| [1]Susmita B, Mangal R, Amit B. Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds. Trends Biotechnol. 2012;30(10):546-554.[2]Winkler T, Sass FA, Duda GN, et al. A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: the unsolved challenge. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(3):232-243.[3]Miron RJ, Zhang YF. Osteoinduction: a review of old concepts with new standards.J Dent Res. 2012;91(8):736-744.[4]Groen N, Tahmasebi N, Shimizu F, et al. Exploring the material-induced transcriptional landscape of osteoblasts on bone graft materials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(11):1691-1700.[5]Chen S, Ryan DA, Dwyer MA, et al. Synergistic effect of wnt modulatory small molecules and an osteoinductive ceramic on C2C12 cell osteogenic differentiation. Bone. 2014;67:109-121.[6]施剑明,邬亚华,耿书国,等.间充质干细胞增殖?衰老及分化:Wnt信号通路经典与非经典的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(41): 6719-6724.[7]Olivares-Navarrete R, Hyzy SL, Hutton DL, et al. Mediation of osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on titanium surfaces by a wnt-integrin feedback loop. Biomaterials. 2011;32(27):6399-6411.[8]Galli C, Piemontese M, Lumetti S, et al. The importance of WNT pathways for bone metabolism and their regulation by implant topography. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:46-59.[9]Wang W, Zhao LZ, Ma QL, et al. The role of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in the effect of implant topography on MG63 differentiation. Biomaterials. 2012;33(32):7993-8002.[10]Olivares-Navarrete R, Hyzy SL, Hutton DL, et al. Role of non-canonical wnt signaling in osteoblast maturation on microstructured titanium surfaces. Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;7(6):2740-2750.[11]Kilpadi KL, Chang PL, Bellis SL. Hydroxylapatite binds more serum proteins, purified integrins, and osteoblast precursor cells than titanium or steel. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2001;57(2):258-267.[12]Sun YX, Zhang JF, Li DJ, et al. Comparing the osteoconductive potential between tubular and cylindrical beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds: an experimental study in rats. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2018;106(5):1934-1940.[13]Lu J, Yu H, Chen C. Biological properties of calcium phosphate biomaterials for bone repair: a review. RSC Advances. 2018;8(4): 2015-2033.[14]毛文文,茹江英.羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4855-4863.[15]Zhao Y, Li Q, Yang Z, et al. Cadmium activates noncanonical wnt signaling to impair hematopoietic stem cell function in mice. Toxicol Sci. 2018;165(1):254-266.[16]Spalthoff S, Zimmerer R, Dittmann J, et al. Heterotopic bone formation in the musculus latissimus dorsi of sheep using β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds: evaluation of different seeding techniques. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(2):77-84.[17]Habibovic P, Groot K. Osteoinductive biomaterials-properties and relevance in bone repair. J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2007;1(1):25-32.[18]Yuan H, Groot KD. Calcium Phosphate Biomaterials: An Overview[M]// Learning from Nature How to Design New Implantable Biomaterialsis: From Biomineralization Fundamentals to Biomimetic Materials and Processing Routes. 2004.[19]Yuan H, DeBruijn JD, Li Y, et al. Bone formation induced by calcium phosphate ceramics in soft tissue of dogs: a comparative study between porous α-TCP and β-TCP. J Mater Sci. 2001;12(1):7-13.[20]Habibovic P, Yuan H, vanderValk CM, et al. 3D microenvironment as essential element for osteoinduction by biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3565-3575.[21]Ilan DI, Ladd AL. Bone graft substitutes. Oper Tech Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;9(4):151-160.[22]Wang Y, Pan J, Zhang Y, et al. Wnt and Notch signaling pathways in calcium phosphate-enhanced osteogenic differentiation: a pilot study. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2019;107(1):149-160.[23]van Dijk LA, Duan R, Luo X, et al. Biphasic calcium phosphate with submicron surface topography in an Ovine model of instrumented posterolateral spinal fusion. JOR Spine. 2018;1(4):e1039.[24]Moorer MC, Riddle RC. Regulation of osteoblast metabolism by wnt signaling. Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):318-330.[25]Kobayashi Y, Maeda K, Uehara S, et al. Regulatory mechanism of osteoclastogenesis by Wnt signaling. Inflamm Regen. 2011;31(5): 413-419.[26]Han XG, Wang DW, Bi ZG, et al. Regulatory effect of estrogen receptor-α-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblast proliferation. J Biol Regul Homoest Agents. 2016;30(2):381-387.[27]Keeble TR, Halford MM, Seaman C, et al. The Wnt receptor Ryk is required for Wnt5a-mediated axon guidance on the contralateral side of the corpus callosum. J Neurosci. 2006;26(21):5840-5848.[28]Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells. 2003;8(7):645-654.[29]Takada I, Mihara M, Suzawa M, et al. A histone lysine methyltransferase activated by non-canonical Wnt signalling suppresses PPAR-γ transactivation. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(11):1273.[30]Katoh M, Katoh M. Wnt signaling pathway and stem cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(14):4042-4045.[31]Schambony A, Wedlich D. Wnt-5A/Ror2 regulate expression of XPAPC through an alternative noncanonical signaling pathway. Dev Cell. 2007;12(5):779-792.[32]Olivaresnavarrete R, Hyzy S, Wieland M, et al. The roles of wnt signaling modulators Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) and Dickkopf-2 (Dkk2) and cell maturation state in osteogenesis on microstructured titanium surfaces. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8):2015-2024. |
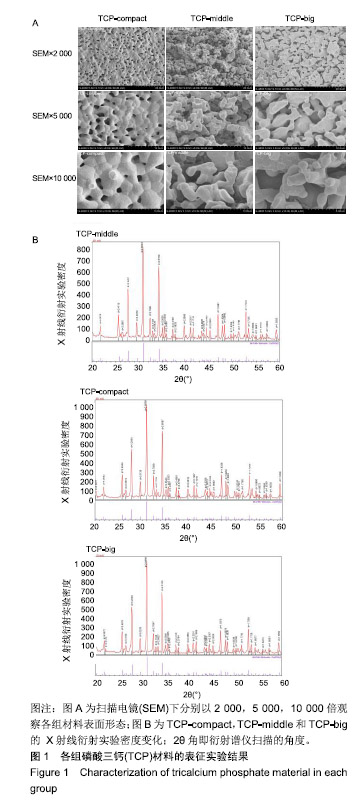
.jpg)
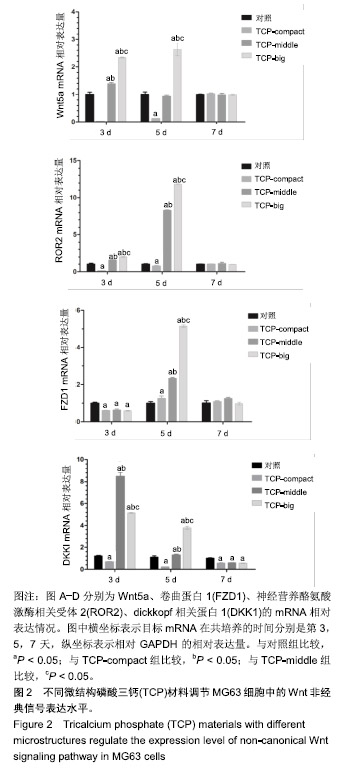
.jpg)
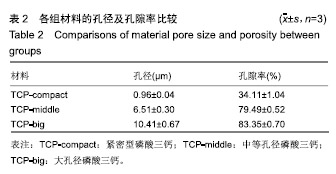
.jpg)