| [1] Su B, O'Connor JP. Nsaid therapy effects on healing of bone, tendon, and the enthesis. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;115(6):892-899.
[2] Mehallo CJ,Drezner JA,Bytomski JR.Practical management: Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (nsaid) use in athletic injuries. Clin J Sport Med. 2006; 16(2):170-174.
[3] Mayer F, Hirschmuller A, Muller S, et al. Effects of short-term treatment strategies over 4 weeks in achilles tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41(7):e6.
[4] Andres BM, Murrell GA. Treatment of tendinopathy: what works, what does not, and what is on the horizon.. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1539-1554.
[5] Fu SC, Hung LK, Shum WT, et al.In vivo low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (lipus) following tendon injury promotes repair during granulation but suppresses decorin and biglycan expression during remodeling. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2010;40(7):422-429.
[6] Lovric V, Ledger M, Goldberg J,et al.The effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on tendon-bone healing in a transosseous-equivalent sheep rotator cuff model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013; 21(2):466-475.
[7] Selfe J, Alexander J, Costello JT, et al. The effect of three different (-135 degrees c) whole body cryotherapy exposure durations on elite rugby league players. PloS one.2014;9(1):e86420.
[8] Hausswirth C, Louis J, Bieuzen F, et al. Effects of whole-body cryotherapy vs. Far-infrared vs. Passive modalities on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in highly-trained runners. PloS one.2011;6(12): e27749.
[9] Ni M, Rui YF, Tan Q,et al.Engineered scaffold-free tendon tissue produced by tendon-derived stem cells. Biomaterials.2013;34(8):2024-2037.
[10] Chen JL,Yin Z,Shen WL, et al. Efficacy of hesc-mscs in knitted silk-collagen scaffold for tendon tissue engineering and their roles.Biomaterials.2010;31(36):9438-9451.
[11] Conze P, van Schie HT, van Weeren R, et al.Effect of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on neovascularization of artificial equine tendon lesions. Regenerative medicine.2014;9(6):743-757.
[12] Geburek F,Mundle K,Conrad S,et al.Tracking of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and histology after intralesional treatment of artificial equine tendon lesions - a pilot study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:21.
[13] Otabe K, Nakahara H, Hasegawa A, et al. Transcription factor mohawk controls tenogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(1):1-8.
[14] Jiang D, Gao P, Zhang Y, et al. Combined effects of engineered tendon matrix and gdf-6 on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-based tendon regeneration. Biotechnology letters.Biotechnol Lett. 2016 ;38(5):885-892.
[15] Huang TF, Yew TL, Chiang ER, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells from a hypoxic culture improve and engraft achilles tendon repair. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(5): 1117-1125.
[16] Moshaverinia A, Xu X, Chen C, et al. Application of stem cells derived from the periodontal ligament or gingival tissue sources for tendon tissue regeneration. Biomaterials.2014;35(9):2642-2650.
[17] Liu H, Zhang C, Zhu S, et al. Mohawk promotes the tenogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the tgfbeta signaling pathway. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio).2015;33(2):443-455.
[18] Liu W, Watson SS, Lan Y, et al.The atypical homeodomain transcription factor mohawk controls tendon morphogenesis.Molecular and cellular biology. 2010;30(20):4797-4807.
[19] Selleri L,Depew MJ,Jacobs Y,et al.Requirement for pbx1 in skeletal patterning and programming chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Development (Cambridge, England).2001;128(18): 3543-3557.
[20] Brendolan A,Ferretti E,Salsi V,et al.A pbx1-dependent genetic and transcriptional network regulates spleen ontogeny.Development (Cambridge, England). 2005; 132(13):3113-3126.
[21] Moens CB,Selleri L.Hox cofactors in vertebrate development. Developmental biology.2006;291(2): 193-206.
[22] van Tuyl M,Liu J, Groenman F, et al. Iroquois genes influence proximo-distal morphogenesis during rat lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290(4):L777-L789.
[23] diIorio P,Alexa K,Choe SK, et al. Tale-family homeodomain proteins regulate endodermal sonic hedgehog expression and pattern the anterior endoderm. Developmental biology.2007;304(1):221-231.
[24] Anderson DM,Beres BJ,Wilson-Rawls J,et al.The homeobox gene mohawk represses transcription by recruiting the sin3a/hdac co-repressor complex. Dev Dyn. 2009;238(3):572-580.
[25] Bilioni A, Craig G, Hill C, et al. Iroquois transcription factors recognize a unique motif to mediate transcriptional repression in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(41):14671-14676.
[26] Anderson DM, Arredondo J, Hahn K, et al. Mohawk is a novel homeobox gene expressed in the developing mouse embryo. Dev Dyn. 2006;235(3):792-801.
[27] Liu H, Liu W, Maltby KM, et al. Identification and developmental expression analysis of a novel homeobox gene closely linked to the mouse twirler mutation. Gene expression patterns: GEP.2006;6(6):632-636.
[28] Chuang HN, Cheng HY, Hsiao KM, et al. The zebrafish homeobox gene irxl1 is required for brain and pharyngeal arch morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 2010; 239(2): 639-650.
[29] Ito Y, Toriuchi N, Yoshitaka T, et al. The mohawk homeobox gene is a critical regulator of tendon differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(23): 10538-10542.
[30] Kimura W, Machii M, Xue X, et al. Irxl1 mutant mice show reduced tendon differentiation and no patterning defects in musculoskeletal system development [J]. Genesis (New York, NY : 2000). 2011;49(1):2-9.
[31] Onizuka N, Ito Y, Inagawa M, et al. The mohawk homeobox transcription factor regulates the differentiation of tendons and volar plates.J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(1):172-180.
[32] Williams EH, McCarthy E, Bickel KD. The histologic anatomy of the volar plate. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23(5):805-810.
[33] Anderson DM, George R, Noyes MB, et al. Characterization of the DNA-binding properties of the mohawk homeobox transcription factor.J Biol Chem. 2012;287(42):35351-35359.
[34] Katzel EB, Wolenski M, Loiselle AE, et al. Impact of smad3 loss of function on scarring and adhesion formation during tendon healing. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(5):684-693.
[35] Berthet E, Chen C, Butcher K, et al. Smad3 binds scleraxis and mohawk and regulates tendon matrix organization. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(9):1475-1483.
[36] Guerquin MJ, Charvet B, Nourissat G,et al. Transcription factor egr1 directs tendon differentiation and promotes tendon repair. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(8): 3564-3576.
[37] Kayama T, Mori M, Ito Y, et al. Gtf2ird1-dependent mohawk (mkx) expression regulates mechanosensing properties of tendon. Mol Cell Biol. 2016;36(8):1297-309.
[38] Guo J,Chan KM,Zhang JF,et al. Tendon-derived stem cells undergo spontaneous tenogenic differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2016;341(1):1-7.
[39] Dunkman AA, Buckley MR, Mienaltowski MJ, et al. The tendon injury response is influenced by decorin and biglycan. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(3):619-630.
[40] Ansorge HL, Hsu JE, Edelstein L, et al.Recapitulation of the achilles tendon mechanical properties during neonatal development: A study of differential healing during two stages of development in a mouse model. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(3):448-456.
[41] Alberton P, Dex S, Popov C, et al. Loss of tenomodulin results in reduced self-renewal and augmented senescence of tendon stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(5):597-609.
[42] Lee JY, Zhou Z, Taub PJ, et al. Bmp-12 treatment of adult mesenchymal stem cells in vitro augments tendon-like tissue formation and defect repair in vivo. PloS one.2011;6(3):e17531.
[43] Violini S, Ramelli P, Pisani LF, et al. Horse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells express embryo stem cell markers and show the ability for tenogenic differentiation by in vitro exposure to bmp-12. BMC Cell Biol. 2009;10:29.
[44] Shen H,Gelberman RH,Silva MJ,et al.Bmp12 induces tenogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. PloS one.2013;8(10):e77613.
[45] Mohanty N, Gulati BR, Kumar R, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization and tenogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from equine umbilical cord blood. In vitro cellular & developmental biology Animal, 2014;50(6):538-548.
[46] Dong Y, Zhang Q, Li Y, et al. Enhancement of tendon-bone healing for anterior cruciate ligament (acl) reconstruction using bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells infected with bmp-2. nt J Mol Sci.2012;13(10):13605-13620.
[47] Schwarting T, Schenk D, Frink M, et al.Stimulation with bone morphogenetic protein-2 (bmp-2) enhances bone-tendon integration in vitro. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(2):99-112.
[48] Branford OA, Klass BR, Grobbelaar AO, et al.The growth factors involved in flexor tendon repair and adhesion formation.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014;39(1): 60-70.
[49] Qiu Y,Wang X,Zhang Y,et al.Development of a refined tenocyte differentiation culture technique for tendon tissue engineering. Cells tissues organs.2013;197(1):27-36.
[50] Farhat YM, Al-Maliki AA, Chen T, et al. Gene expression analysis of the pleiotropic effects of tgf-beta1 in an in vitro model of flexor tendon healing. PloS one.2012;7(12):e51411.
[51] Shinkai Y, Tachibana M. H3k9 methyltransferase g9a and the related molecule glp. Genes Dev.2011;25(8): 781-788.
[52] Tachibana M,Sugimoto K,Nozaki M, et al. G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone h3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev.2002; 16(14):1779-1791.
[53] Tachibana M, Ueda J, Fukuda M, et al. Histone methyltransferases g9a and glp form heteromeric complexes and are both crucial for methylation of euchromatin at h3-k9. Genes Dev. 2005;19(7):815--826.
[54] Tachibana M,Nozaki M,Takeda N,et al.Functional dynamics of h3k9 methylation during meiotic prophase progression. EMBO J. 2007;26(14):3346-3359.
[55] Wada S,Ideno H,Shimada A,et al.H3k9mtase g9a is essential for the differentiation and growth of tenocytes in vitro. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015;144(1):13-20. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。
文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。.jpg) 文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。
文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。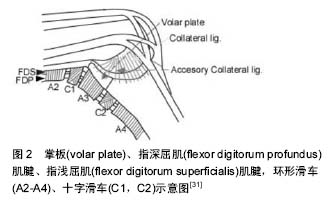
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。
文题释义:
Mkx(Mohawk):又被称为Irxl,是三氨基环酸超家族的成员之一。Mkx是肌腱发育过程中肌腱细胞所表达的非典型的同源异型盒基因,在许多组织器官发育过程中都是必要的,包括细胞的增殖、分化等过程。Mkx具有转录抑制活性,且包括了3个小阻遏域。Mkx作为一个转录抑制因子,是通过招募Sin3A / DHAC抑制复合物而发挥作用的。
掌板:也叫掌侧韧带,为一长方形的致密纤维软骨板,位于掌指关节及指间关节掌侧。其中掌指关节掌板其远端厚而坚韧,附于近节指骨底掌唇,近端薄而松弛,呈膜状附于掌骨颈掌侧,并与深筋膜交织,两侧与侧副韧带相连。远侧指间关节的掌板为远侧指间关节掌侧一长方形质地坚韧的致密纤维软骨扳,远端厚而坚韧。坚固地附于远节指骨底掌倒唇,构成关节囊的掌面,同时也构成屈肌腱的底面,近端薄而松弛为膜样结构,并与骨膜相延续。