| [1] Alhabashneh R, Khader Y, herra Z, et al. The association between periodontal disease and metabolic syndrome among outpatients with diabetes in Jordan. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015;14:67. [2] Gurav AN. Management of diabolical diabetes mellitus and periodontitis nexus: are we doing enough? World J Diabetes. 2016;7(4):50-66. [3] Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, et al. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia. 2012;55(1): 21-31. [4] Wu YY, Xiao E, Graves, DT. Diabetes mellitus related bone metabolism and periodontal disease. Int J Oral Sci. 2015;7(2): 63-72. [5] 贾金铃,贾凝,程玲.老年2型糖尿病患者牙周病发生及相关因素[J].广州医药,2016,47(4):45-48. [6] 张东,李晶,秦猛,等.老年牙周病与心血管疾病互为诱因的机制探讨[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,5(36):2553-2555. [7] Aral CA, Kesim S, Greenwell H, et al. Alveolar bone protective and hypoglycemic effects of systemic propolis treatment in experimental periodontitis and diabetes mellitus. J Med Food. 2015;18(2):195-201. [8] Hong JW, Noh JH, Kim DJ. The Prevalence and associated factors of periodontitis according to fasting plasma glucose in the korean adults. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(14):e3226. [9] Grover HS, Luthra S. Molecular mechanisms involved in the bidirectional relationship between diabetes mellitus and periodontal disease. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2013;17(3): 292-301. [10] Kim EK, Lee SG, Choi YH, et al. Association between diabetes-related factors and clinical periodontal parameters in type-2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health. 2013;13:64. [11] Sima C, Thomas E. Therapeutic targets for management of periodontitis and diabetes. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(15): 2216-2237. [12] 王赘,刘洪臣,鄂玲玲,等.米诺环素对人牙周膜成纤维细胞的生物学作用[J].上海口腔医学,2010,19(2):162-167. [13] Zhu WJ, Liang M. Periodontal ligament stem cells: current status, concerns, and future prospects. Stem Cells Int. 2015; 2015:972313. [14] Su F, Liu SS, MaJL, et al. Enhancement of periodontal tissue regeneration by transplantation of osteoprotegerin- engineered periodontal ligament stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):22. [15] Kim HS, Park JW, Yeo SI, et al. Effects of high glucose on cellular activity of periodontal ligament cells in vitro. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;74(1):41-47. [16] Patil VS, Patil VP, Gokhale N, et al. Chronic periodontitis in type 2 diabetes mellitus: oxidative stress as a common factor in periodontal tissue injury. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(4): BC12-BC16. [17] Liu JQ, Wu Y, Wang B, et al. High levels of glucose induced the caspase-3/parp signaling pathway, leading to apoptosis in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;66(2 ):229-237.[18] Devanoorkar A, Kathariya R, Guttiganur N, et al. Resistin: a potential biomarker for periodontitis influenced diabetes mellitus and diabetes induced periodontitis. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:930206. [19] Kim SY, Lee JY, Park YD, et al. Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67504. [20] 房明.高糖、糖基化终产物刺激下人牙周膜成纤维细胞生物学性能变化的体外研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.[21] Ren WW, Chen SL, Qiu J, et al. Role and mechanism of bcl-2 and bax in high glucose-mediated apoptosisof human periodontal ligament cells. Zhongugo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2014;18(51):8254-8260.[22] Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, et al. 10-Year Follow up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1577-1589. [23] Wong MG, Perkovic V, Chalmers J, et al. Long-term benefits of intensive glucose control for preventing end-stage kidney disease: advance-on. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(5):694-700. [24] The advance collaborative group. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2560-2572. [25] Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(2):129-139. [26] 刘加强,刘洪臣,王懿,等.高糖对人牙周膜细胞的生物学作用[J].上海口腔医学,2011,20(3):225-229.[27] 魏伟平,薛耀明,高方,等.高糖对INS-1细胞损伤存在记忆效应[J].南方医科大学学报,2011,31(4): 682-685. [28] Liu JQ, Jiang Y, Mao J, et al. High levels of glucose induces a dose-dependent apoptosis in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts by activating caspase-3 signaling pathway. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2013;170:1458-1471. [29] Zhang L, Ding Y, Rao GZ, et al. Effects of IL-10 and glucose on expression of OPG and RANKL in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2016;49(4):e4324. [30] Sternfeld T, Tischleder A, Schuster M, et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential and apoptosis of blood mononuclear cells in untreated HIV-1 infected patients. HIV Med. 2009; 10(8):512-519.[31] Rao RV, Niazi K, Mollahan P, et al. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell-death program: a novel HSP90-independent role for the small chaperone protein p23. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(3):415-425. [32] Sawa T, Nishimura F, Ohyama H, et al. In vitro induction of activation-induced cell death in lymphocytes from chronic periodontal lesions by exogenous Fas ligand. Infect Immun. 1999;67(3):1450-1454.[33] Lossdörfer S, Götz W, Jäger A. Parathyroid hormone modifies human periodontal ligament cell proliferation and survival in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 2006;41(6):519-526.[34] 苏红,周波,段雅倩.转录共激活子p300及表观修饰在高糖致人系膜细胞代谢记忆中的汇聚作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2013,38(3): 173-179.[35] 楼旭丹,汪海东,夏世金,等.糖尿病血管病变中的表观遗传现象[J].复旦学报(医学版),2014,41(2):257-263.[36] 徐瑾,廖云飞,衷诚群,等.表观遗传修饰炎症相关基因在高血糖“代谢记忆”中的作用及机制[J].中国老年学染志,2015,35(4):1039-1041. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。
文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。.jpg) 文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。
文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。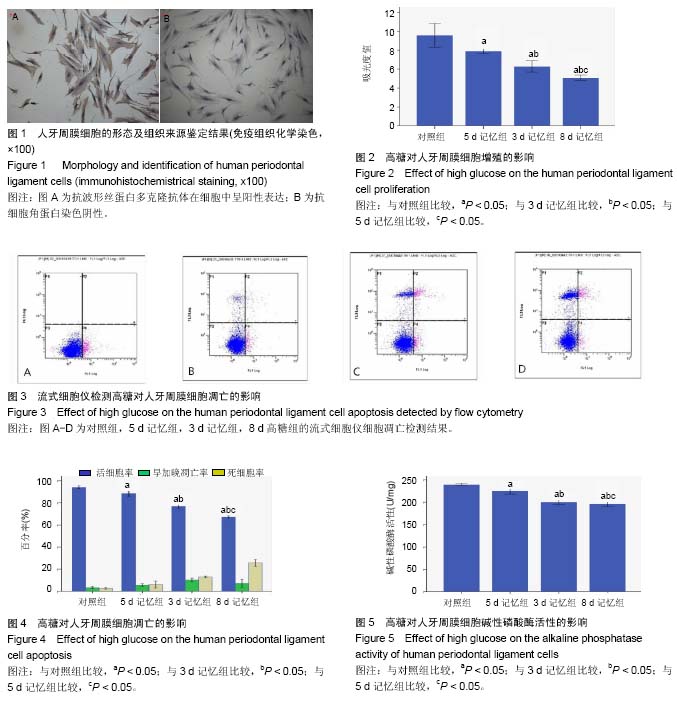
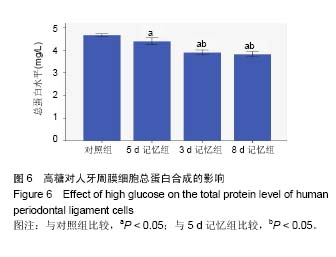
.jpg) 文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。
文题释义:
人牙周膜细胞:是参与牙周组织再生的最重要细胞之一,高糖对牙周膜细胞的增殖和凋亡,生物学活性,信号通路等均有影响。有研究发现人牙周膜细胞对高糖影响存在“代谢记忆”效应,具体表现在细胞增殖,凋亡,碱性磷酸酶活性,细胞总蛋白分泌等方面。
代谢记忆:指因为糖尿病患者血糖水平长时间较高,就会使靶细胞对早期的血糖环境产生记忆,后期即使血糖得以控制,靶细胞仍处于“高血糖”记忆状态,仍然不能降低糖尿病相关并发症的发病率。