| [1] Carter CW, Hoellwarth J, Weiss JM. Clinical outcomes as a function of meniscal stability in the discoid meniscus: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32(1):9-14.
[2] Ahn JH, Lee SH, Yoo JC, et al. Bilateral discoid lateral meniscus in knees:evaluation of the contralateral knee in patients with symptomatic discoid lateral meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2010; 26(10): 1348-1356.
[3] Patel NM, Cody SR, Ganley TJ. Symptomatic bilateral discoid menisci in children: A comparison with unilaterally symptomatic patients. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32(1):5-8.
[4] Ahn JH, Lee SH, Yoo JC, et al. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy with repair of the peripheral tear for symptomatic discoid lateral meniscus in children: Results of minimum 2 years of follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24(8):888-898.
[5] Bin SI, Jeong SI, Kim JM, et al. Arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for horizontal tear of discoid lateral meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2002; 10(1):20-24.
[6] Kato Y, Oshida M, Aizawa S, et al. Discoid lateral menisci in Japanese cadaver knees. Mod Rheumatol. 2004; 14(2):154-159.
[7] Lee CH, Song IS, Jang SW, et al. Results of arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for lateral discoid meniscus tears associated with new technique. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25(1):30-35.
[8] Jochymek J, Peterková T.Long-Term outcomes of surgical management of symptomatic fibular discoid meniscus in childhood. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015; 82(5):353-357.
[9] Ahn JH, Kim KI, Wang JH, et al. Long-term results of arthroscopic reshaping for symptomatic discoid lateral meniscus in children. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31(5): 867-873.
[10] Chedal-Bornu B, Morin V, Saragaglia D.Meniscoplasty for lateral discoid meniscus tears: Long-term results of 14 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2015; 101(6): 699-702.
[11] Carter CW, Hoellwarth J, Weiss JM. Clinical outcomes as a function of meniscal stability in the discoid meniscus: A preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32(1):9-14.
[12] Wasser L, Knörr J, Accadbled F, et al.Arthroscopic treatment of discoid meniscus in children: Clinical and MRI results. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011; 97(3): 297-303.
[13] Atay OA, Pekmezci M, Dorol MN, et al.Discoid meniscus: An ultrastructural study with transmission electron microscopy. Am J Sports Med.2007; 35(3): 475-478.
[14] Papadopoulos A, Kirkos JM, Kapetanos GS. Histomorphologic study of discoid meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(3):262-268.
[15] Woods GW, Whelan JM. Discoid meniscus. Clin Sports Med. 1990; 9(3):695-706.
[16] Kocher MS, Klingele K, Rassman SO. Meniscal disorders: Normal, discoid, and cysts. Orthop Clin North Am.2003;34(3): 329-340.
[17] Rao SK, Rao PS. Clinical, radiologic and arthroscopic assessment and treatment of bilateral discoid lateral meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007(5); 15:597-601.
[18] Kushare I, Klingele K, Samora W. Discoid meniscus: Diagnosis and management. Orthop Clin North Am. 2015; 46(4):533-540.
[19] Fields LK, Caldwell PE 3rd. Arthroscopic saucerization and repair of discoid lateral meniscal tear. Arthrosc Tech.2015; 4(2):185-188.
[20] Harato K, Niki Y, Nagashima M, et al.Arthroscopic visualization of abnormal movement of discoid lateral meniscus with snapping phenomenon.Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(3): 235-238.
[21] Ahn JH, Lee YS, Ha HC, et al. A novel magnetic resonance imaging classification of discoid lateral meniscus based on peripheral attachment.Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(8):1564-1569.
[22] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等.儿童症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤对前交叉韧带形态及信号影响的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2015,9(1):21-24.
[23] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 成人症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤对前交叉韧带形态及信号影响的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2013,2(12):685-690.
[24] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 儿童症状性外侧盘状半月板患者前交叉韧带形态及信号变化的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(7):607-612.
[25] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 成人症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤患者前交叉韧带形态及信号变化的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(10):857-862.
[26] Good CR, Green DW, Griffith MH, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of symptomatic discoid meniscus in children: classification, technique, and results. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23(2):157-163.
[27] Klingele KE, Kocher MS, Hresko T, et al. Discoid lateral meniscus: prevalence of peripheral rim instability. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004; 24:79-82.
[28] Lee MH, Choi SH, Woo SY. Quantitative analysis of the difference between an intact complete discoid lateral meniscus and a torn complete discoid meniscus on MR imaging: a feasibility study for a new classification. Skeletal Radiol. 2010; 39(12):1193-1197.
[29] Yoo WJ, Choi IH, Chung CY, et al. Discoid lateral meniscus In children: Limited knee extension and meniscal instability in the posterior segment.J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28(5):544-548.
[30] 孙晓新,周伟,梁春雨,等. 症状性与非症状性儿童外侧盘状半月板MRI形态学差异的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(11):996-999.
[31] Yoo WJ, Lee K, Moon HJ, et al.Meniscal morphologic changes on magnetic resonance imaging are associated with symptomatic discoid lateral meniscal tear in children. Arthroscopy.2012;28(3):330-336. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。
文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。.jpg) 文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。
文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。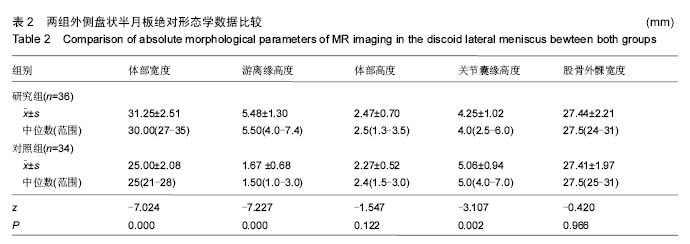
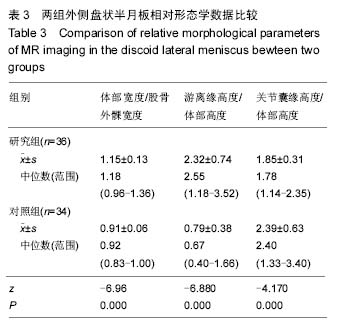
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。
文题释义:
盘状半月板:盘状半月板也称盘状软骨,是一种先天性半月板解剖变异。因其自身形态失去正常半月形而呈近似圆盘形而得名。其中外侧盘状半月板的发生率明显高于内侧,而且其在东亚人群中的发病率较高。
症状性外侧盘状半月板:相较正常形态半月板而言,由于外侧盘状半月板自身形态学及组织学存在异常,因此更容易损伤。而外侧盘状半月板损伤后会引发膝关节疼痛、弾响、交锁以及屈伸活动受限等临床症状,因此称为症状性外侧盘状半月板。