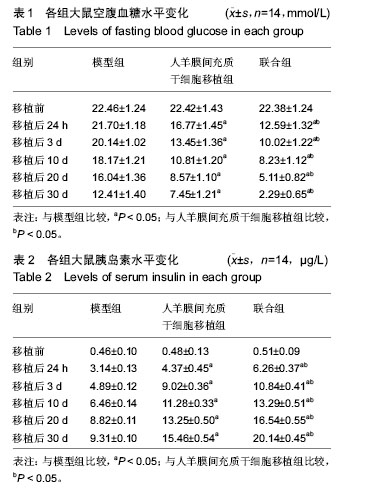
| [1] Studholme S.Diabetic retinopathy.J Perioper Pract. 2008;18(5):205-210.[2] Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, et al.Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047-1053.[3] Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, et al. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(1):226-229.[4] Lund RD, Wang S, Lu B, et al. Cells isolated from umbilical cord tissue rescue photoreceptors and visual functions in a rodent model of retinal disease Stem Cells. 2007;25(3):602-611.[5] Wolbank S, Stadler G, Peterbauer A, et al. Telomerase immortalized human amnion- and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: maintenance of differentiation and immunomodulatory characteristics. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(7):1843-1854.[6] Wu XH, Liu CP, Xu KF, et al. Reversal of hyperglycemia in diabetic rats by portal vein transplantation of islet-like cells generated from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(24):3342-3349.[7] Jurewicz M, Yang S, Augello A, et al. Congenic mesenchymal stem cell therapy reverses hyperglycemia in experimental type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2010;59(12):3139-3147.[8] Ezquer F, Ezquer M, Contador D, et al. The antidiabetic effect of mesenchymal stem cells is unrelated to their transdifferentiation potential but to their capability to restore Th1/Th2 balance and to modify the pancreatic microenvironment. Stem Cells. 2012;30(8):1664-1674.[9] Schultz GS, Strelow S, Stern GA, et al. Treatment of alkali-injured rabbit corneas with a synthetic inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33(12):3325-3331.[10] Kadam SS, Sudhakar M, Nair PD, et al. Reversal of experimental diabetes in mice by transplantation of neo-islets generated from human amnion-derived mesenchymal stromal cells using immuno-isolatory macrocapsules. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(8):982-991.[11] 张路,方宁,陈代雄,等. 人羊膜间充质细胞具有向心肌样细胞分化的特性[J].中国生物工程杂志,2007,27(12): 84-89.[12] 梁黎,梁建凤,洪文澜,等.儿童糖尿病酮症酸中毒25年回顾分析[J].临床儿科杂志,2000,18(3):173-176.[13] 杨柏梁,郭丽,任淑萍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对糖尿病大鼠疗效观察[J].中国公共卫生,2009,25(8):973-974.[14] Lei CT, Wu XL, Peng J, et al. Time-dependent expression of PEDF and VEGF in blood serum and retina of rats with oxygen-induced retinopathy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015;35(1): 135-139.[15] 孙卫,郑学芝,崔荣军,等.葛根素对2型糖尿病大鼠胰岛素抵抗及脂肪分化相关蛋白基因表达的影响[J].医学导报, 2008,27(10):1159-1161.[16] Yan HT, Su GF. Expression and significance of HIF-1 α and VEGF in rats with diabetic retinopathy. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(3):237-240.[17] Mancini JE, Croxatto JO, Gallo JE. Proliferative retinopathy and neovascularization of the anterior segment in female type 2 diabetic rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013;5(1):68.[18] 刘伟.用葛根芩连汤治疗糖尿病的效果探析[J].当代医药论丛,2014,19:46-47.[19] 刘秀英.葛根芩连汤治疗糖尿病经验浅识[J].实用中医内科杂志,2007,21(7):74.[20] 黄能培.葛根芩连汤联合二甲双胍治疗湿热证2型糖尿病的疗效[J].求医问药:学术版,2012,10(6):299,868.[21] Zhao R, Qian L, Jiang L. Identification of retinopathy of prematurity related miRNAs in hyperoxia-induced neonatal rats by deep sequencing. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 16(1):840-856.[22] 金莉,安文灿,安文铎.葛根芩连汤治疗糖尿病120例[J].长春中医药大学学报,2012,28(2):315.[23] Wohlfart P, Lin J, Dietrich N, et al. Expression patterning reveals retinal inflammation as a minor factor in experimental retinopathy of ZDF rats. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(4):553-558.[24] Guo C, Zhang Z, Zhang P, et al. Novel transgenic mouse models develop retinal changes associated with early diabetic retinopathy similar to those observed in rats with diabetes mellitus. Exp Eye Res. 2014;119:77-87.[25] 蒿长英,陈明霞,郭平,等.糖网明目颗粒对糖尿病大鼠视网膜病变防治作用及机制研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2015,22(1):62-66.[26] Thiraphatthanavong P, Wattanathorn J, Muchimapura S, et al. The combined extract of purple waxy corn and ginger prevents cataractogenesis and retinopathy in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:789406.[27] Xiong FL, Sun XH, Gan L, et al. Puerarin protects rat pancreatic islets from damage by hydrogen peroxide. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;529(1-3):1-7.[28] 潘竞锵,韩超.刘惠纯,等.葛根芩连汤降血糖作用的实验研究[J].中国新药杂志,2000,9(3):167.[29] 岳丽菁,毛盼,唐敏,等.中药单体葛根素对糖尿病大鼠视网膜血管内皮生长因子?蛋白激酶的影响[J].中国中医眼科杂志,2013,23(1):13-16.[30] 武志黔,郝改梅,薛晓兴,等.葛根芩连汤对2型糖尿病模型大鼠作用的研究[J].环球中医药, 2014,7(3):161-167. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)