| [1] Bennell KL,Hall M,Hinman RS.Osteoarthritis year in review 2015: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(1):58-70.
[2] Ji JB,Li XF,Liu L,et al.Effect of low intensity pulsed ultrasound on expression of TIMP-2 in serum and expression of mmp-13 in articular cartilage of rabbits with knee osteoarthritis.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015; 8(12):1043-1048.
[3] Seo JG,Moon YW,Cho BC,et al.Is Total Knee Arthroplasty a Viable Treatment Option in Octogenarians with AdvancedOsteoarthritis.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2015;27(4):221-227.
[4] 新苏雅拉图,张虎雄,刘峰,等.老年骨关节炎患者全膝关节置换术后关节功能的影响因素[J].中国老年学杂志,2013, 33(12):2915-2916.
[5] Haase E,Lange T,Lutzner J,et al.Indication for total knee arthroplasty: evidence mapping.Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2015;109(8):605-614.
[6] Bae KC,Cho CH,Lee KJ,et al.Efficacy of intra-articular injection of thrombin-based hemostatic agent in the control of bleeding after primary total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2014;26(4):236-240.
[7] Zanasi S.Innovations in total knee replacement: new trends in operative treatment and changes in peri-operative management.Eur Orthop Traumatol. 2011;2(1-2):21-31.
[8] Shen HL,Li Z,Feng ML,et al.Analysis on hidden blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in treating knee osteoarthritis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(11): 1653-1656.
[9] 周凯,罗雪梅,张焱,等.全膝表明置换术117例患者性别差异及原因分析[J].现代临床医学,2015,41(4): 284-285.
[10] Dy CJ,Lyman S,Boutin-Foster C,et al.Do patient race and sex change surgeon recommendations for TKA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(2):410-417.
[11] 张生海,付立明,马兆吉,等.全膝关节置换前后老年骨关节炎患者关节功能评估及影响因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(4):499-503.
[12] 白国玺,徐小会,段永宏,等.全膝关节置换术治疗晚期类风湿性关节炎的早期临床随访研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(35):6926-6930.
[13] Craik JD,El Shafie SA,Singh VK,et al.Revision of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty versus primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(4): 592-594.
[14] Mook WR,Petri M,Greenspoon JA,et al.The Comprehensive Arthroscopic Management Procedure for Treatment of Glenohumeral Osteoarthritis. Arthrosc Tech. 2015;4(5):e435-441.
[15] Riis A,Rathleff MS,Jensen MB,et al.Low grading of the severity of knee osteoarthritis pre-operatively is associated with a lower functional level after total knee replacement: a prospective cohort study with 12 months' follow-up. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(11): 1498-1502.
[16] Zhang Q,Guo W,Liu Z,et al.Minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of osteonecrosis versusosteoarthritis: a matched-pair comparison.Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(2):333-339.
[17] Kuijer PP,Kievit AJ,Verbeek JH,et al.Knee joint replacement and individual susceptibility for progression of knee osteoarthritis and tibial cartilage volume loss: not only genes run in the family.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(10): 1817-1818.
[18] 李玉安,谷长跃,王佳音,等.膝关节置换术及假体的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(6):1462-1464.
[19] 张启栋,郭万首,刘朝晖,等.内翻畸形膝骨关节炎软骨磨损的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(23): 2345-2350.
[20] Jevsevar D,Donnelly P,Brown GA,et al. Viscosupplementation for Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Systematic Review of the Evidence.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(24):2047-2060.
[21] 沈彬,裴福兴.膝关节骨关节炎诊治进展[J].现代临床医学, 2013,39(5):390-394.
[22] 叶一林,柴卫兵,卢宏章,等.伴有关节外畸形的膝骨关节炎行全膝关节置换术的治疗体会[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2014,7(5):399-403.
[23] Parratte S,Ollivier M,Opsomer G,et al.Is knee function better with contemporary modular bicompartmental arthroplasty compared tototal knee arthroplasty? Short-term outcomes of a prospective matched study including 68 cases.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(5):547-552.
[24] Kim YH,Park JW,Kim JS,et al.Long-Term Clinical Outcomes and Survivorship of Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty with Use of a Constrained Condylar Knee Prosthesis.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(10): 1804-1809.
[25] Arirachakaran A,Choowit P,Putananon C,et al.Is unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) superior to total knee arthroplasty (TKA)? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(5):799-806.
[26] 司枫.老年膝关节骨关节炎应用全膝关节置换术疗效观察[J].包头医学院学报,2013,29(5):47-49.
[27] 胡三莲,丁佳凤,许鑫,等.全膝关节置换术后患者居家康复锻炼效果的影响因素分析[J].护士进修杂志,2012, 27(10): 919-921.
[28] 张冠英.全膝置换术治疗老年骨关节炎(OA)的疗效及其影响因素[J].中外医疗,2013,32(10):61-62.
[29] Nagai K,Muratsu H,Matsumoto T,et al.Influence of intra-operative parameters on postoperative early recovery of active knee flexion in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2013;37(11): 2153-2157.
[30] Kerkhoffs GM,Servien E,Dunn W,et al.The influence of obesity on the complication rate and outcome of total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis and systematic literature review.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(20): 1839-1844.
[31] Lee SY,Bae JH,Kim JG,et al.The influence of surgical factors on dislocation of the meniscal bearing after Oxford medial unicompartmental knee replacement: a case-control study.Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B(7): 914-922.
[32] Chang CB,Kim TK,Kang YG,et al.Prevalence of osteoporosis in female patients with advanced knee osteoarthritis undergoing total knee arthroplasty.J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29(10):1425-1431.
[33] Nemes S,Rolfson O,W-Dahl A,et al.Historical view and future demand for knee arthroplasty in Sweden.Acta Orthop. 2015;86(4):426-431.
[34] Burnett RS, Barrack RL.Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty is currently of no proven clinical benefit: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1): 264-276.
[35] Huang Z,Ma J,Shen B,et al.General anesthesia: to catheterize or not? A prospective randomized controlled study of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(3):502-506.
[36] 侯来永,王廉,谢欲晓,等.全膝关节置换术后个性化系统康复的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2008,23(8): 707-710.
[37] Oberbek J,Synder M.Impact of Body Mass Index (BMI) on Early Outcomes of Total Knee Arthroplasty. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2015;17(2):127-134.
[38] Mackie A,Muthumayandi K,Shirley M,et al.Association between body mass index change and outcome in the first year after total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(2):206-209.
[39] Dusad A,Pedro S,Mikuls TR,et al.Impact of Total Knee Arthroplasty as Assessed Using Patient-Reported Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life Indices: Rheumatoid Arthritis Versus Osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(9):2503-2511.
[40] Bae DK,Song SJ,Yoon KH,et al.Comparative study of tibial posterior slope angle following cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty using one of three implants. Int Orthop. 2012;36(4):755-760. |
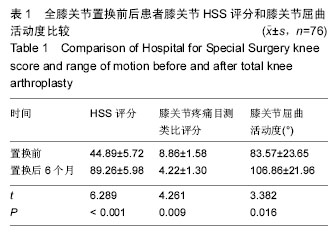
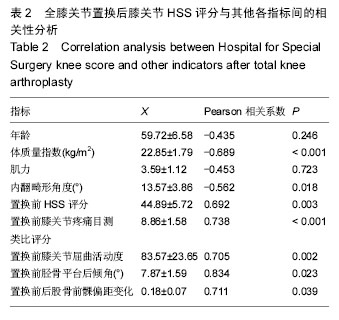
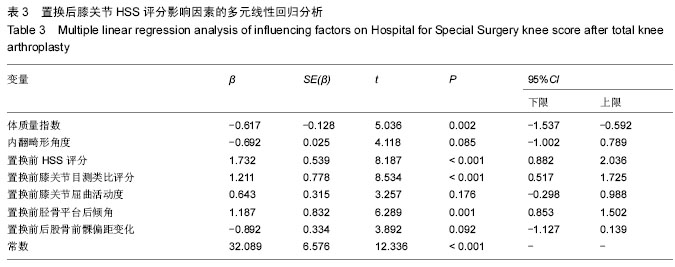
.jpg)
.jpg)