| [1] Sabah SA, Henckel J, Koutsouris S, et al. Are all metal-on-metal hip revision operations contributing to the National Joint Registry implant survival curves? : a study comparing the London Implant Retrieval Centre and National Joint Registry datasets.Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(1):33-39. [2] Browne JA, Bechtold CD, Berry DJ, et al. Failed Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasties: A Spectrum of Clinical Presentations and Operative Findings. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(9):2313-2320.[3] Du HR, Cho Y, Lee S, et al. Extent of vertical cementing as a predictive factor for radiolucency in revision total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(8):2710-2717.[4] Brodén C, Mukka S, Muren O, et al. High risk of early periprosthetic fractures after primary hip arthroplasty in elderly patients using a cemented, tapered, polished stem.Acta Orthop.2015;86(2):169-174.[5] Marks R. Impact of Obesity on Complications following Primary Hip Joint Arthroplasty Surgery for Osteoarthritis. J Arthritis. 2015; s1:3.[6] 金大地. SL非骨水泥假体柄在髋关节翻修术中的应用: 2007全国骨坏死及髋关节疾病学术会议[C].大连:2007.[7] Mahmoud SS, Pearse EO, Smith TO, et al. Outcomes of total hip arthroplasty, as a salvage procedure, following failed internal fixation of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Bone Joint J.2016;98-B(4):452-460.[8] Schrama JC, Fenstad AM, Dale H, et al. Increased risk of revision for infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients with total hip replacements.Acta Orthop. 2015;86(4):469-476.[9] Lee G W, Park KS, Kim DY, et al. Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty after Core Decompression with Tantalum Rod for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Clin Orthop Surg.2016;8(1):38-44.[10] Zhu Y, Chen W, Sun T, et al. Risk factors for the periprosthetic fracture after total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Surg. 2015;104(3):139-145 [11] 廖威明,康焱,傅明,等.人工髋关节置换术后假体脱位原因分析与处理[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(4):261-265.[12] Garland A, Rolfson O, Garellick G, et al. Early postoperative mortality after simultaneous or staged bilateral primary total hip arthroplasty: an observational register study from the swedish Hip arthroplasty register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:77.[13] 金佳,艾红珍. 高龄患者人工髋关节置换术后并发症的观察及护理[J]. 护士进修杂志,2011,26(3):256-258.[14] 孙强,鲁尧,王洪勋,等. 改良记忆合金环抱器治疗髋关节置换术后股骨假体周围骨折的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志, 2015, 31(7):637-640.[15] Lainiala O, Elo P, Reito A, et al. Comparison of extracapsular pseudotumors seen in magnetic resonance imaging and in revision surgery of 167 failed metal-on-metal hip replacements. Acta Orthop.2014;85(5):474-479.[16] Rahman WA, Amenábar T, Hetaimish BM, et al. Outcome of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in Management of Failed Metal-on-Metal Hip Arthroplasty.J Arthrop. 2016;31(11): 2559-2563.[17] 曾羿,沈彬,杨静,等. 大直径股骨头金属对金属全髋关节置换术的中期随访结果[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(7):385-391.[18] 王华溢,杨重飞,朱锦宇,等. 大直径金属对金属全髋置换假体松动原因分析一例报道[J]. 中华关节外科杂志电子版, 2015, (4): 98-100.[19] Liu W, Wahafu T, Cheng M, et al. Iconography : The influence of obesity on primary total hip arthroplasty outcomes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(3):289-296. [20] 甄平,李旭升,田琦,等. 手术治疗双侧人工关节置换术后一侧假体周围感染[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(10): 1079-1082.[21] 林谋明,姚小福,毛平,等. 人工关节置换假体周围感染的临床分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2015(7):1620-1622.[22] 曹建刚,刘军. 关节假体周围感染预防的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2015(2):250-253.[23] 吕增亮,葛武. 髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染的危险因素分析[J].中国临床研究, 2015, 28(11):1496-1497.[24] Menendez ME, Memtsoudis SG, Opperer M, et al. A nationwide analysis of risk factors for in-hospital myocardial infarction after total joint arthroplasty. Int Orthop.2015;39(4): 777-786.[25] Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, Roy AG, et al. A comparison of clinical results of hip resurfacing arthroplasty and 28 mm metal on metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomised trial with 3-6 years follow-up. Hip Int.2010;20(1):1-13.[26] Fernandez-Sampedro M, Salas-Venero C, Fariñas-Álvarez C, et al. 26Postoperative diagnosis and outcome in patients with revision arthroplasty for aseptic loosening. BMC Infect Dis. 2015;15:232.[27] Hu D, Yang X, Tan Y, et al. Ceramic-on-Ceramic Versus Ceramic-on-Polyethylene Bearing Surfaces in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2015;38(4):e331-e338.[28] Nwachukwu BU, Gurary EB, Lerner V, et al. Effect of smoking and soft tissue release on risk of revision after total knee arthroplasty: a case- control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:245.[29] Cadossi M, Mazzotti A, Baldini N, et al. New couplings, old problems: Is there a role for ceramic-on-metal hip arthroplasty?. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016; 104(1):204-209.[30] Goveia VR, Mendoza YQ, Ferreira JA, et al. Profile of hip arthroplasty patients in a teaching hospital. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2015;42(2):106-110.[31] 杨立宇,杨礼庆,付勤. 人工髋关节置换术后感染翻修治疗临床观察[J]. 海南医学,2016,27(14):2295-2299.[32] 郭文彤. 人工髋关节置换术后翻修原因及临床疗效[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2015,19(19):178-180.[33] Sebestyén A, Mester S, Vokó Z, et al. Wintertime surgery increases the risk of conversion to hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2015 ;26(3):1109-1117.[34] 曹群英,罗菊英,程娅南. 89例髋关节置换翻修术后患者的护理[J]. 湖北科技学报:医学版, 2015,29(2):147-148.[35] 张利勇. 人工髋关节置换术后翻修的原因分析及假体选择[J]. 中外医疗, 2015, 34 (34):96-98.[36] 郭国栋,樊根涛,郭亭,等. 人工髋关节置换后感染二期翻修中的彻底清创[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(48):7741-7746.[37] 甄平,李旭升,田琦,等. 圆锥形生物翻修柄髋关节置换治疗90岁以上高龄患者Dorr C型股骨髓腔的髋部骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(18):1633-1638. |
.jpg)
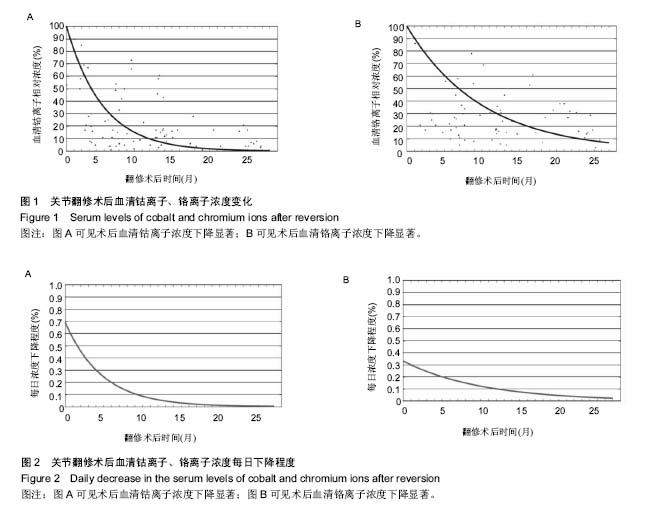
.jpg)
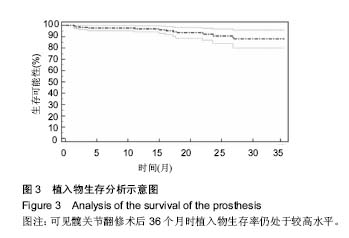
.jpg)