中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 538-544.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.008
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
miR-155通过抑制SMAD5调控成骨细胞骨分化
邱诗阳1,付希佳2,白晓雪3,杨 军1
- 1中国医科大学附属盛京医院南湖院区创伤骨科,辽宁省沈阳市 110004;2朝阳市中心医院神经内科,辽宁省朝阳市 122000;3吉林大学第一医院干部病房,吉林省长春市 130021
miR-155 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts by inhibiting SMAD5 expression
Qiu Shi-yang1, Fu Xi-jia2, Bai Xiao-xue3, Yang Jun1
- 1Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110004, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Neurology, Chaoyang Central Hospital, Chaoyang 122000, Liaoning Province, China; 3Department of Cadre’s Ward, the First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。
文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。
文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。摘要
背景:诱导成骨细胞分化为骨细胞是组织工程中的研究热点,但分化过程中的调节机制尚未完全阐明。MicroRNA是一类内源性小RNA分子,可通过与靶基因mRNA的3’端非编码区结合在转录后水平调控基因表达。研究证实,microRNA在骨细胞分化过程中起到重要的调节作用。
目的:研究miR-155对成骨细胞骨分化的调节作用以及作用机制。
方法:取小鼠成骨细胞系MC3T3-E1细胞,加入小鼠骨形态发生蛋白2(200 μg/L)进行成骨诱导,并与诱导第1,3,7,14天,通过qRT-PCR检测miR-155 mRNA的表达。并将MC3T3-E1细胞分为对照组、诱导组、miR-155组和miR-155 inhibitor组,对照组用α-MEM培养基培养,诱导组在培养基中加入骨形态发生蛋白2进行成骨诱导,miR-155组和miR-155 inhibitor组在成骨诱导之前分别转染miR-155和miR-155拮抗剂,诱导2周。
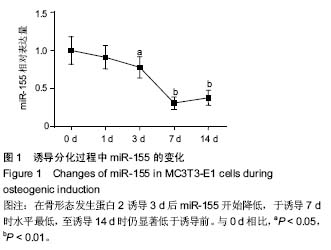
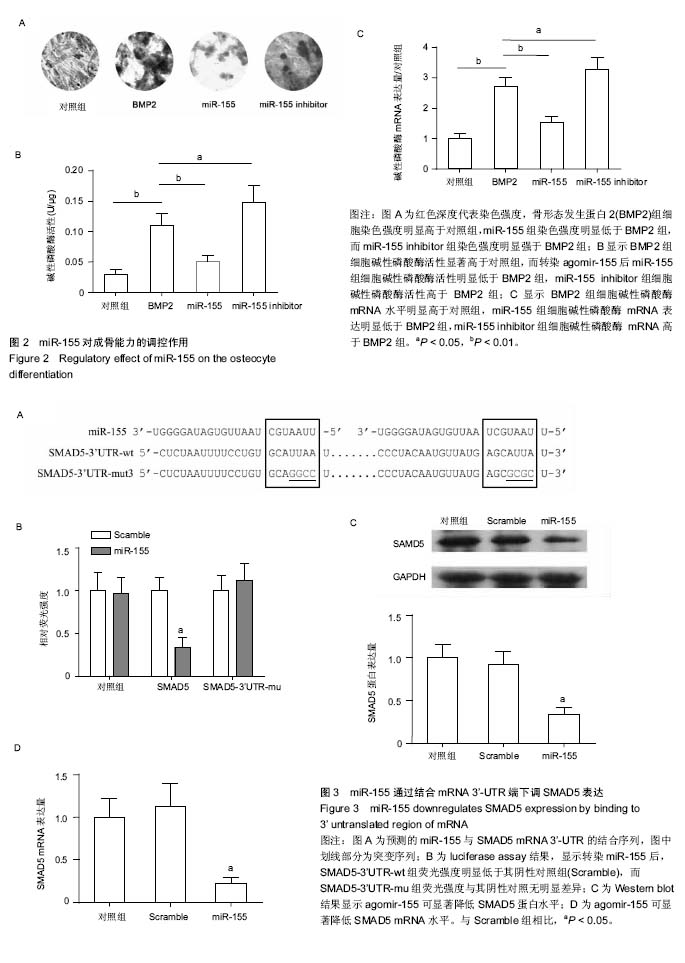
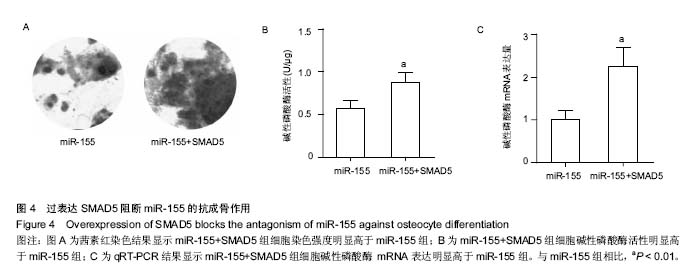
结果与结论:①茜素红染色及碱性磷酸酶活性测定:经骨形态发生蛋白2诱导后,miR-155 mRNA表达呈时间依赖性下调。诱导组MC3T3-E1细胞茜素红着色强度、碱性磷酸酶活性和mRNA表达也显著高于对照组(P < 0.01);miR-155组茜素红着色强度明显低于诱导组,碱性磷酸酶活性和mRNA也明显低于对照组(P < 0.01),而miR-155 inhibitor组则呈反向变化(P < 0.05);②荧光报告基因检测和western blot检测:miR-155可与SMAD5 mRNA 3’非编码区结合,并明显降低MC3T3-E1细胞中SMAD5蛋白和mRNA表达(P < 0.01)。结果表明,miR-155可通过负性调控SMAD5表达,抑制MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨分化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-2618-0786(杨军)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。
文题释义:
骨形态发生蛋白:能够诱导动物或人体间充质细胞分化为骨、软骨、韧带、肌腱和神经组织。与胚胎骨骼形成有关的蛋白质,在骨形成的数个阶段均起作用,由形态发生的早期阶段开始,并延续至出生后。在中枢神经的发生中也起着关键作用。
靶基因:即目的基因,在分子遗传中,它不仅要具有识别结合功能,还应该具有与位点结合后能表达你所需要的相应功能的作用。