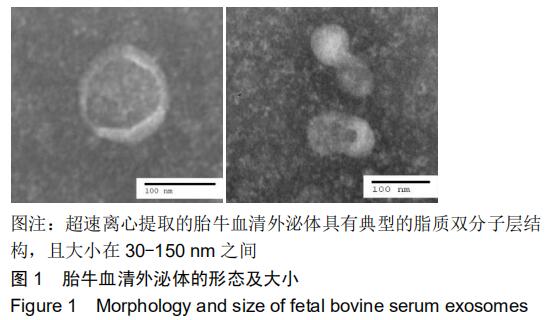
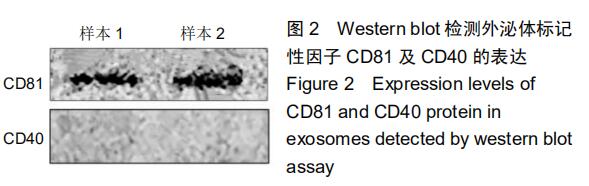
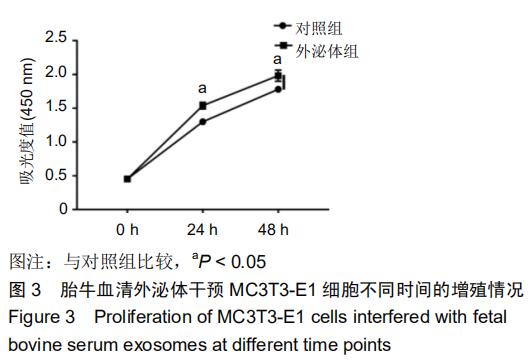
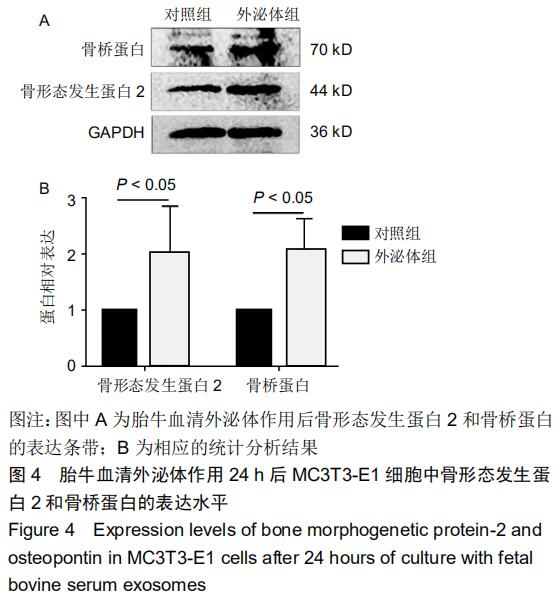
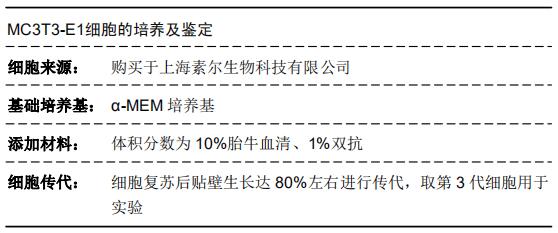
[1] HADJIDAKIS DJ, ANDROULAKIS II. Bone remodeling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1092:385-396.
[2] XIE Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG L, et al. The roles of bone-derived exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in regulating bone remodelling. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(5):1033-1041.
[3] QIN Y, SUN R, WU C, et al. Exosome: A Novel Approach to Stimulate Bone Regeneration through Regulation of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5): E712.
[4] GRAVALLESE EM. Bone Wasn't Built in a Day: Destruction and Formation of Bone in the Rheumatic Diseases. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2017;128:24-43.
[5] COUGHLAN T, DOCKERY F. Osteoporosis and fracture risk in older people. Clin Med (Lond). 2014;14(2):187-191.
[6] DEVINE H, VERINA D. Young Adults with Multiple Myeloma. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2017;33(3):316-331.
[7] WANG T, GUO S, ZHANG H. Synergistic Effects of Controlled-Released BMP-2 and VEGF from nHAC/PLGAs Scaffold on Osteogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3516463.
[8] BAILEY S, KARSENTY G, GUNDBERG C, et al. Osteocalcin and osteopontin influence bone morphology and mechanical properties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2017;1409(1):79-84.
[9] BATAGOV AO, KUROCHKIN IV. Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3'-untranslated regions. Biol Direct. 2013;8:12.
[10] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THÉRY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255-289.
[11] HARDING C, HEUSER J, STAHL P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J Cell Biol. 1983;97(2):329-339.
[12] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983;33(3):967-978.
[13] KHAN FM, SALEH E, ALAWADHI H, et al. Inhibition of exosome release by ketotifen enhances sensitivity of cancer cells to doxorubicin. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(1):25-33.
[14] OH HJ, SHIN Y, CHUNG S, et al. Convective exosome-tracing microfluidics for analysis of cell-non-autonomous neurogenesis. Biomaterials. 2017;112:82-94.
[15] KORITZINSKY EH, STREET JM, STAR RA, et al. Quantification of Exosomes. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(7):1587-1590.
[16] LI X, YANG Z. Regulatory effect of exosome on cell apoptosis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017;42(2):215-220.
[17] HE C, ZHENG S, LUO Y, et al. Exosome Theranostics: Biology and Translational Medicine. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):237-255.
[18] LI W, LI C, ZHOU T, et al. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):145.
[19] LI Y, HAN C, WANG J, et al. Exosomes Mediate the Beneficial Effects of Exercise. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:333-353.
[20] LAI A, KINHAL V, NUZHAT Z, et al. Proteomics Method to Identification of Protein Profiles in Exosomes. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1710:139-153.
[21] MELO SA, MOUTINHO C, ROPERO S, et al. A genetic defect in exportin-5 traps precursor microRNAs in the nucleus of cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(4):303-315.
[22] ZHANG J, LI S, LI L, et al. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13(1):17-24.
[23] POURAKBARI R, KHODADADI M, AGHEBATI-MALEKI A, et al. The potential of exosomes in the therapy of the cartilage and bone complications; emphasis on osteoarthritis. Life Sci. 2019; 236:116861.
[24] CUI Y, LUAN J, LI H, et al. Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote ST2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microRNA expression. FEBS Lett. 2016;590(1): 185-192.
[25] KAWAKUBO A, MATSUNAGA T, ISHIZAKI H, et al. Zinc as an essential trace element in the acceleration of matrix vesicles- mediated mineral deposition. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(12): 1161-1165.
[26] QIN Y, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961.
[27] EITAN E, ZHANG S, WITWER KW, et al. Extracellular vesicle- depleted fetal bovine and human sera have reduced capacity to support cell growth. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26373.
[28] SUNG BH, KETOVA T, HOSHINO D, et al. Directional cell movement through tissues is controlled by exosome secretion. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7164.
[29] SUNG BH, WEAVER AM. Exosome secretion promotes chemotaxis of cancer cells. Cell Adh Migr. 2017;11(2):187-195.
[30] DE GASSART A, GEMINARD C, FEVRIER B, et al. Lipid raft-associated protein sorting in exosomes. Blood. 2003;102(13): 4336-4344.
[31] SKOTLAND T, SANDVIG K, LLORENTE A. Lipids in exosomes: Current knowledge and the way forward. Prog Lipid Res. 2017; 66:30-41.
[32] SU SA, XIE Y, FU Z, et al. Emerging role of exosome-mediated intercellular communication in vascular remodeling. Oncotarget. 2017;8(15):25700-25712.
[33] LU X. The Role of Exosomes and Exosome-derived microRNAs in Atherosclerosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(40):6182-6193.
[34] MILANE L, SINGH A, MATTHEOLABAKIS G, et al. Exosome mediated communication within the tumor microenvironment. J Control Release. 2015;219:278-294.
[35] HELWA I, CAI J, DREWRY MD, et al. A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents. PLoS One. 2017;12(1): e0170628.
[36] INDER KL, RUELCKE JE, PETELIN L, et al. Cavin-1/PTRF alters prostate cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicle content and internalization to attenuate extracellular vesicle-mediated osteoclastogenesis and osteoblast proliferation. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3:23784.
[37] 田笑,金玉翠,马长艳.前列腺癌细胞外泌体抑制成骨细胞分化[J].南京医科大学学报,2019,39(8):1167-1171.
[38] KHUSHMAN M, BHARDWAJ A, PATEL GK, et al. Exosomal Markers (CD63 and CD9) Expression Pattern Using Immunohistochemistry in Resected Malignant and Nonmalignant Pancreatic Specimens. Pancreas. 2017;46(6):782-788.
[39] MUNAGALA R, AQIL F, JEYABALAN J, et al. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016;371(1):48-61.
[40] BENINSON LA, FLESHNER M. Exosomes in fetal bovine serum dampen primary macrophage IL-1β response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) challenge. Immunol Lett. 2015;163(2):187-192.
[41] SHELKE GV, LÄSSER C, GHO YS, et al. Importance of exosome depletion protocols to eliminate functional and RNA-containing extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3:24783.
|