中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (24): 3529-3534.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.24.005
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨颈骨折修复后股骨头坏死7个相关因素:199例回顾分析
谢 康,高维陆,常 俊,尹宗生
- 安徽医科大学第一附属医院关节与骨肿瘤外科,安徽省合肥市 230022
Seven risk factors of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation in femoral neck fractures: a retrospective analysis of 199 cases
Xie Kang, Gao Wei-lu, Chang Jun, Yin Zong-sheng
- Department of Joint and Bone Tumor Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。
文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。
.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。
文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。摘要
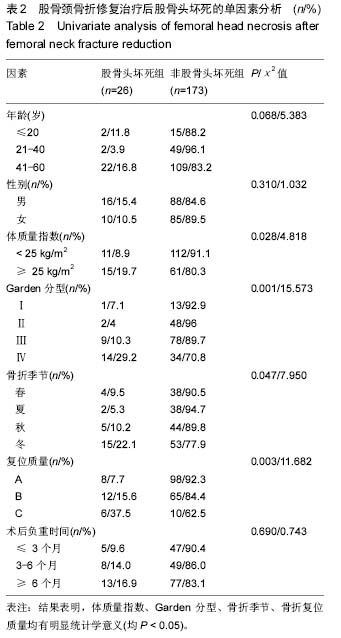
背景:股骨颈骨折内固定后发生股骨头坏死率较高,其危险因素一直没有明确的专家共识。
目的:回顾性提出和分析60岁以下股骨颈骨折内固定后发生股骨头坏死的相关危险因素。
方法:对199例60岁以下股骨颈骨折行闭合复位空心钉内固定的病例进行回顾性分析。对年龄,性别,体质量指数,Garden分型,骨折季节,骨折复位质量,内固定后完全负重下床时间7个因素进行统计分析,评估这些因素与股骨头坏死之间的关系。
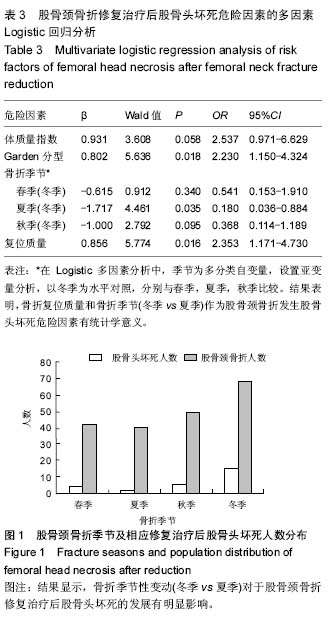
结果与结论:①199例股骨颈骨折患者内固定后股骨头坏死发生率13%;②体质量指数,Garden分型,骨折季节季节性变动及骨折复位质量与内固定后股骨头坏死密切相关。患者年龄、性别,内固定后负重时间与内固定后股骨头坏死无明显相关性;③Logistic回归多因素分析,Garden分型、骨折复位质量和骨折季节性变动(冬季vs夏季)对于股骨颈骨折后股骨头坏死的发展有明显影响;④结果提示,股骨颈骨折的Garden分型及骨折复位质量对股骨颈骨折术后愈合有很大的影响;冬季骨折可能是股骨颈骨折内固定后发生股骨头坏死的危险因素。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-1489-8232(谢康)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。
文题释义:
股骨颈骨折:股骨颈骨折大多数是外旋暴力所引起的螺旋形骨折或斜形骨折。随着受伤姿式、外力方向及程度不同,在X射线投影上出现骨折的不同部位、不同角度和不同移位,由此将股骨颈骨折可区分为4种类型,与治疗和预后有较密切的关系。
相关分析(correlation analysis):相关分析是研究现象之间是否存在某种依存关系,并对具体有依存关系的现象探讨其相关方向以及相关程度,是研究随机变量之间的相关关系的一种统计方法。
股骨颈骨折内固定:内固定的形式很多,归纳约有以下几种类型:①Smith-Petersen三刃钉内固定:自1929年Smith-Petersen首次创用三刃钉以来,使股骨颈骨折的疗效显著提高,至今仍为常用的内固定方法之一。②滑动式内固定:现有各种不同式样的压缩钉或针。压缩钉或针可在套筒内滑动,当骨折线两侧有吸收时,钉向套筒内滑动缩短以保持骨折端密切接触,早期承重更利于骨折端的嵌插。③加压式内固定:此种内固定物带有压缩装置,能使骨折端互相嵌紧以利愈合。常用的有Charnley带有弹簧的压缩螺丝钉和Siffert使用的螺丝栓(Corkscrew Bolt)等。④多针(或钉)内固定:根据股骨上端骨结构和生物力学原则分别插入2-4根螺丝钉或钢钉,不但固定牢靠,而且可减少对股骨头的损伤。如Moore或Hagia针等。