中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 980-984.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.06.028
• 生物材料临床实践 clinical practice of biomaterials • 上一篇
膨体聚四氟乙烯假体隆鼻整形的效果:随机对照临床试验方案
李建民
- 青海大学附属医院耳鼻喉科,青海省西宁市 810001
Effect of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene prosthesis in rhinoplasty: study protocol for a randomized controlled clinical trial
Li Jian-min
- Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Qinghai University Affiliated Hospital, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
膨体聚四氟乙烯:膨体聚四氟乙烯是一种新型的医用高分子材料,由四氟乙烯树脂经拉伸等特殊加工方法制成。白色,富有弹性和柔韧性,具有微细纤维连接而形成的网状结构,这些微细纤维形成无数细孔,使膨体聚四氟乙烯可任意弯曲超过360°,血液相容性好,耐生物老化,用于制造人造血管、心脏补片等医用制品。
生物相容性:生物相容性是指材料与生物体之间相互作用后产生的各种生物、物理、化学等反应的一种概念,就是材料植入人体后与人体相容程度,也就是说是否会对人体组织造成毒害作用。
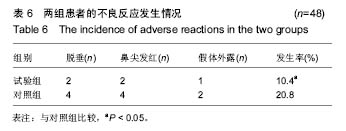
背景:在隆鼻整形术中,当前使用较多的材料有肋软骨、耳软骨、造牙材料、固体硅胶软组织等,但在长期的临床实践中,术后排斥反应、假体下移、鼻梁假体表面皮肤发红等不良反应发生率较高,导致效果不甚满意。
目的:探讨聚四氟乙烯假体隆鼻矫正低鼻伴鼻小柱短小的疗效,并进一步验证其生物相容性。
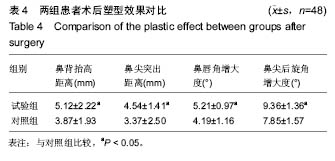
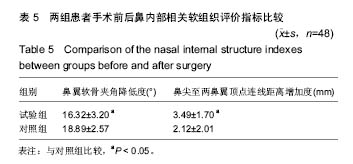
方法/设计:研究为前瞻性、单中心、随机对照、开放性临床试验方案,在中国青海省西宁市,青海大学附属医院完成。选取2014年1月至2015年6月入院的在耳鼻喉科进行隆鼻整形术的患者100例,随机分为试验组和对照组,每组50例。试验组采用聚四氟乙烯假体植入,对照组采用固体硅胶软组织植入,术后随访12个月。主要观察指标为两组患者术后12个月满意度;次要观察指标为术后12个月两组鼻部塑型指标变化情况,两组超声检查显示的鼻内部软组织改变情况以及不良反应发生率。试验经中国青海省西宁市青海大学附属医院伦理委员会批准。研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求。参与者对治疗方案和过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书。
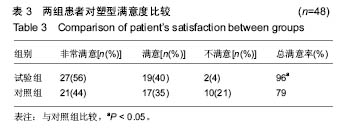
讨论:膨体聚四氟乙烯假体与硅胶假体应用于隆鼻术均具有较高的生物安全性。与硅胶假体比较,膨体聚四氟乙烯假体隆鼻术能有效矫正低鼻伴鼻小柱短小,手术创伤小,术后鼻部外观好,患者满意高,可作为软组织填充材料广泛应用于鼻整形外科。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)