中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (12): 1883-1888.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.12.014
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
高脂饲料配合链脲佐菌素诱导2型糖尿病模型大鼠的椎间盘形态
刘光源,戴慕巍,田发明,袁雷亮,耿林丹,卑明健,张 柳,王文雅
- 华北理工大学,河北省石家庄市 063000
Morphology of the intervertebral disc in high fat combined with streptozotocin-induced type II diabetic rats
Liu Guang-yuan, Dai Mu-wei, Tian Fa-ming, Yuan Lei-liang, Geng Lin-dan, Bei Ming-jian, Zhang Liu, Wang Wen-ya
- North China University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang 063000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。
文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。
.jpg) 文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。
文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。摘要
背景:高脂饲料配合低剂量链脲佐菌素诱导大鼠2型糖尿病模型是目前常用的2型糖尿病动物模型,目前尚无此模型对椎间盘结构影响的相关报道。椎体终板硬化是造成椎间盘退变的重要因素之一。
目的:评估高脂饲料配合低剂量链脲佐菌素诱导2型糖尿病大鼠模型是否适用于2型糖尿病相关椎间盘退变研究。
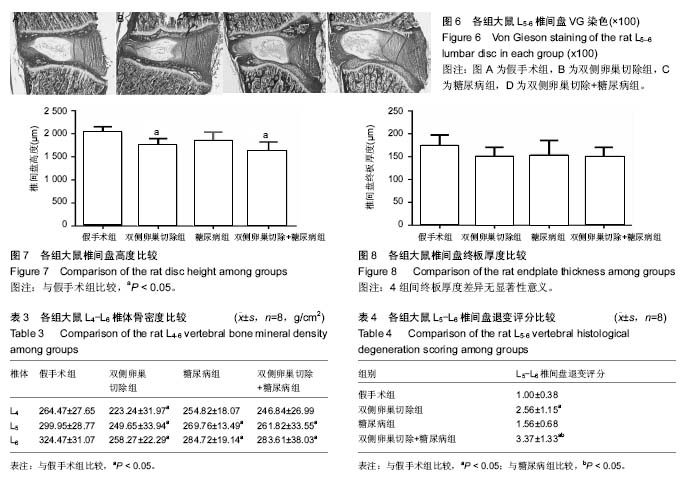
方法:32只3月龄雌性SPF级SD大鼠随机分为4组,即假手术组、双侧卵巢切除组、糖尿病组、双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组,每组8只。分别进行双侧卵巢切除术和/或高脂饲料配合低剂量链脲佐菌素处理。监测各组大鼠体质量、血糖及糖耐量,链脲佐菌素处理后8周检测骨密度后处死动物,取L5-6节段脱钙后正中矢状位切片行VG染色并进行椎间盘退变评分,分析椎间盘高度和终板厚度。
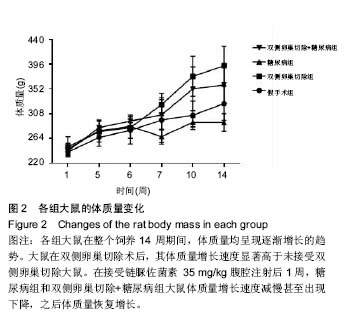
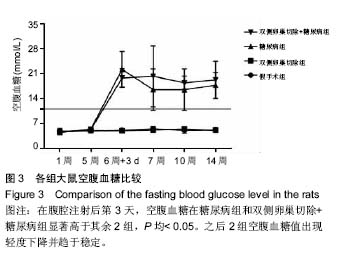
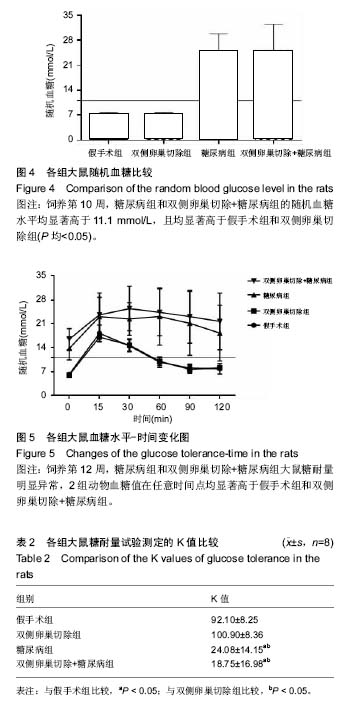
结果与结论:①糖尿病组和双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组大鼠空腹血糖、随机血糖分别显著高于假手术组和双侧卵巢切除组(P < 0.05),糖尿病组和双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组大鼠胰岛素敏感性分别显著低于假手术组和双侧卵巢切除组(P < 0.05);②双侧卵巢切除组L4-L6椎体骨密度显著低于假手术组(P < 0.05),糖尿病组和双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组L5-L6椎体骨密度均显著低于假手术组(P < 0.05);③双侧卵巢切除组和双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组L5-L6椎间盘退变评分分别显著高于假手术组和糖尿病组(P < 0.05);双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组表现与双侧卵巢切除组相仿,可见髓核细胞软骨化生及黏液变性,其评分结果显著高于假手术组和糖尿病组(P均< 0.05),但与双侧卵巢切除组相比差异未见显著性意义;④与假手术组相比,双侧卵巢切除组和双侧卵巢切除+糖尿病组椎间盘高度明显降低(P < 0.05);4组间终板厚度差异无显著性意义;⑤综上所述,虽然高脂饲料配合低剂量链脲佐菌素诱导2型糖尿病大鼠模型具备糖尿病特征表现,但未观察到其间盘组织较正常大鼠有显著改变,可能不适于2型糖尿病相关椎间盘退变研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-1522-7318(刘光源)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。
文题释义:
链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型:这种模型主要反映了1型糖尿病的病理生理状态。Srinivasan等在这一模型的基础上利用高脂饲料喂养大鼠诱导发生胰岛素抵抗,制作了2型糖尿病大鼠模型,其在病程、代谢特征上与人类2型糖尿病较为接近。目前这一模型已被广泛用于2型糖尿病的治疗等研究中。
椎间盘退变与糖尿病的关系:目前研究显示,椎间盘退变可能与高血糖、微血管病变和糖基化终产物等2型糖尿病相关改变有关,但2型糖尿病导致椎间盘退变的机制仍不明确。