| [1] Bao Y,Hu M,Gao G,et al.Multivariate analysis for pelvic floor dysfunction.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2015;40(11):1229-1233.
[2] Ma X, Shang S, Xie B,et al.Study on morphological characteristics of uterosacral and cardinal ligament in patients with severe pelvic organ prolapse based on MRI.Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi.2015;50(9): 668-672.
[3] Wang Y,Han J,Zhang K,et al.Relevance between expectations before treatment, new symptoms and satisfaction after treatment in patients with pelvic organ prolapse.Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2015;50(9): 664-667.
[4] Fitchett JR,Bhatta S,Sherpa TY,et al.Non-surgical interventions for pelvic organ prolapse in rural Nepal: a prospective monitoring and evaluation study.JRSM Open.2015;6(12):2054270415608117.
[5] Chapple CR,Osman NI,Mangera A,et al.Application of Tissue Engineering to Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Stress Urinary Incontinence.Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2015;7(2):63-70.
[6] 李红,刘晓玲,程琳.更年期女性压力性尿失禁的流行病学调查和影响因素分析[J].中国妇幼保健, 2015,30(29): 5049-5051.
[7] 孟文彬,宋静慧,杨有莲.盆底功能障碍性疾病的研究进展[J].国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志,2016,35(1):1-5.
[8] Berrocal J,Clavé H,Casson M,et al.Conceptual advances in the surgical management of genital prolapse.The TVM technique emergence.J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod.2004;33:577-587.
[9] 李怀芳,童晓文.聚丙烯网片在女性全盆底功能重建中的应用[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2007,23(8):602-604.
[10] Kim T,Sridharan I,Ma Y,et al.Identifying distinct nanoscopic features of native collagen fibrils towards early diagnosis of pelvic organ prolapse. Nanomedicine. 2015.pii: S1549-9634(15)00213-0.
[11] Chang TC,Hsiao SM,Chen CH,et al.Clinical Outcomes and Urodynamic Effects of Tailored Transvaginal Mesh Surgery for Pelvic Organ Prolapse.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:191258.
[12] Gomelsky A.Commentary on "Pain Scores and Exposure Rates after Polypropylene Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse".South Med J.2015;108(12):722-723.
[13] Illston JD,Garris JB,Richter HE,et al.Pain Scores and Exposure Rates after Polypropylene Mesh for Pelvic Organ Prolapse.South Med J.2015;108(12):715-721.
[14] Eser A, Unlubilgin E, Hizli F, et al.Is There a Relationship Between Pelvic Organ Prolapse and Tissue Fibrillin-1 Levels? Int Neurourol J. 2015;19(3): 164-170.
[15] 姜卫国,洪淑惠.女性盆底功能障碍性疾病的诊治进展[J].山东医药,2015,45:26-29.
[16] 鞠慧影.女性盆底功能障碍性疾病采用盆底肌肉训练的康复效果观察[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(31):45-46.
[17] 刘丽,滕惠芳.早期盆底康复治疗对产后盆底功能障碍的疗效分析[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2015,37(9):1091- 1093.
[18] 张晋,李辉,白枫,等.产后盆底肌肉生物反馈训练加电刺激治疗临床观察[J].中国计划生育学杂志, 2015,23(11): 773-774.
[19] 徐扬,刘娟,左玲,等.生物反馈电刺激治疗对不同分娩方式产后盆底功能障碍的效果[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2015, 19(21):119-120.
[20] 李孝红,袁红梅,徐世琴,等.右美托咪定用于盆腔器官脱垂老年患者盆底重建术的麻醉效果[J].中国药房, 2015, 26(33):4626-4628.
[21] 李宝恒,黄惠娟,宋岩峰.Avaulta盆底重建术治疗重度盆腔器官脱垂的疗效及对患者生活质量的影响[J].中国妇产科临床杂志,2015,16(6):512-515.
[22] 高桂香,王鲁文,刘冬霞,等.盆底重建术临床疗效及术后网片侵蚀暴露相关因素研究[J].现代妇产科进展, 2015, 27(11):844-847.
[23] 李琦,王建六.生物源性补片在女性盆底重建外科中的应用与研究进展[J].中国妇产科临床杂志, 2013,14(2): 182-185.
[24] Peppas G,Gkegkes ID,Makris MC,et al.Biological mesh in hernia repair, abdominal wall defects, and reconstruction and treatment of pelvic organ prolapse:A Review of the Clinical Evidence.Am Surg. 2010;76(11):1290-1299.
[25] Reid RI.A Comparative Analysis of Biomaterials Currently Used in Pelvic Reconstruc tive Surgery[M]//von Theobold P,Zimmerman CW,Davila GW. New Techniques in Genital Prolapse Surgery.London: Springer London Ltd, 2011:105-133.
[26] Valentin JE,Turner NJ,Gilbert TW,et al.Functional skeletal muscle formation with a biologic scaffold.Biomaterials.2010;31(29):7475-7484.
[27] Yuteri-Kaplan LA,Gutman RE.The use of biological materials in urogynecologic reconstruction:a systematic review.Plast Reconstr Surg.2012;130 (5 Suppl 2):242S-253S.
[28] Min H,Li H,Bingshu L,et al.Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of the application of adjuvant material in the repair of anterior vaginal wall prolapsed. Arch Gynecol Obstet.2013;287(5):919-936.
[29] Feldner PC,Castro RA,Cipolotti LA,et al. Anterior vaginal wall prolapse:a randomized controlled trial of SIS graft versus traditional colporrhaphy.Int Urogynecol J.2010;21(9):1057-1063.
[30] Reid RI,Luo K.Site -specific prolapse surgery. II. Vaginal paravaginal repair augmented with either synthetic mesh or remodelling xenograft.Int Urogynecol J.2011;22(5):601-609.
[31] Armitage S,Seman EI,Keirse MJ.Use of surgisis for treatment of anterior and posterior vaginal prolapse.Obstet Gynecol Int.2012;2012:376251.
[32] Dahlgren E,Kjalhede P, PROP-PELVICOL Study Group. Long-termoutcome of porcine skin graft in surgical treatment of recurrent pelvic organ prolapse. An open randomized controlled multicenter study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand.2011;90(12):1393-1401.
[33] 孙秀丽,杨欣,耿京,等.猪小肠黏膜下层生物补片在盆腔器官脱垂手术治疗中应用的初步观察[J].中华妇产科杂志, 2013,48(8):575-578.
[34] Liu L,Li D,Wang Y,et al. Evaluation of the biocompatibility and mechanical properties of xenogeneic (porcine) extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffold for pelvic reconstruction. Int Urogynecol J. 2011;22(2):221-227.
[35] Mouritsen L,Kronschnabl M,Lose G.Long-term results of vaginal repairs with and without xenograft reinforcement. Int Urogynecol J.2010;21(4):467-473.
[36] Nieuwoudt A,Jeffery S.Anatomical and functional outcomes of a subintestinal submucosa (surgisis) graft to augment anterior repair: a prospective observational study.Int Urogynecol J.2011;22(12):1541-1542.
[37] Maher C,Feiner B,Baessler K,et al.Surgical management of pelvic organ prolapse in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;4: CD004014.
[38] Balaklava SF.Decellularized allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue as a bioscaffold for regenerative medicine:factors that influence the host response.Ann Biomed Eng.2014;42(7):1517-1527.
[39] Orenstein SB,Qiao Y,Klueh U,et al. Activation of human mononuclear cells by porcine biologic meshes in vitro.Hernia.2010;14(4):401-407.
[40] Vandevord PJ,Broadrick KM,Krishnamurthy B,et al.A comparative study evaluating the in vivo incorporation of biological sling materials.Urology. 2010;75(5): 1228-1233.
[41] Sicari BM,Johnson SA,Siu BF,et al.The effect of source animal age upon the in vivo remodeling characteristics of an extracellular matrix scaffold.Biomaterials. 2012; 33(22):5524-5533. |
.jpg)
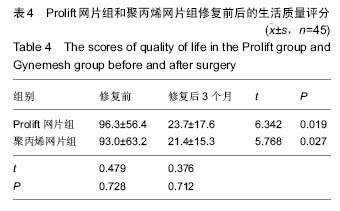
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)