| [1] Otto WR,Sarraf CE.Culturing and differentiating human mesenchymal stem cells for biocompatible scaffolds in regenerative medicine.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;806: 407-426.[2] Shearn JT,Kinneberg KRC,Dyment NA,et al.Tendon tissue engineering: Progress, challenges, and translation to the clinic.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2011;11(2):163-173.[3] Yang Z,Shi Y,Wei X,et al.Fabrication and Repair of Cartilage Defects with a Novel Acellular Cartilage Matrix Scaffold.Tissue Eng Part C Methods.2010;16(5): 865-876.[4] Jonsson L,Gatzinsky V,Jennische E,et al.Piglet Model for Studying Esophageal Regrowth after Resection and Interposition of a Silicone Stented Small Intestinal Submucosa Tube.Eur Surg Res.2011;46(4):169-179.[5] Kim KS,Lee JY,Kang YM,et al.Small intestine submucosa sponge for in vivo support of tissue-engineered bone formation in the presence of rat bone marrow stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(6): 1104-1113.[6] Xu Y,Wu J,Guan J,et al.Physiochemical and biological properties of modified collagen sponge from porcine skin.J Wuhan Univ Technol.2009;24(4):619-626.[7] Lim JY,Kim SH,Khang G,et al.Preparation and Characterization of Tissue Engineered Scaffold Using Porcine Small Intestinal Submucosa and Hyaluronic Acid. Polym-Korea.2008;32(5):415-420.[8] Huber A,Badylak SF.Phenotypic changes in cultured smooth muscle cells: limitation or opportunity for tissue engineering of hollow organs?J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;6(7):505-511.[9] Hong HK,Lee SK,Song Y,et al.Biodisc Regeneration Using Annulus Fibrosus Cell with Hyaluronic Acid Impregnated Small Intestinal Submucosa Sponge. Polym-Korea.2010;34(3):282-288. [10] Kato H,Suga H,Eto H,et al.Reversible adipose tissue enlargement induced by external tissue suspension: possible contribution of basic fibroblast growth factor in the preservation of enlarged tissue.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):2029-2040.[11] Marconi S,Castiglione G,Turano E,et al.Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells systemically injected promote peripheral nerve regeneration in the mouse model of sciatic crush.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012; 18(11-12):1264-1272.[12] Ackbar R,Ainoedhofer H,Gugatschka M,et al.Decellularized ovine esophageal mucosa for esophageal tissue engineering.Technol Health Care. 2012;20(3):215-223.[13] Morey AF.Re:Small Intestinal Submucosa Urethral Wrap at the Time of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Placement as a Salvage Treatment Option for Patients with Persistent/Recurrent Incontinence Following Multiple Prior Sphincter Failures and Erosions.J Urol. 2012;188(3):865-866.[14] Mcadams PD,Jordan G H.Re: Long-term Results of Small Intestinal Submucosa Graft in Bulbar Urethral Reconstruction.Eur Urol.2012;62(4):728.[15] Owen TJ,Lantz GC,Hiles MC,et al.Cal cifi cati on pot en tial of small int es tinal s ubmucosa in a rat s ubcut aneous model.J Surg Res.1997;71(2):179. [16] Wissink MJ,Beernink R,Pieper JS,et al.Bingding and release of basic fibroblast growth factor from heparinized cllagen matrices.Biomaterials. 2001;22: 2291-2292.[17] Tanaka Y,Kubotal A,Yokokural S,et al.Optical mechanical refinement of human amniotic membrane by dehydration and cross-linking.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2012;9(6):731-737.[18] Cholasa RH,Hsu HP,Spectorb M.The reparative response to cross-linked collagen-based scaffolds in a rat spinal cordgap model.Biomaterials. 2012;33(7): 2050-2059.[19] Cintron JR,Abcarian H,Chaudhry V,et al.Treatment of fistula-in-ano using a porcine small intestinal submucosa anal fistula plug.Tech Coloproctol. 2013; 17(2):187-191.[20] Kalaji N,Deloge A,Sheibat-Othman N,et al.Controlled release carriers of growth factors FGF-2 and TGF beta1: synthesis,characterization and kinetic modelling. J Biomed Nanotechnol.2010;6(2):106-116.[21] Hodde JP,Record RD,Liang HA,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor in porcine-derived extracellular matrix.Endothelium.2001;8(1):11.[22] Chen MK,Badylak SF.Small bowel tissue engineering using small intestinal submucosa as a scaffold.J Surg Res.2001;99(2):352.[23] McPherson TB,Badylak SF.Characterization of fibronectin derived from porcine small intestinal submucosa.Tissue Eng.1998;4(1):75.[24] Liatsikos EN,Dinlenc CZ,Kapoor R,et al.Laparoscopic ureteral reconstruction with small intestinal submucosa. J Endourol.2001;15(2):217.[25] McDevitt CA,Wildey GM,Catrone RM.Transforming growth factor- beta1 in a sterilized tissue derived from the pig small intestine submucosa.J Biomed Mater Res A.2003;67(2): 637-640.[26] Hurst RE,Bonner RB.Mapping of the distribution of significant proteins and proteoglycans in small intestinal submucosa by fluorescence microscopy.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2001;12(11):1267-1279.[27] Layman H,Li X,Nagar E,et al.Enhanced angiogenic efficacy through controlled and sustained delivery of FGF-2 and G-CSF from fibrin hydrogels containing ionic-albumin microspheres.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2012;23(1-4):185-206.[28] Leeuwenburgh SC,Jo J,Wang H,et al.Mineralization,biodegradation,and drug release behavior of gelatin apatite composite microspheres for bone regeneration. iomacromolecules.2010;11(10):2653-2659. |
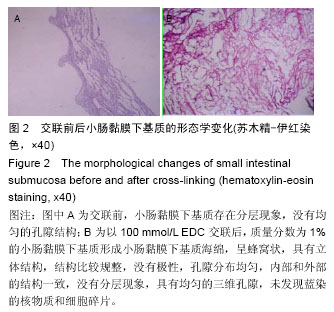
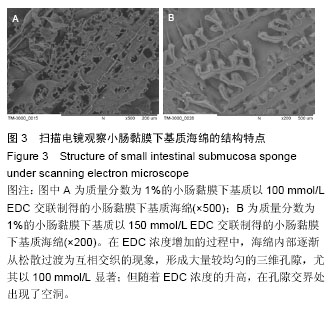
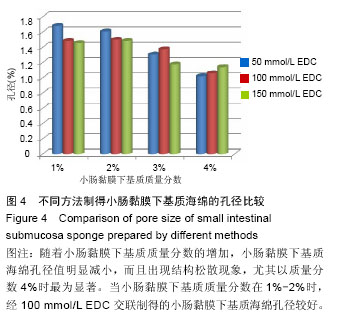
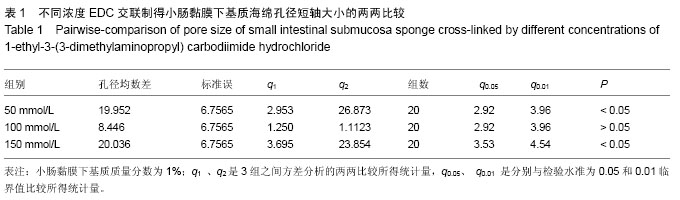
.jpg)


.jpg)