中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (24): 3555-3561.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.24.009
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
多西紫杉醇与骨髓间充质干细胞联合干预对人肝癌细胞株SMMC-7721的影响
李京云1,焦 婷2
- 河北大学附属医院,1放疗科,2肿瘤内科,河北省保定市 071000
Combined use of docetaxel and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721
Li Jing-yun1, Jiao Ting2
- 1Department of Radiotherap, 2Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。
文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。
文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。摘要
背景:多西紫杉醇为细胞周期特异性抗肿瘤药,单药抗肿瘤具有较好的缓解率,但对于化疗相对不敏感的肿瘤,多西紫杉醇单一化疗有效率较低。研究报道,利用骨髓间充质干细胞可以提高靶向药物局部富集肿瘤的能力。
目的:验证多西紫杉醇及骨髓间充质干细胞联合干预人肝癌细胞株SMMC-7721的作用。
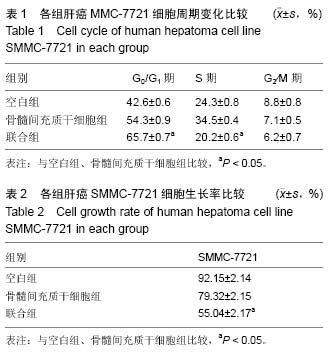
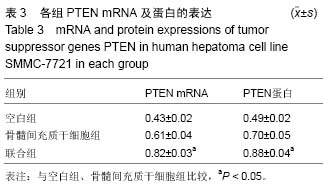
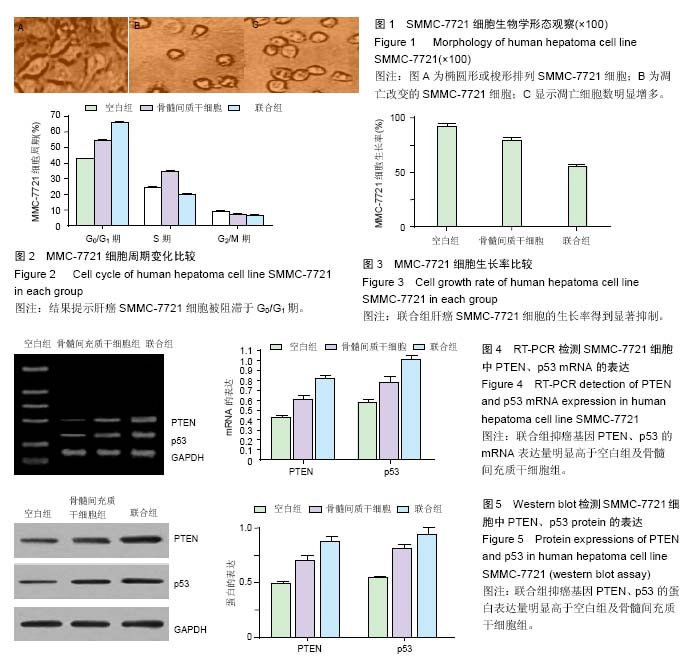
方法:体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞,选取对数生长的SMMC-7721肝癌细胞,将其随机分为空白组,骨髓间充质干细胞组及联合组(多西紫杉醇与骨髓间充质干细胞联合)。采用流式细胞技术检测肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的周期变化;利用MTT法检测肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的生长率;采用聚合酶链法及免疫印迹法检测抑癌基因PTEN、p53的mRNA及蛋白表达情况。
结果与结论:①流式细胞技术检测显示:多西紫杉醇及骨髓间充质干细胞联合干预可以抑制肝癌SMMC-7721细胞增殖,与空白组比较,骨髓间充质干细胞组及联合组处于G0/G1期的细胞明显增多;②MTT检测显示:干预48 h后,与空白组比较,骨髓间充质干细胞组肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的生长率得到抑制,与骨髓间充质干细胞组比较,联合组肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的生长率得到显著抑制(P < 0.05);③RT-PCR检测显示:抑癌基因PTEN、p53的mRNA表达量在联合组明显高于空白组及骨髓间充质干细胞组;④Western blot检测显示:与其他2组比较,联合组明显上调抑癌基因PTEN、p53的蛋白表达量(P < 0.05);⑤结果提示,骨髓间充质干细胞能够抑制体外培养的肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的生长,联合多西紫杉醇干预后,肝癌SMMC-7721细胞的生长率可以得到显著抑制。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-0042-1705(李京云)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。
文题释义:
多西紫杉醇:是以紫杉树中的化学物质为基础而合成出来的一种药物。药物作用机制与紫杉醇相似,即抑制微管的解聚,抑制细胞分裂。适用于局部晚期非小细胞性肺癌或转移性乳腺癌的治疗。
间充质干细胞:是干细胞家族的重要成员,来源于发育早期的中胚层和外胚层,属于多能干细胞,间充质干细胞最初在骨髓中发现,因其具有多向分化潜能、造血支持和促进干细胞植入、免疫调控和自我复制等特点而日益受到人们的关注。