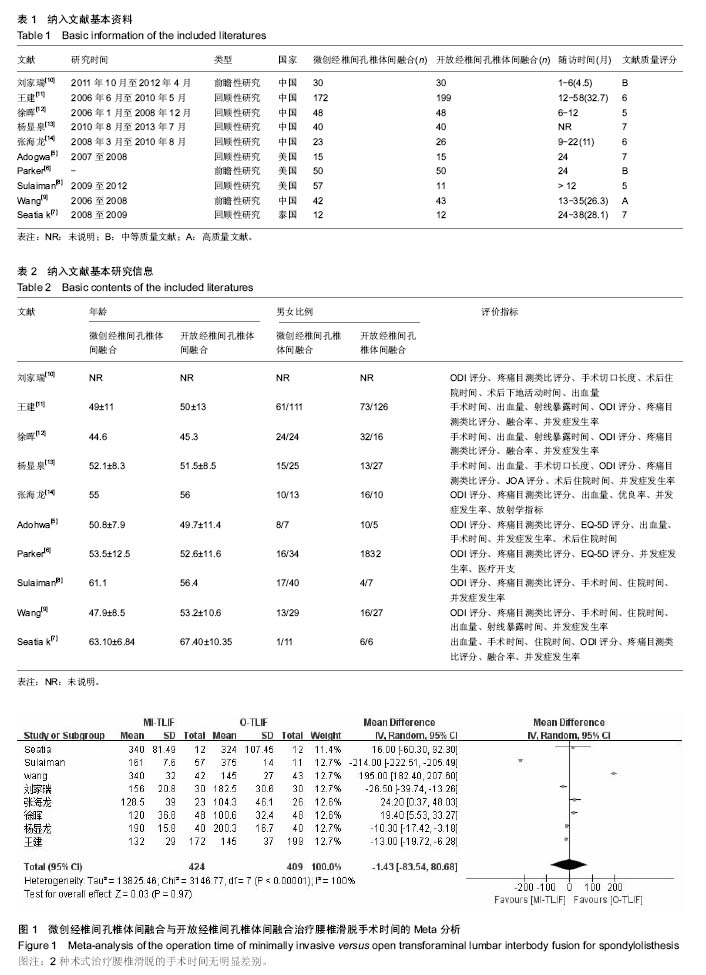
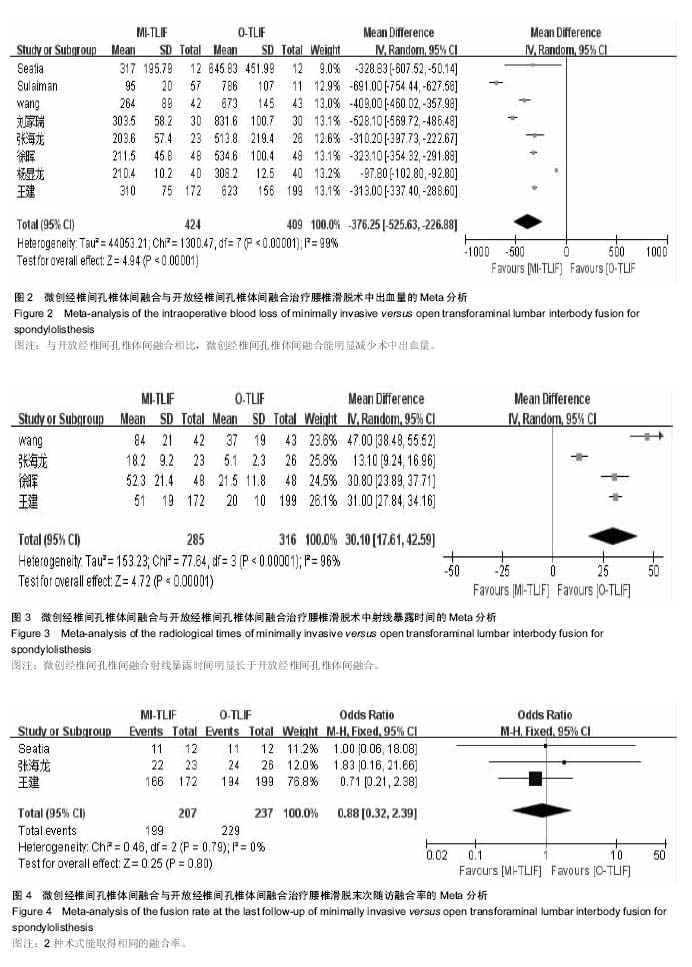
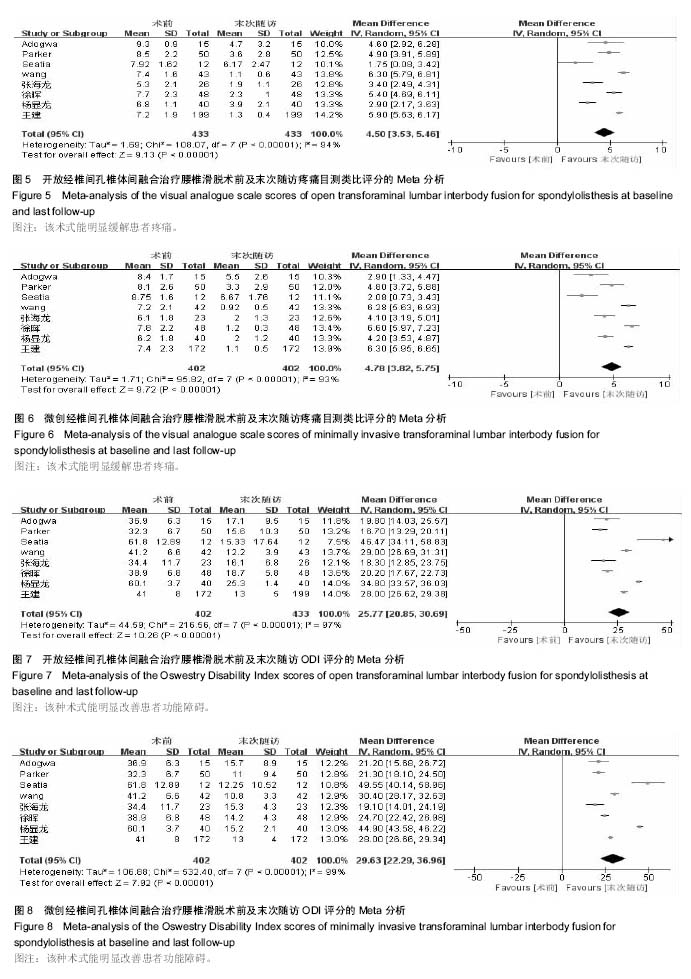
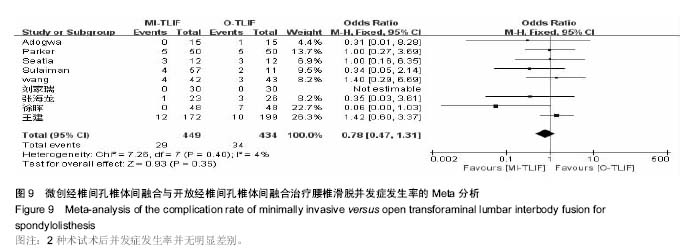
结果与结论:共纳入10篇文献,其中回顾性研究7篇,随机对照研究3篇,共纳入病例963例,微创组489例,开放组474例。①Meta分析结果显示:在手术时间、术后并发症发生率、末次随访融合率等方面2组差异无显著性意义,说明2种术式均能明显改善患者疼痛及功能障碍;②在术中出血量、术中射线暴露时间等方面差异有显著性意义;③结果说明,微创经椎间孔椎体间融合创伤小、术中及术后出血少,与开放经椎间孔椎体间融合相比具有相似的术后功能改善情况,且不增加手术时间和并发症的发生率,是一种安全、有效的手术方式。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-8287-0402(闫兵山)
中图分类号:
.jpg)