中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (39): 5807-5812.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.39.005
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
椎弓根螺钉固定局部减压与选择性椎间融合修复退变性腰椎侧凸
李 丹1,罗 旭1,杨 俊2
- 1武警湖南省总队医院,湖南省长沙市 410000;2解放军第四二一医院,广东省广州市 510318
Local decompression and selective interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation technique for the treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis
Li Dan1, Luo Xu1, Yang Jun2
- 1Armed Police Corps Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha 410000, Hunan Province, China; 2the 421 Hospital of PLA, Guangzhou 510318, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
退变性脊柱侧凸:指骨骼发育成熟后,因脊柱的退行性变而出现的脊柱侧凸,退变性腰椎侧凸多见于中、老年人,随着人体进入中老年衰退期而伴随着进行性非对称性椎间盘和关节突关节退变从而导致的脊柱代偿性或失代偿性侧凸畸形,其中以退变性胸腰段、腰段脊柱侧凸最为常见。
退变性腰椎侧凸:腰椎退变性病变导致的腰椎冠状位10°以上但小于40°的成角畸形,称之为退变性腰椎侧凸,其在普通人群中的发病率为1.4%-12%。退变性腰椎侧凸的病理基础主要为:腰椎椎间盘的退变、小关节退变和方向的改变、相应节段的椎管形态发生改变、出现椎管狭窄。
摘要
背景:对于严重的退变性腰椎侧凸所引起的腰背痛,保守治疗多数无效,一般需要外科干预手术治疗。修复方式多为对“责任椎”进行减压、坚强固定、选择性椎间植骨融合为主,重新建立腰椎正常曲度和脊柱的平衡及良好的稳定性。
目的:探讨采用椎弓根螺钉固定局部减压与选择性椎间融合修复退变性腰椎侧凸的效果。
方法:回顾性分析2011年1月至2014年1月武警湖南省总队医院收治的57例退变性腰椎侧凸患者,根据患者自身的临床特点,均采用选择性椎间融合、局部减压和椎弓根螺钉置入内固定的修复方案,以影像学分析及Suk标准评价固定、减压、植骨融合情况,日本骨科学会评分评价疗效优良率。
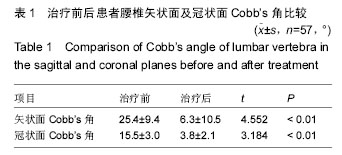
结果与结论:①手术时间157-255 min,平均176 min;出血量480-1 700 mL,平均835 mL;术后引流量140-210 mL,平均155 mL;②57例患者获得12-38个月随访,术后X射线提示,治疗后冠状面Cobb’s角(3.8±2.1)°,侧凸矫正率为54%;治疗后矢状面Cobb’s角(6.3±10.5)°,前凸矫正率为35%。Suk标准评定椎间融合率为95%;根据日本骨科学会腰背痛评分评估末次随访时患者的疗效优良率为91%;③术中硬膜囊破裂引发脑脊液漏2例,神经损伤1例,椎弓根螺钉拔出失败1例,无感染,无血管损伤;④结果说明,结合患者影像学资料与自身临床特点,采用椎弓根螺钉固定局部减压与选择性椎间融合修复退变性腰椎侧凸,可使退变的侧凸腰椎在冠状面和矢状面上均得到不同程度的重建和稳定,修复效果满意。
ORCID: 0000-0003-1523-4750(李丹)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
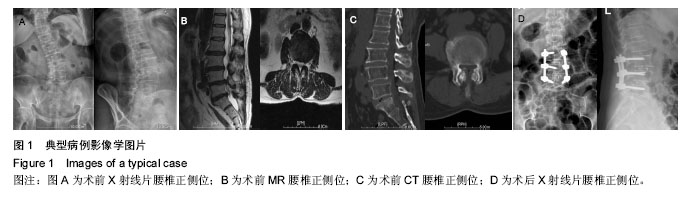
.jpg)