中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7301-7306.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.001
• 骨及关节损伤动物模型 Animal models of bone and joint injuries • 下一篇
高浓度骨桥蛋白诱导双足直立雌性小鼠脊柱侧凸模型
唐 峰1,谢 宁1,吴 涛2,刘 军2,王彬彬2,王 洋1,徐立璋1
- 1解放军第二军医大学附属长征医院脊柱外科,上海市 200003;2南京医科大学第二附属医院骨科,江苏省南京市 210011
A scoliosis model of bipedal female mouse induced by high-concentration osteopontin
Tang Feng1, Xie Ning1, Wu Tao2, Liu Jun2, Wang Bin-bin2, Wang Yang1, Xu Li-zhang1
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, Shanghai Changzheng Hospital, The Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210011, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。
文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。
.jpg) 文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。
文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。摘要
背景:近年来相关研究证实骨桥蛋白水平增高可能导致特发性脊柱侧凸发生发展。建立合适的青少年特发性脊柱侧凸动物模型对于此类疾病的研究与治疗具有重大意义。
目的:观察高浓度骨桥蛋白诱导双足直立雌性小鼠脊柱侧凸的发生情况,为建立理想的青少年特发性脊柱侧凸药物模型提供依据。
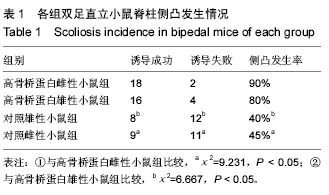
方法:选取同周龄C3H/HeJ小鼠,随机分为高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性小鼠及雄性小鼠各20只,并设立对照雄性小鼠组及对照雌性小鼠组各20只。4组小鼠均于3周龄施行上肢截肢合并鼠尾切除术建立双足直立小鼠模型,术后放置特殊鼠笼诱导直立状态。高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性小鼠组及高浓度骨桥蛋白雄性小鼠组每日腹腔注射高浓度(40 μg/kg)骨桥蛋白,对照组腹腔注射生理盐水,诱导3个月后,行小动物脊柱X射线检查,测量Cobb角大于10°定为侧凸诱导成功,评估侧凸发生率及严重程度。
结果与结论:①高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性小鼠组18只发生脊柱侧凸,Cobb角16°-38°,平均(25.8±6.7)°,高浓度骨桥蛋白雄性小鼠组16只发生脊柱侧凸,Cobb角11°-34°,平均(20.9±6.8)°;对照雄性小鼠组8 只发生脊柱侧凸,Cobb角12°-21°,平均(15.6±3.1)°;对照雌性小鼠组9 只发生脊柱侧凸,Cobb角11°-24°,平均(17.1±4.5)°;②高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性、雄性小鼠组脊柱侧凸发生率均明显高于对照雌性、雄性小鼠组(P < 0.05),而脊柱侧凸发生率在高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性组与雄性组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但其侧凸角度高浓度骨桥蛋白雌性组较高浓度骨桥蛋白雄性组明显加重(P < 0.05);③结果表明,高浓度骨桥蛋白水平诱导的雌性双足直立小鼠其侧凸发生率更高,侧凸严重程度更重,其更贴近于人类特发性脊柱侧凸女性高发的实际情况。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2742-0633(谢宁)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。
文题释义:
青少年特发性脊柱侧凸病因:迄今为止,可能参与其发生发展的病因学研究涉及多个方面:神经系统、代谢系统、骨生长因素、生物力学因素及环境等因素,但其具体发病机制至今未能探明。自从2001年开始研究热点集中于基因、前庭、姿势、本体感觉和生物力学等方面。目前的观点认为,青少年特发性脊柱侧凸是一类多因素共同参与的疾病,涉及多个系统的脊柱生长发育畸形,其病情的进展受到骨骼生长及生物力学等方面的多重影响从而导致侧弯。
骨桥蛋白的作用:骨桥蛋白是一类分泌型多功能糖蛋白,总体呈酸性,其基因在人类定位于人类染色体4。骨桥蛋白基因编码含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列,经表达修饰后可与特异的αvβ5细胞表面整合素蛋白结合,促进细胞间的黏附以及介导细胞增殖、迁移等多种功能。骨桥蛋白还能与CD44、羟基磷灰石等特异性结合,在不同组织发挥重要作用。骨桥蛋白主要富集于骨组织,参与许多骨代谢异常疾病的病理生理过程。