| [1] Hellström M, Kalén M, Lindahl P, et al. Role of PDGF-B and PDGFR-beta in recruitment of vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes during embryonic blood vessel formation in the mouse. Development. 1999; 126(14):3047-3055.
[2] Hoofnagke JH, Carithers RL, Shaprio C, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure: summary of a workshop. Hepatology. 1995;21(1): 240-252.
[3] Zanet J, Pibre S, Jacquet C, et al. Endogenous Myc controls mammalian epidermal cell size, hyperproliferation, endoreplication and stem cell amplication. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 8): 1693-1704.
[4] Landau E, Tirosh R, Pinson A, et al. Protection of thrombin receptor expression under hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(4): 2281-2287.
[5] Liu W, Kong H, Zeng X, et al. Iptakalim inhibits PDGF-BB-induced human airway smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration. Exp Cell Res. 2015;336(2): 204-210.
[6] Virakul S, Dalm VA, Paridaens D, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Enhances Adipogenesis in Orbital Fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(9):5457-5464.
[7] Saito Y, Hojo Y, Tanimoto T, et al. Protein kinase C-alpha and protein kinase C-epsilon are required for Grb2-associated binder-1 tyrosine phosphorylation in response to platelet-derived growth factor.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(26):23216-23222.
[8] Lindqvist A, Nilsson BO, Ekblad E, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors expressed in response to injury of differentiated vascular smooth muscle in vitro: effects on Ca2+ and growth signals. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001;173(2):175-184.
[9] Li L, Xu M, Li X, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) induced by hypoxia promotes the survival of pulmonary arterial endothelial cells through the PI3K/Akt/Stat3 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35(2):441-451.
[10] Sun L, Zhao R, Lan X, et al.Goniolactone C, a styryl lactone derivative, inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation via PDGFR/ERK signaling. Molecules. 2014;19(12): 19501-19515.
[11] Gressot LV, Doucette TA, Yang Y, et al.Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b drives malignant progression in aPDGFB-dependent proneural glioma model by suppressing apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(9):2047-2054.
[12] Lynes J, Wibowo M, Koschmann C, et al. Lentiviral-induced high-grade gliomas in rats: the effects of PDGFB, HRAS-G12V, AKT, and IDH1-R132H. Neurotherapeutics. 2014;11(3):623-635.
[13] Doucette TA, Kong LY, Yang Y,et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 promotes angiogenesis and drives malignant progression in glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14(9):1136-1145.
[14] Hu G, Yao H, Chaudhuri AD, et al. Exosome-mediated shuttling of microRNA-29 regulates HIV Tat and morphine-mediated neuronal dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3:e381.
[15] Yao H, Duan M, Yang L, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB restores human immunodeficiency virus Tat-cocaine-mediated impairment of neurogenesis: role of TRPC1 channels. J Neurosci. 2012;32(29): 9835-9847.
[16] Geng H, Lan R, Singha PK, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid increases proximal tubule cell secretion of profibrotic cytokines PDGF-B and CTGF through LPA2- and Gαq-mediated Rho and αvβ6 integrin-dependent activation of TGF-β. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(4):1236-1249.
[17] Phipps MC, Xu Y, Bellis SL. Delivery of platelet-derived growth factor as a chemotactic factor for mesenchymal stem cells by bone-mimetic electrospun scaffolds. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40831.
[18] Zhang Y, Cheng N, Miron R, et al. Delivery of PDGF-B and BMP-7 by mesoporous bioglass/silk fibrin scaffolds for the repair of osteoporotic defects. Biomaterials. 2012;33(28):6698-6708.
[19] Yoshida S, Iwasaki R, Kawana H,et al. PDGFBB promotes PDGFRα-positive cell migration into artificial bone in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 421(4):785-789.
[20] Fukuda K, Ogawa M, Taniguchi H, et al. Molecular Approaches to Studying Microbial Communities: Targeting the 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene. J UOEH. 2016;38(3):223-232.
[21] Li B, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Fine Mapping of Two Additive Effect Genes for Awn Development in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) . PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e0160792.
[22] Hackmann K, Kuhlee F, Betcheva-Krajcir E, et al. Ready to clone: CNV detection and breakpoint fine-mapping in breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility genes by high-resolution array CGH. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016;159(3):585-590.
[23] Mukae H, Noguchi S, Naito K, et al. The Importance of Obligate Anaerobes and the Streptococcus anginosus Group in Pulmonary Abscess: A Clone Library Analysis Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid. Respiration. 2016; 92(2):80-89.
[24] Tuo D, Shen W, Yan P, et al. Rapid Construction of Stable Infectious Full-Length cDNA Clone of Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus Using In-Fusion Cloning. Viruses. 2015;7(12):6241-6250.
[25] Zheng X, Tong W, Liu F, et al. Genetic instability of Japanese encephalitis virus cDNA clones propagated in Escherichia coli. Virus Genes. 2016;52(2):195-203.
[26] O'Halloran DM. STITCHER: A web resource for high-throughput design of primers for overlapping PCR applications. Biotechniques. 2015;58(6):325-328.
[27] Camilo CM, Lima GM, Maluf FV, et al. HTP-OligoDesigner: An Online Primer Design Tool for High-Throughput Gene Cloning and Site-Directed Mutagenesis. J Comput Biol. 2016;23(1):27-29.
[28] Sun J, Wang L, Dong MM, et al. Construction and identification of multiple genes Co silence of plasmid shRNA. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(12):22053-22062.
[29] Cheng A, Zhang Y, Mei H, et al. Construction of recombinant pEGFP-N1-hPer2 plasmid and its expression in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2016;11(4):2768-2772.
[30] Shyma KP, Gupta SK, Gupta JP, et al. Restriction site detection in repetitive nuclear DNA sequences of Trypanosoma evansi for strain differentiation among different isolates. J Parasit Dis. 2016;40(3):1087-1090.
[31] Zarrin M, Erfaninejad M. Molecular variation analysis of <i>Aspergillus flavus</i> using polymerase chain reaction-restrictionfragment length polymorphism of the internal transcribed spacer rDNA region. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1628-1632.
[32] Thomsen MC, Ahrenfeldt J, Cisneros JL, et al. A Bacterial Analysis Platform: An Integrated System for Analysing Bacterial Whole GenomeSequencing Data for Clinical Diagnostics and Surveillance. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0157718.
[33] Garrigue I, Moulinas R, Recordon-Pinson P, et al. Contribution of next generation sequencing to early detection of cytomegalovirus UL97 emerging mutants and viral subpopulations analysis in kidney transplant recipients. J Clin Virol. 2016;80:74-81.
[34] Zhang R, Duan G, Shi Q, et al. Construction of a recombinant Lactococcus lactis strain expressing a fusion protein of Omp22 and HpaA from Helicobacter pylori for oral vaccine development. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38(11):1911-1916.
[35] Liu X, Fu G, Ji Z, et al. A Recombinant DNA Plasmid Encoding the sIL-4R-NAP Fusion Protein Suppress Airway Inflammation in an OVA-Induced Mouse Model of Asthma. Inflammation. 2016;39(4):1434-1440.
[36] Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D, Stasinopoulos M, et al. Polyol accumulation in muscle and liver in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2016; 30(6): 999-1007.
[37] Cairns RA, Mak TW. Lung Cancer Resets the Liver's Metabolic Clock. Cell Metab. 2016;23(5):767-769.
[38] Liu F, Song Y, Liu D.Hydrodynamics-based transfection in animals by systemic administration of plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999;6(7):1258-1266.
[39] Wang CH, Jawan B, Lee TH, et al. Single injection of naked plasmid encoding alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone protects against thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322(1):153-161. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。
文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。.jpg) 文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。
文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。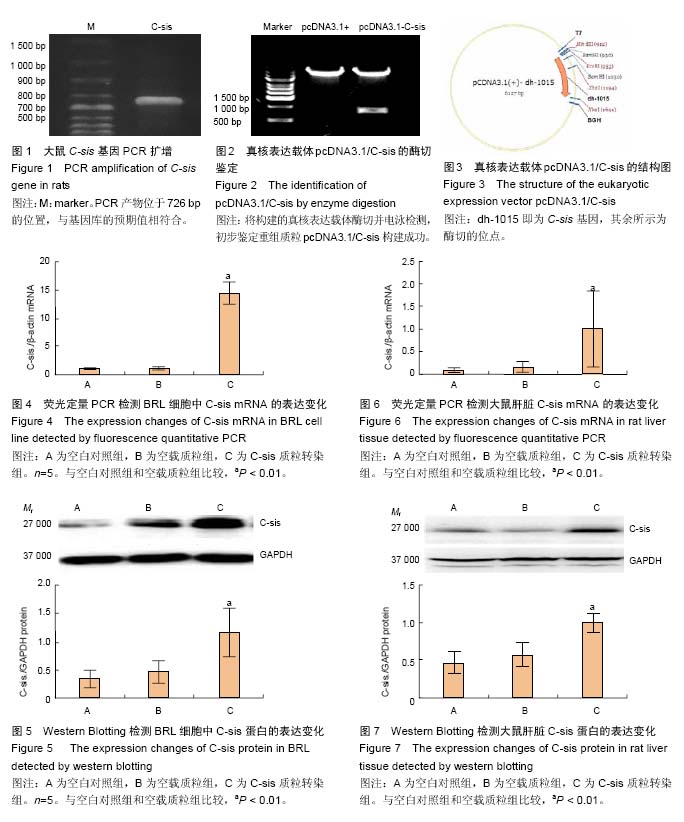
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。
文题释义:
基因克隆:是20世纪70年代发展起来的一项具有革命性的研究技术,可概括为分、切、连、转、选。“切”是指用序列特异的限制性内切酶切开载体DNA,或者切出目的基因;“连”是指用DNA连接酶将目的DNA同载体DNA连接起来,形成重组的DNA分子;“转”是指通过特殊的方法将重组的DNA分子送入宿主细胞中进行复制和扩增;“选”则是从宿主群体中挑选出携带有重组DNA分子的个体。最终目的在于通过相应技术手段,将目的基因导入宿主细胞,在宿主细胞内目的基因被大量的复制。
C-sis:是血小板衍生生长因子B链的编码基因。C-sis的基本功能是通过多种机制促使有丝分裂信号向胞内转导并促进细胞增殖。C-sis编码的蛋白血小板衍生生长因子B是一种较强的促有丝分裂源和化学诱导剂,可刺激间胚叶来源细胞的分裂、增殖,对血管的再生及创伤愈合有良好的促进作用。故C-sis具有促进细胞增殖并抑制凋亡,进而促进组织修复的功能。