| [1] 王金涛,周顺利,易锦,等.分期推拿治疗膝痹病69例[J].北京中医药,2010,29(12):927-928. [2] 余庆阳,黄巍.膝骨关节炎从痹论治的病因与证候探讨[J].风湿病与关节炎,2015,4(3):40-43. [3] 李坤,肖四旺,陈孟交,等.丹紫康膝冲剂对大鼠膝骨性关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2014, 34(3):20-23. [4] 欧云生,安 洪.鼠骨关节炎动物模型建立的现状[J].中国比较医学杂志,2004,14(1):41-44. [5] Guzman RE,Evans MG,Bore S,et al.Mono-iodoacetate- induced histologic changes in subchondrla bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotial joints: an animal model of osteoarthritis.Taxied Pathol.2003;31(6):619-624. [6] Mahr S,Menard J,Krenn V,et al.Sexual dimorphism in the osteoarthritis of STR/ort mice may eh link to articulra cytokines.Ann Rheum Dis.2003;62(12): 1234-1237. [7] Yamamoto H,Iwase N.Spontaneous osteoarthritis lesions in a new mutant strain of the mouse.J Exp Anim Sic.1998;47(2):131-135. [8] Yamamoto H,Iwase N,Kohno M.Histopathological characterization of spontaneously developing osteoarthropathy in the BCBC/Y mouse established newly from B6C3F1 mice. ExpToxicol Pathol.1999; 51(1):15-20. [9] Muraoka T,Hagino H,Okano T,et al.Role of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis development: a comparative study of two strains of guinea pigs with and without spontaneously occurring osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum.2007;56(10):3366-3374. [10] 熊勇,张照庆,夏数数,等.改良伸直位固定法建立兔膝骨性关节炎模型的研究[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2010,12(5): 19-21. [11] Muehleman C,Green J,Williams JM,et al.The effect of bone remodeling inhibition by zoledronic acid in an animal model of cartilage matrix damage.Osteoarthr Cartilage.2002;10(3): 226-233. [12] Kikuchi T,Sakuta T,Yamaguchi T.Intra-articular injection of collagenase induces experimental osteoarthritis in mature rabbit.Osteoarthr Cartilage.1998;6(3):177-186. [13] Bouchgua M,Alexander K,D`Anjou MA,et al.Use of routine elinical multimodality imaging in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis- -partⅠ.Osteoarthr Cartilage.2009; 17(12): 188-196. [14] Díaz-Gallego L,Prieton JG,Coronel P,et al.Apoptosis and nitric oxide in an experimental model of osteoarthritis in rabbit after hyaluronic acid treatment. J Orthop Res.2005;23(6):1370-1376. [15] Hulmes DJ,Marsden ME,Strachan RK,et al. Intra-aricular hyaluronate in experimental rabbit osteoarthritis can prevent changes in cartilage proteoglycan content.Osteoarthr Cartilage.2004; 12(3):232-238. [16] 汪青春,沈培芝,王海彬.骨关节炎动物模型的建立及选择[J].中医正骨,1998,10(3):39-40. [17] Videman T.Experimental osteoarthritis in the rabbit:comparison of different periods of repeated immobilization. Acta Orthop Scand.1982;53(3): 339-347. [18] 胡炯,杜宁,代岭辉,等.建立膝骨性关节炎关节软骨缺损的动物模型的研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2009,17(11): 3-16. [19] 李澄.SD大鼠膝关节骨性关节炎模型的建立及其病理特征[D].中山大学,2010. [20] 周海蓉,肖振良.健骨胶囊对免骨性关节炎软骨及滑膜影响的实验研究[J].中国中医药科技,2008,15(5):337-338. [21] 郭玉冬,王宸,魏波,等.骨关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].东南大学学报:医学版,2012, 31(5):652-656. [22] 熊勇,彭锐,夏数数,等.兔膝骨性关节炎关节液中白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α表达与艾灸的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(41):7700-7703. [23] 钟远鸣,全迪,贺启荣,等.舒筋汤熏洗加被动功能锻炼治疗膝骨性关节炎的实验研究[J].广西中医药,2008,31(1): 42-46. [24] 罗灿峤,莫木琼,钟觉民.不同的脱钙液在骨组织制片中的比较应用[J].中国实用医药,2011, 6(19):27-28. [25] 程永.膝痹病经筋病机与针刺治疗探讨[J].实用中医药杂志,2012,28(8):695-696. [26] 葛广勇,赵建宁,刘刚,等.膝骨性关节炎模型的分期特征[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(4): 47-49. [27] Mankin HJ,Dorfman H,Lippiello L,et al. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips.Ⅱ.Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data.J Bone Surg Am.1971;53(3):523-537. [28] 于娟,李莎莎,叶莹仪,等.关节腔内注射高乌甲素对兔膝骨性关节炎的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2013,23(8): 34-37. [29] 黄少君,孙升云,徐梅,等.淫羊藿对早期兔膝骨性关节炎软骨的影响[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版, 2014, 35(3):273-278. [30] 谢希,高洁生.骨关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].医学综述, 2005,11(1):67-69. [31] 钱洁,邢雪松,梁军.大鼠膝关节骨性关节炎动物模型的两种实验方案[J].实验室研究与探索,2014,33(11):23-27. 许文娟.树脂石膏与传统石膏应用在四肢骨折患者的效果优劣分析[J].医学美学美容:中旬刊,2013,22(10): 55-56. |
.jpg)

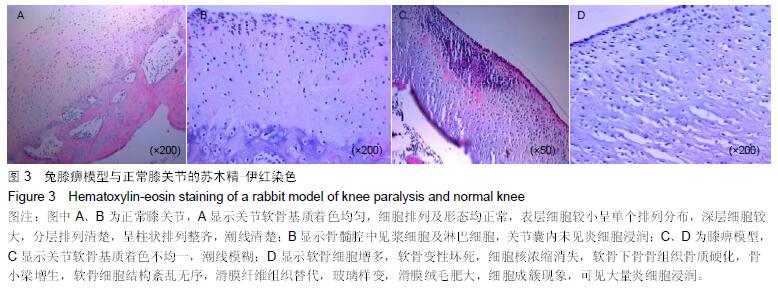
.jpg)
.jpg)