| [1] Kulkarni SS, Joffraud M, Boutant M, et al. Mfn1 Deficiency in the Liver Protects Against Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Enhances the Hypoglycemic Effect of Metformin. Diabetes. 2016;65(12):3552-3560.[2] 胡燕, 梁治学, 王金权,等. 2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗的发病机制研究进展[J]. 中国保健营养旬刊, 2014, 24(2):28 31. [3] Yuan H, Hu Y, Zhu Y, et al. Metformin ameliorates high uric acid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. Mol cell Endocrinol. 2017,443:138-145.[4] Bazotte RB,Silva LG,Schiavon FP. Insulin resistance in the liver: deficiency or excess of insulin? Cell Cycle. 2014;13(16): 2494-2500.[5] Lu CH, Hung YJ, Hsieh PS. Additional effect of metformin and celecoxib against lipid dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in high-fat fed rats with insulin resistance and fatty liver. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;789:60-67.[6] Sam WJ, Roza O, Hon YY, et al. Effects of SLC22A1 Polymorphisms on Metformin-Induced Reductions in Adiposity and Metformin Pharmacokinetics in Obese Children With Insulin Resistance. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;57(2):219-229.[7] Yoo HJ, Kim BH, Baik SH. Salsalate and adipo¬nectin ameliorate hepatic steatosis by inhibition of the hepatokine fetuin A. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;86(7):960-969.[8] Mori K, Emoto M, Inaba M. Fetuin A: a multifunctional protein. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, 2011;5(2): 124-146.[9] Ou HT, Chen PC, Wu MH. Effect of metformin by employing 2-hour postload insulin for measuring insulin resistance in Taiwanese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Formos Med Assoc.2017;116(2):80-89.[10] Sztalryd C, Kimmel AR. Perilipins: lipid droplet coat proteins adapted for tissue specific energy storage and utilization and lipid cytoprotection. Biochimie.2014;96: 96 101.[11] Mitchell PL, Nachbar R, Lachance D, et al. Treatment with a novel agent combining docosahexaenoate and metformin increases protectin DX and IL-6 production in skeletal muscle and reduces insulin resistance in obese diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(3):313-319.[12] Khan S, Jena G. Sodium butyrate reduces insulin-resistance, fat accumulation and dyslipidemia in type-2 diabetic rat: A comparative study with metformin. Chem Biol Lnteract. 2016; 254:124-134.[13] Garabadu D, Krishnamurthy S. Metformin attenuates hepatic insulin resistance in type-2 diabetic rats through PI3K/Akt/GLUT-4 signalling independent to bicuculline-sensitive GABAA receptor stimulation. Pharmaceutical biology. 2017;55(1):722-728.[14] Doyle MA, Singer J, Lee T, et al. Improving treatment and liver fibrosis outcomes with metformin in HCV-HIV co-infected and HCV mono-infected patients with insulin resistance: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2016;17(1): 331.[15] Zhao W, Li A, Feng X, et al. Metformin and resveratrol ameliorate muscle insulin resistance through preventing lipolysis and inflammation in hypoxic adipose tissue. Cellular signalling.2016;28(9):1401-1411.[16] Elmadhun NY, Lassaletta AD, Chu LM. Metformin alters the insulin signaling pathway in ischemic cardiac tissue in a swine model of metabolic syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;145(1):258-265. [17] Pandey AK, Gutch M, Mittal M,et al. Can metformin be used in type 1 diabetes with insulin resistance: Experience from tertiary care health center. J Assoc Physicians India. 2016; 64(1):91.[18] Yogalakshmi B, Bhuvaneswari S, Sreeja S .Grape seed proanthocyanidins and metformin act by different mechanisms to promote insulin signaling in rats fed high calorie diet. J Cell Commun Signal.2014;8(1):13-22.[19] Luo T, Nocon A, Fry J, et al. AMPK Activation by Metformin Suppresses Abnormal Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Adipose Tissue and Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Diabetes.2016;65(8):2295-2310.[20] Neels JG, Grimaldi PA. Physiological functions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor β. Physiol Rev.2014;94(3):795-858.[21] Bacha F, Klinepeter Bartz S. Insulin resistance, role of metformin and other non-insulin therapies in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Pediatric diabetes. 2016;17(8):545-558.[22] Sharma AK, Srinivasan BP. Triple verses glimepiride plus metformin therapy on cardiovascular risk biomarkers and diabetic cardiomyopathy in insulin resistance type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2009;38(5):433-444.[23] Park SE,Lee NS,Park JW . Association of urinary RBP4 with insulin resistance, inflammation, and microalbuminuria. Eur J Endocrinol.2014;171(4):443-449.[24] Glueck CJ, Goldenberg N, Sieve L, et al. An observational study of reduction of insulin resistance and prevention of development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women with polycystic ovary syndrome treated with metformin and diet. Metabolism.2008;57(7):954-960.[25] Dehkordi EH, Sattari F, Khoshdel A,et al. Effect of folic acid and metformin on insulin resistance and inflammatory factors of obese children and adolescents. J Res Med Sci 2016;21: 71.[26] Bermudez-Pirela VJ, Cano C, Medina MT, et al. Metformin plus low-dose glimeperide significantly improves Homeostasis Model Assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA(IR)) and beta-cell function (HOMA(beta-cell)) without hyperinsulinemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Ther. 2007;14(2):194-202 |
.jpg) 文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。
文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。.jpg) 文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。
文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。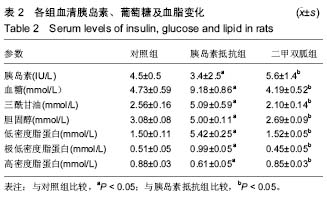
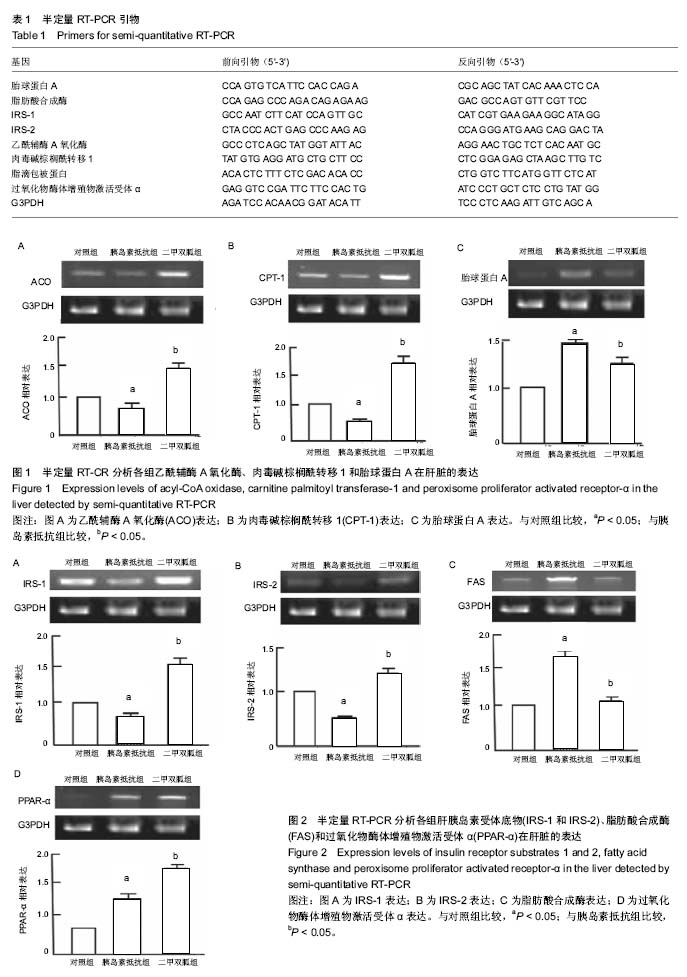

.jpg) 文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。
文题释义:
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。胰岛素抵抗易导致代谢综合征和2型糖尿病。
胰岛素受体:是一个四聚体,由两个α亚基和两个β亚基通过二硫键连接。两个α亚基位于细胞质膜的外侧,其上有胰岛素的结合位点;两个β亚基是跨膜蛋白,起信号转导作用。