中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 957-961.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.06.024
• 膜生物材料 membrane biomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
正确测量成年男性腹股沟后壁裁剪合适的补片修复腹股沟疝
涂志强,王卫星
- 武汉大学人民医院普外科,湖北省武汉市 430060
Correct measurement of the posterior wall size of adult male inguinal hernia used for herniorrhaphy
Tu Zhi-qiang, Wang Wei-xing
- Department of General Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
无张力疝修补术:美国医师Lichtenstein首先于1986年提出无张力疝修补术的概念。这种修补以人工生物材料作为补片用以加强腹股沟管的后壁,此法克服了传统手术(即不用补片的缝合修补法)对正常组织解剖结构的干扰,层次分明,而且修补后周围组织无张力,故命名为“无张力疝修补术”。目前常用的有平片式无张力疝修补术和疝环充填式无张力疝修补术。
医用聚丙烯编织材料:分为多丝聚丙烯(SURGICAL)、双丝聚丙烯(PROLEN)、单丝聚丙烯(MARLEX)等。材料中丝的结构对网片特性有影响(编织网丝越多,补片柔软性越好,然而感染的机会越大)。Rutkow术所用的圆锥形网塞为多丝聚丙烯,补片为单丝聚丙烯,具有良好的组织相容性及较大的抗张力强度,为目前最为适宜的疝修补材料,但它皱缩的性质,给临床应用带来较多问题,为降低该性质带来的不良影响,需适当加大补片的尺寸和术中固定补片。
背景:目前国内行疝补片手术,一般根据经验裁剪补片大小,缺乏可靠的依据。
目的:通过Rutkow术中测量中国籍成年男性人群腹股沟后壁大小,根据测量结果进行补片裁剪,对治疗效果进行评价。
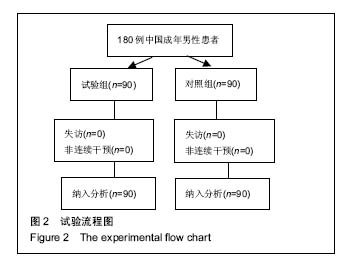
方法:精细测量180例行无张力疝修补术的中国籍成年男性患者的腹股沟后壁大小,计算出适合中国成年男性腹股沟组织解剖结构的补片尺寸数据,并将180例患者随机分为2组,每组90例,试验组测量腹股沟后壁大小后进行补片裁剪的Rutkow术,对照组根据经验进行补片裁剪的Rutkow术,比较两组患者各项临床指标以及并发症发生率和复发率。
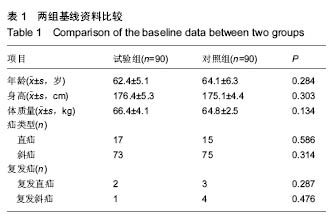
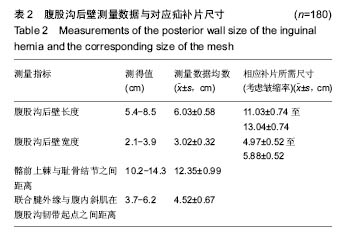
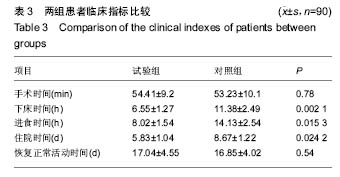
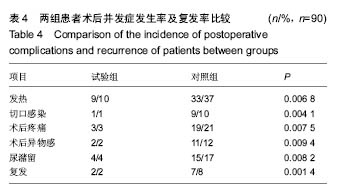
结果与结论:①耻骨结节与腹内斜肌在腹股沟韧带起点之间距离为(6.03±0.58) cm;弓状下缘的最高点至腹股沟韧带的垂直距离为(3.02±0.32) cm,相应补片尺寸长度应当大于(13.04±0.74) cm,宽度应当大于(5.88±0.52) cm;②试验组下床活动时间、进食时间、住院时间均小于对照组(P < 0.05);两组手术时间、恢复正常活动时间比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③试验组术后并发症发生率及复发率明显低于对照组(P < 0.01);④结果表明,测量腹股沟后壁大小后进行补片裁剪的Rutkow术用于腹股沟疝修补,效果明显,并发症和复发率低。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)