| [1] Barkagan M, Steinvil A, Berchenko Y,et al.Impact of routine manual aspiration thrombectomy on outcomes of patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction: A meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol. 2015;204:189-195.
[2] Barchielli A, Profili F, Balzi D,et al.Trends in occurrence, treatment, and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction in Tuscany Region (Central Italy), 1997-2010.Epidemiol Prev. 2015;39(3): 167-175.
[3] Dai G, Xu Q, Luo R, et al.Atorvastatin treatment improves effects of implanted mesenchymal stem cells: meta-analysis of animal models with acute myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015;15(1):170.
[4] Bajaj NS, Kalra R, Aggarwal H,et al.Comparison of Approaches to Revascularization in Patients With Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease Presenting With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Meta-analyses of Randomized Control Trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4(12).pii: e002540.
[5] Hu X, Huang H, Yin Y,et al.Who is the culprit for the patient with acute myocardial infarction, plaque rupture or essential thrombocytosis? Int J Cardiol. 2015;204: 175-176.
[6] Wu H, Qian J, Wang Q, et al.Thrombin induced platelet-fibrin clot strength measured by thrombelastography is a novel marker of platelet activation in acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2014;172(1):e24-25.
[7] Tosenberger A, Ataullakhanov F, Bessonov N, et al. Modelling of platelet-fibrin clot formation in flow with a DPD-PDE method.J Math Biol. 2015.
[8] Swieringa F, Kuijpers MJ, Lamers MM, et al. Rate-limiting roles of the tenase complex of factors VIII and IX in platelet procoagulant activity and formation of platelet-fibrin thrombi under flow. Haematologica. 2015; 100(6):748-756.
[9] Ninivaggi M, Feijge MA, Baaten CC,et al. Additive roles of platelets and fibrinogen in whole-blood fibrin clot formation upon dilution as assessed by thromboelastometry. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(3): 447-457.
[10] Kavitha S, John F, Indira M.Amelioration of inflammation by phenolic rich methanolic extract of Ocimum sanctum Linn. leaves in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarction.Indian J Exp Biol. 2015;53(10):632-640.
[11] Kasiman K, Lundholm C, Sandin S,et al.Common Familial Effects on Ischemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction: A Prospective Population-Based Cohort Study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2014;1:3.
[12] Oliveira GB, Avezum A, Roever L. Cardiovascular Disease Burden: Evolving Knowledge of Risk Factors in Myocardial Infarction and Stroke through Population-Based Research and Perspectives in Global Prevention.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015;2:32.
[13] 于晓羽,代倩,程淑群,等. 溶栓前肝素治疗对急性心肌梗死溶栓疗效的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014, 14(3):277-286.
[14] 王云飞,华琦,李静. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死溶栓治疗的疗效与安全性[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2013,11(4): 47-51.
[15] 吕俊远,王磊,李晰,等. 胺碘酮治疗急性心肌梗死溶栓术后再灌注心律失常的Meta分析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2013,13(9):1110-1115.
[16] 赵志青. 心肌梗死后的组织修复与治疗[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2014,22(4):304-311.
[17] 郑博,王新刚,龚艳君,等. 直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术前负荷剂量阿托伐他汀治疗对急性心肌梗死患者近期预后的影响[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志,2013,21(1):41-45.
[18] 罗莘. 急诊介入治疗合并院前心脏骤停急性心肌梗死临床疗效分析[J]. 当代医学,2013,19(7):61-63.
[19] 王宁,王贵松,于海奕,等. 远隔缺血后适应在急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术中的心肌保护作用[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2014,46(6):838-843.
[20] 牛兆倬. 左西孟旦对心功能低下的冠脉搭桥术患者肾脏保护作用的临床研究[D].山东大学,2014.
[21] 陈庆伟. 急诊冠状动脉搭桥术在急性心肌梗死治疗中的临床作用探讨[J]. 中国民康医学,2014,26(24):64-65.
[22] 高峰. 术前NLR与急性心肌梗死后行冠脉搭桥术患者围术期结果相关性研究[D].河北大学,2014.
[23] Jeong YH, Bliden KP, Shuldiner AR,et al. Thrombin-induced platelet-fibrin clot strength: relation to high on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity, genotype, and post-percutaneous coronary intervention outcomes. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(4):713-724.
[24] 李琦. 富血小板纤维蛋白对牙周膜前体细胞成骨分化的影响及机制研究[D].吉林大学,2013.
[25] Chen TM, Tzeng YS, Tsai JC, et al.Single-donor allogeneic platelet fibrin glue and osteoconductive scaffold in orbital floor fracture reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2013;70(3):370-374.
[26] White NJ, Martin EJ, Brophy DF,et al.Examining platelet-fibrin interactions during traumatic shock in a swine model using platelet contractile force and clot elastic modulus.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2011;22(5):379-387.
[27] 杨世茂,王明国,李静,等. 富血小板纤维蛋白与富血小板血浆体外释放生长因子的比较及其对脂肪干细胞增殖分化的影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2012,30(6):641-644.
[28] 冯玉华,董静,卢蕾,等. 富血小板纤维蛋白诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向许旺细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(49):9157-9161.
[29] Gurbel PA, Bliden KP, Navickas IA,et al.Adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet-fibrin clot strength: a new thrombelastographic indicator of long-term poststenting ischemic events.Am Heart J. 2010;160(2):346-354.
[30] 孙英华,王稚英. 富血小板纤维蛋白凝胶和膜显微与超微结构研究[J]. 中国医学工程,2011,19(7):65-67.
[31] 陈诚,李淑慧,张文丽,等. 富血小板纤维蛋白释放转化生长因子β1对骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(45):7233-7238.
[32] 雍志军. 自体富血小板纤维蛋白(PRF)修复兔膝关节软骨全层缺损的实验研究[D].第四军医大学,2014.
[33] Sugita C, Yamashita A, Moriguchi-Goto S,et al.Factor VIII contributes to platelet-fibrin thrombus formation via thrombin generation under low shear conditions. Thromb Res. 2009;124(5):601-607.
[34] 刘南霞.富血小板纤维蛋白对牙髓组织再生性影响的研究[D].第四军医大学,2013.
[35] 许丰伟,柳忠豪. Choukroun富血小板纤维蛋白在口腔种植骨缺损中的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(4):741-744.
[36] Chimenti I, Smith RR, Li TS, et al. Relative roles of direct regeneration versus paracrine effects of human cardiosphere-derived cells transplanted into infarcted mice. Circ Res. 2010;106(5):971-980.
[37] Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992;359 (6398):843-845.
[38] Yan L, Zhu TB, Wang LS, et al. Inhibitory effect of hepatocyte growth factor on cardiomyocytes apoptosis is partly related to reduced calcium sensing receptor expression during a model of simulated ischemia/ reperfusion. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(4):2695-2701.
[39] Angoulvant D, Ivanes F, Ferrera R,et al. Mesenchymal stem cell conditioned media attenuates in vitro and ex vivo myocardial reperfusion injury. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010;30(1):95-102. |
.jpg)

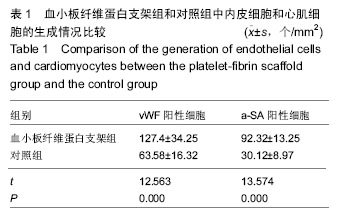
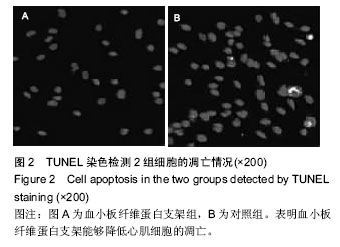

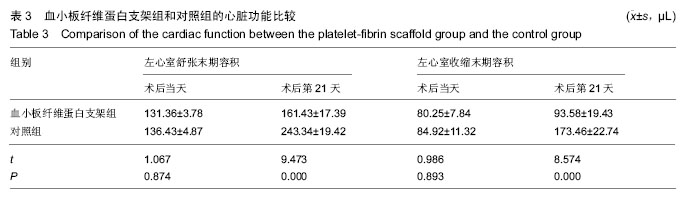
.jpg)
.jpg)