中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (16): 2391-2396.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.16.015
• 药物控释材料 drug delivery materials • 上一篇 下一篇
高吸型壳聚糖敷料的创面止血及促愈合效果
毛 珺1,周应山2,吴 庭3
- 1武汉纺织大学医院全科,湖北省武汉市 430073;2新型纺织材料绿色加工及其功能化省部共建教育部重点实验室,武汉纺织大学,湖北省武汉市 430073;3武汉市第三医院,湖北省武汉市 430073
High-absorbing chitosan dressings for hemostasis and wound healing
Mao Jun1, Zhou Ying-shan2, Wu Ting3
- 1Hospital of Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan 430073, Hubei Province, China; 2Key Laboratory for Green Processing and Functionalization of Textile Materials, Ministry of Education, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan 430073, Hubei Province, China; 3Wuhan Third Hospital, Wuhan 430073, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
高吸型壳聚糖敷料:是一种羧乙基甲壳胺纤维,将甲壳胺纤维分散在醇类中,通过与丙烯酸的迈克尔加成反应,经分离、洗涤、干燥得到羧乙基甲壳胺纤维。这种羧乙基甲壳胺纤维,羧化取代度控制在0.01-0.8范围内,羧化壳聚糖纤维分子链间的氢键被部分破坏,亲水基团大量引入,使得敷料中羧化壳聚糖纤维内部和纤维之间能吸收大量的渗出液,相对于一般甲壳胺纤维制备的常规壳聚糖敷料而言,提升其止血和吸液能力。
高吸型壳聚糖敷料修复烧伤创面:在炎症阶段,壳聚糖能激活巨噬细胞,促进其迁移,以达到清除伤口分泌物的作用;在肉芽阶段,壳聚糖能加速Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的分泌,从而促进肉芽组织的生长;在上皮化阶段,敷料中壳聚糖分子链在创面溶菌酶的作用下,降解产生的N-乙酰葡胺糖和葡糖胺烯糖小分子能被创面吸收,促进上皮细胞的再生,显著提高创面愈合速度和质量。高吸型壳聚糖分子链上定位接枝的羧化基团会给出质子,致使壳聚糖分子链上氨基质子化,增加壳聚糖纤维的聚阳离子特性,赋予其高抗菌性,相对以往壳聚糖敷料来说,促愈合、抗菌性有所提高。
背景:通过化学改性可提升壳聚糖敷料自身的高吸液性、高容量吸液性、高抗菌性等方面的性能。
目的:观察高吸型壳聚糖敷料的创面止血及促愈合效果。
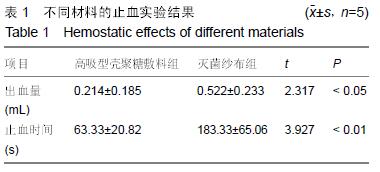
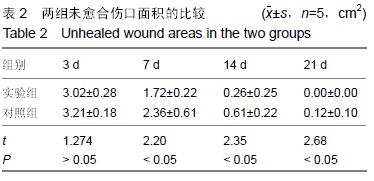
方法:①小静脉止血实验:制作家兔皮肤对称性渗血伤口,两侧伤口分别敷以高吸型壳聚糖敷料和灭菌纱布,记录止血时间和出血量;②Ⅱ度烫伤创面修复实验:取清洁级SD大鼠40只,制作背部深Ⅱ度烫伤创面,随机分为2组,实验组创面局部以高吸型壳聚糖敷料包扎,对照组以凡士林纱布包扎,修复后3,7,14,21 d,观察愈合情况,取创面组织进行病理组织学分析。
结果与结论:①小静脉止血实验:高吸型壳聚糖敷料组出血量与止血时间均低于灭菌纱布组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);②Ⅱ度烫伤创面修复实验:实验组修复后7,14,21 d的未愈合创面面积均低于对照组(P < 0.05)。修复后3 d,两组均可见创面皮肤表皮的鳞状上皮层坏死、真皮层内毛囊及皮肤附属器结构破坏,同时可见损伤皮肤组织内有不等数量的中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞浸润。修复后21 d,对照组上皮修复较好,有少许淋巴细胞浸润,可见痂皮;实验组上皮修复良好,可见完整新生鳞状上皮层,无炎症细胞浸润;③结果表明:高吸型壳聚糖敷料具有良好的创面止血和促创面愈合效果。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程

.jpg)