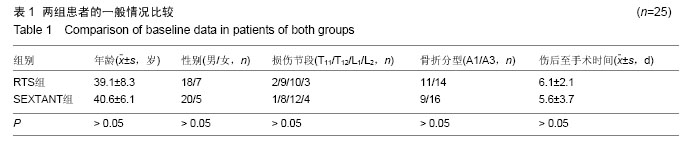
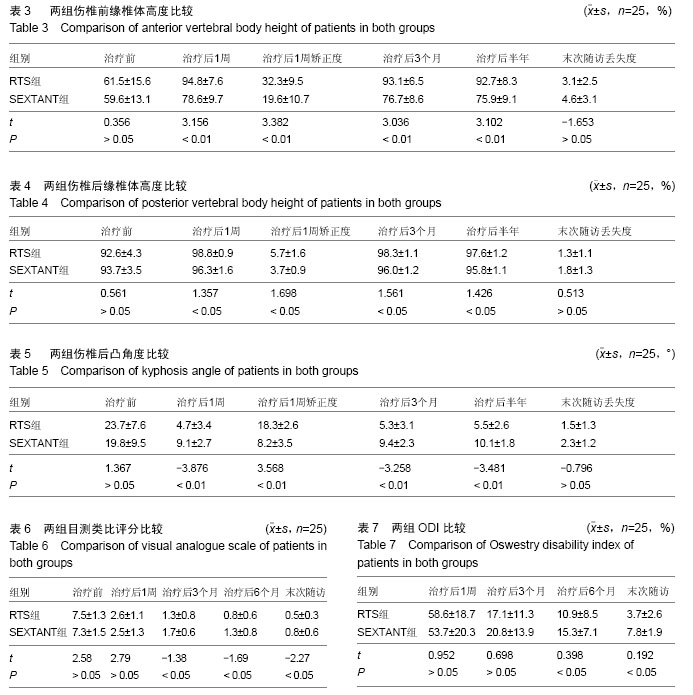
| [1] 李长青,罗刚,周跃,等.新型微创经皮椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(6): 522-525.[2] Ni WF, Huang YX, Chi YL, et al.Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for neurologic intact thoracolumbar burst fractures.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(8):530-537. [3] 明江华,郑慧锋,赵奇,等.Sextant经皮椎弓根钉棒微创系统治疗胸腰椎骨折:随访评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(48):8343-8348.[4] 明江华,郑慧锋,赵奇,等. Sextant经皮椎弓根螺钉固定矫正胸腰椎单节段椎体骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(35):5654-5659.[5] 刘涛,李长青,周跃,等.新型经皮椎弓根螺钉系统的设计与生物力学测试[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2010, 30(6):594-599.[6] Ma LT, Gong Q, Li T,et al.Relationship between the angle of vertebral screws and spinal lateral angulation after fixation of thoracolumbar fractures via an anterior approach.Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4):8135-8146.[7] Truszczyńska A, R?pa?a K, ?ukawski S,et al.Evaluation of functional outcomes in individuals 10 years after posterior lumbar interbody fusion with corundum implants and decompression: a comparison of 2 surgical techniques. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20(10): 1400-1406.[8] Masala S,Taglieri A,Chiaravalloti A,et al. Thoraco-lumbar traumatic vertebral fractures augmentation by osteo-conductive and osteo-inductive bone substitute containing strontium-hydroxyapatite: our experience. Neuroradiology. 2014;56(6):459-466.[9] Jackson KL,Yeoman C,Chung WM,et al. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion: two-year results with a modular interbody device. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(5) : 591-598.[10] 王善金,杨明杰,潘杰,等.微创经皮椎弓根螺钉技术应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(5):479-481.[11] Kim DY,Lee SH,Chung SK,et al.Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open pedicle screw fixation.Spine. 2005;30:123-129.[12] Rampersaud YR, Annand N, Dekutoski MB. Use of minimally invasive surgical techniques in the management of thoracolumbar trauma: current concepts. Spine. 2006;31(1lS):S96-S102.[13] Hodus DL, Nieuwland R, Boateng KB,et al. Creatine kinase inhibits ADP-induced platelet aggregation.Sci Rep. 2014;4:6551.[14] Behringer M, Montag J, Kilian Y,et al. The repeated bout effect: is the blunted creatine kinase response an effect of an altered enzyme inactivation kinetic? J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2014;55(12):1431-1437.[15] Meyerzu Schwabedissen HE, Siegmund W, Kroemer HK, et al. Creatine kinase elevation caused by a combination of fluvastatin and telmisartan in a patient heterozygous for the CYP2C9*3 and ABCC2 -24C > T variants: a case report.BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:688.[16] Johnsen SH, Lilleng H, Bekkelund S. Creatine kinase as predictor of blood pressure and hypertension. Is it all about body mass index? A follow-up study of 250 patients. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014;16(11): 820-826. [17] Bagai A, Schulte PJ, Granger CB, et al. Prognostic implications of creatine kinase-MB measurements in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Am Heart J. 2014;168(4):503-511. [18] Kato A, Sakakibara H, Tsuboi H. et al. Depressive symptoms of female nursing staff working in stressful environments and their association with serum creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase-a preliminary study.Biopsychosoc Med. 2014;8:21. [19] Kim S,Um TH,Cho CR,et al.False-positive elevation of creatine kinase MB mass concentrations caused by macromolecules in a patient who underwent nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma.Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(5):405-407.[20] Pokora L,Kempa K,Chrapusta SJ,et al. Effects of downhill and uphill exercises of equivalent submaximal intensities on selected blood cytokine levels and blood creatine kinase activity. Biol Sport. 2014;31(3): 173-178.[21] Nnadi E,Manafa P,Okocha E,et al. Evaluation of creatine kinase activity and inorganic phosphate concentration in adult nigerian homozygous and heterozygous hemoglobin phenotypes. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014;4(5):697-700.[22] Laoutidis ZG Kioulos KT. Antipsychotic-induced elevation of creatine kinase: a systematic review of the literature and recommendations for the clinical practice. Psychopharmacology. 2014;231(22):4255-4270.[23] Assaker R. Minimal access spinal technologies: state-of-the-art,indications, and techniques. Joint Bone Spine. 2004;71(6):459-469.[24] 汪群,隋福革,汪丽静,等.经皮椎弓根钉棒置入结合椎体成形治疗胸腰椎压缩性骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(17):2716-2721.[25] 刘俊涛,王小勇,黄建军,等.经皮微创椎弓根钉技术与切开复位内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(1):71-73.[26] 郭瑛,黄智,李伟,等.经皮经伤椎短节段椎弓根螺钉治疗单节段胸腰段椎体骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2015,17(6): 493-496.[27] 朱卉敏,张锴,王衡,等.经皮椎弓根螺钉固定同时经伤椎置钉治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2015,17(6) 515-518.[28] Kim BG, Dan JM, Shin DE.Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(1):133-146.[29] 王放,贺西京.短节段椎弓根钉棒固定治疗无神经损伤胸腰椎骨折对长期生活质量的影响[J].中国骨伤,2015, 28(1):12-16.[30] 邓昭,田伟,袁强,等.术中即时三维导航引导经皮微创椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗颈椎骨折的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志, 2015,65(10):752-756.[31] 顾勇杰,孙韶华,李国庆,等.经皮与经肌间隙椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(9):910-913.[32] 刘亮,蔡丰,刘晓东,等.经皮与开放椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗单节段无神经症状胸腰椎骨折的临床对比研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,14(9):713-716.[33] 张志成,李放,任大江,等.无神经功能障碍胸腰段屈曲牵张型损伤:经皮与开放椎弓根螺钉固定的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(12):1063-1067.[34] 蔡斌,张文捷,张震祥,等.经皮椎弓根钉治疗单椎体A型胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 30(5):456-459.[35] 孔祥清,孟纯阳,张卫红.微创经皮穿刺椎弓根内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(8);692-695.[36] 李春,刘艺明,王善松,等.经皮微创椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰段骨折疗效分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(5):361-363.[37] 张鹭,吴军,路锟,等.两种手术方式对胸腰段椎体骨折患者术后感染的影响研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015, 25(19):4500-4501.[38] Kim DY,Lee SH,Chung SK,et al. Comparison of multifidus muscle atrophy and trunk extension muscle strength: percutaneous versus open podicle screw fixalion.Spine. 2005;30(1):123-129.[39] 钱济先,纪振钢,高浩然,等.微创经皮并结合伤椎椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013, 21(16):1591-1596.[40] 张伟,李海音,李杰,等.微创减压联合经皮固定与传统开放手术治疗伴神经损害胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(5):420-426.[41] Gelb D,Ludwig S,Karp JE,et al. Successful treatment of thoracolumbar fractures with short-segment pedicle instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(5): 293-301.[42] 王许可,李长青,王洪伟,等.联合单向及万向椎弓根螺钉经伤椎经皮内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013, 29(5):431-437.[43] 周英杰,赵刚,黄孝敏.自旋转撑开椎弓根螺钉系统的生物力学分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(12): 1073-1077. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)